 |
|
HOME
|
US Navy -
ships
|
US Navy - air
units
|
USMC - air
units
|
International
Navies
|
Weapon Systems
|
Special Reports |
|
Aircraft Weapon System AGM-158C LRASM - Long Range Anti Ship Missile + AGM-158 JASSM / AGM-158B JASSM-ER / AGM-158D JASSM-D |
 |
| 01/26 |
|
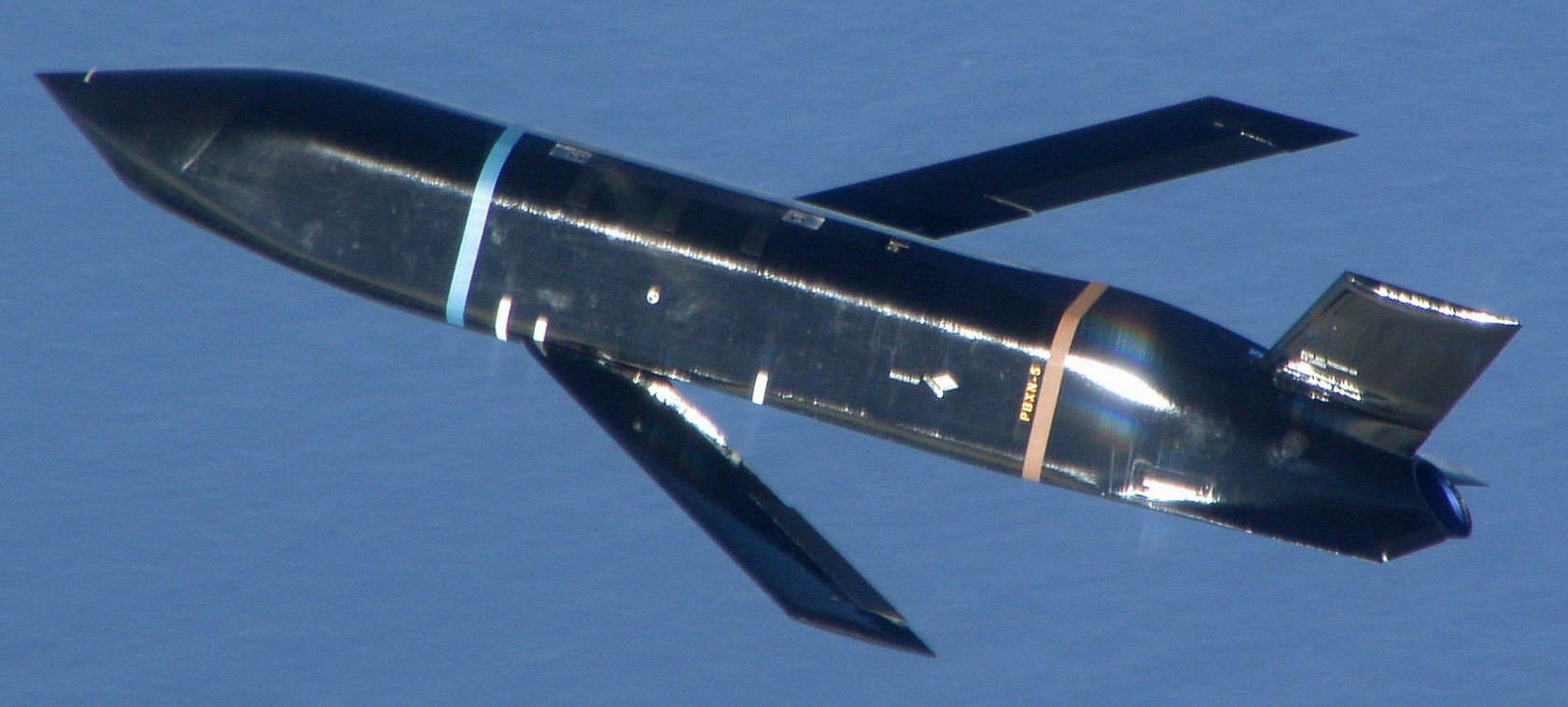
AGM-158C LRASM (Long Range Anti-Ship Missile) ... is a stealth air launch anti-ship cruise missile developed for the United States Air Force and United States Navy. Derived from the AGM-158B JASSM-ER, the LRASM was intended to pioneer more sophisticated autonomous targeting capabilities than the U.S. Navy's current Harpoon anti-ship missile, which has been in service since 1977. Design: Unlike current anti-ship missiles, the LRASM is expected to be capable of conducting autonomous targeting, relying on on-board targeting systems to independently acquire the target without the presence of prior, precision intelligence, or supporting services like Global Positioning Satellite navigation and data-links. These capabilities will enable positive target identification, precision engagement of moving ships and establishment of initial target cueing in extremely hostile environments. The missile will be designed with counter-countermeasures to evade hostile active defense systems. The LRASM is based on the AGM-158B JASSM-ER, but incorporates a multi-mode passive RF, a new weapon data-link and altimeter, and an uprated power system. It can be directed to attack enemy ships by its launch platform, receive updates via its datalink, or use onboard sensors to find its target. LRASM will fly towards its target at medium altitude then drop to low altitude for a sea skimming approach to counter missile defenses. The AGM-158B JASSM-ER was estimated to have a maximum range of 500 nmi (930 km). However, LRASM's range is shorter than the JASSM-ER it is based upon, due to the extra space for the navigation/sensor/passive radar needs. Lockheed Martin has claimed the missile's range is greater than 200 nmi (370 km). To ensure survivability to and effectiveness against a target, the LRASM is equipped with a BAE Systems-designed seeker and guidance system, integrating jam-resistant GPS/INS, an imaging infrared (IIR infrared homing) seeker with automatic scene/target matching recognition, a data-link, and passive electronic support measures (ESM) and radar warning receiver sensors. Artificial intelligence software combines these features to locate enemy ships and avoid neutral shipping in crowded areas. Automatic dissemination of emissions data is classified, located, and identified for path of attack; the data-link allows other assets to feed the missile a real-time electronic picture of the enemy battlespace. Multiple missiles can work together to share data to coordinate an attack in a swarm. Aside from short, low-power data-link transmissions, the LRASM does not emit signals, which combined with the low-RCS JASSM airframe and low IR signature reduces detectability. Unlike previous radar-only seeker-equipped missiles that went on to hit other vessels if diverted or decoyed, the multi-mode seeker ensures the correct target is hit in a specific area of the ship. An LRASM can find its own target autonomously by using its passive radar homing to locate ships in an area, then using passive measures once on terminal approach. Like the JASSM, the LRASM is capable of hitting land targets. LRASM is designed to be compatible with the Mark 41 Vertical Launching System used on many U.S. Navy warships and to be fired from aircraft, including the B-1 Lancer. For surface launches, LRASM will be fitted with a modified Mk 114 jettisonable rocket booster to give it enough power to reach altitude. Although priority development is on air and surface-launched variants, Lockheed is exploring the concept of a submarine-launched variant, and deployment from a topside canister launcher for smaller ships. As part of OASUW Increment 1, the LRASM will be used only as an air-launched missile to be deployed from the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and B-1B Lancer, which has the capacity to carry 24 LRASMs. In 2020, the U.S. Navy began the process of integrating the LRASM onto the P-8 Poseidon maritime patrol aircraft, to be completed by 2026. Some naval advisors have proposed increasing the LRASM's capabilities to serve dual functions as a ship-based land attack weapon in addition to anti-ship roles. By reducing the size of its 1,000 lb (450 kg) warhead to increase range from some 300 mi (480 km) to 1,000 mi (1,600 km), the missile would still be powerful enough to destroy or disable warships while having the reach to hit inland targets. With the proper guidance system, a single missile would increase the Navy's flexibility rather than needing two missiles specialized for different roles. Specifications: Designer: DARPA Manufacturer: Lockheed Martin Mass: 2,760 lb (1,250 kg) (est) Length: 14 ft / 128 inches (4.26 m) Width: >25 in (>635 mm) Height: 18 in (450 mm) (est) Wingspan: 8 ft 10 in (2.7 m) Warhead: 1,000 lb (453.6 kg) WDU-42/B HE blast fragmentation penetrator Detonation mechanism: FMU-156/B fuze Engine: Williams F107-WR-105 turbofan Operational range: 200 nmi (370 km) / JASSM-ER = >500 nmi (926 km) Steering system: Moving wings, 2 horizontal tailplanes & 1 vertical stabilizer Guidance system: GPS, INS, IIR (EO), with AI guidance in on-board sensors (to detect high-value target) Variants: AGM-158 JASSM (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile) ... is a low detection standoff air-launched cruise missile developed by Lockheed Martin. It is a large, stealthy long-range weapon with a 1,000-pound (450 kg) armor piercing warhead. AGM-158B JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile-Extended Range) Using a more efficient engine and larger fuel volume in an airframe with the same external dimensions as the JASSM, the JASSM-ER is intended to have a range of over 575 mi (925 km) compared to the JASSM's range of about 230 mi (370 km). Other possible improvements were studied but ultimately not pursued, including a submunition dispenser warhead, new types of homing head, and a new engine giving ranges in excess of 620 mi (1,000 km). The JASSM-ER has 70% hardware commonality and 95% software commonality with the original AGM-158 JASSM. AGM-158B-2 ... upgrades position JASSM to add additional 21st Century Security® capabilities for warfighters through future planned software and hardware upgrades. AGM-158B-2 configuration adds improvements to the system, including a modernized Missile Control Unit (MCU), enhanced Software (C++) and the latest JASSM GPS Anti-jam Receiver (JAGR-v5). AGM-158D JASSM-D (former AGM-158 XR) In 2024, Lockheed Martin unveiled a concept for a longer range version of the AGM-158 dubbed the AGM-158 XR (eXtreme Range). The AGM-158 XR is longer in order to fit more fuel. It can be carried on bombers and by fighters including the F-35, F-15, and F/A-18, but due to the missile's larger size and heavier weight it cannot be carried by lighter fighters like the F-16. It is speculated that the JASSM-XR's range could be around 1,000 mi (1,600 km). In 2018 the AGM-158 XR was designated as AGM-158D JASSM-D. Launching platforms: B-2 Spirit B-1B Lancer F-15E Strike Eagle F-16 Fighting Falcon/Viper F/A-18E/F Super Hornet F-35 Lightning II P-8 Poseidon (integrating) Current and future users: United States Air Force United States Navy Royal Australian Air Force Finnish Air Force Polish Air Force German Air Force Royal Netherlands Air Force Japan Air Self-Defense Force Italian Air Force sources: wikipedia + Lockheed Martin |
| images |
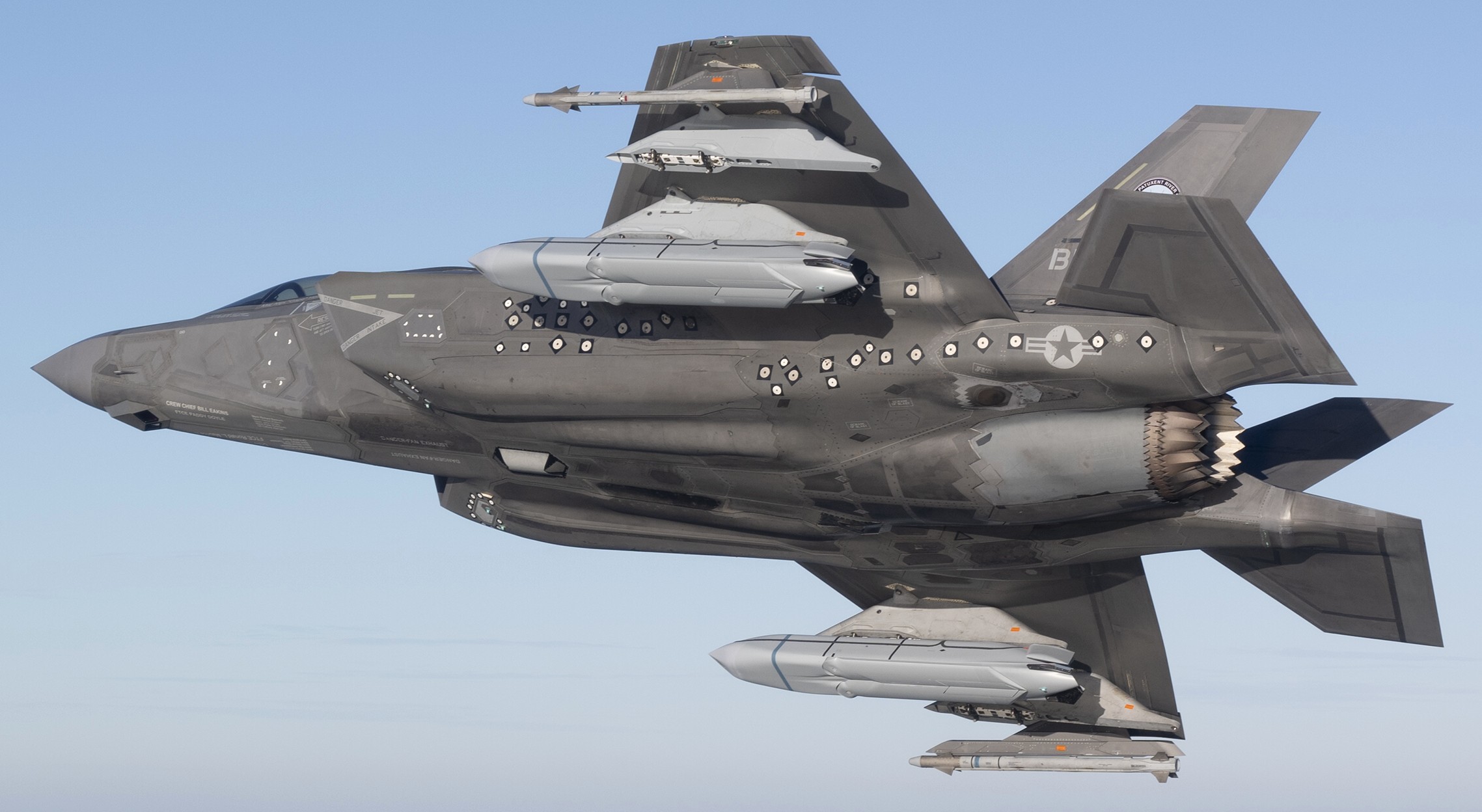 two AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) on an US Navy F-35B Lightning II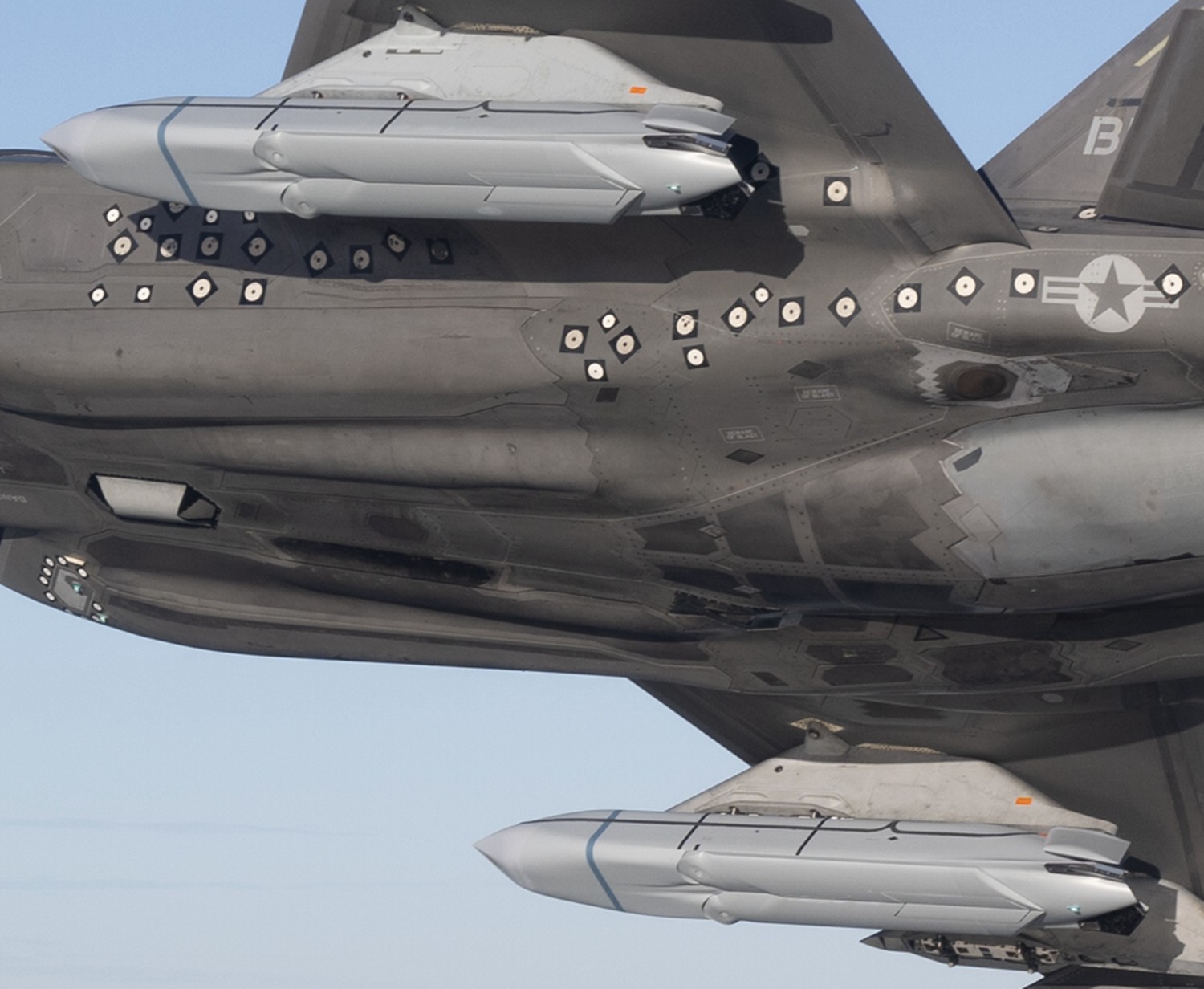  cutout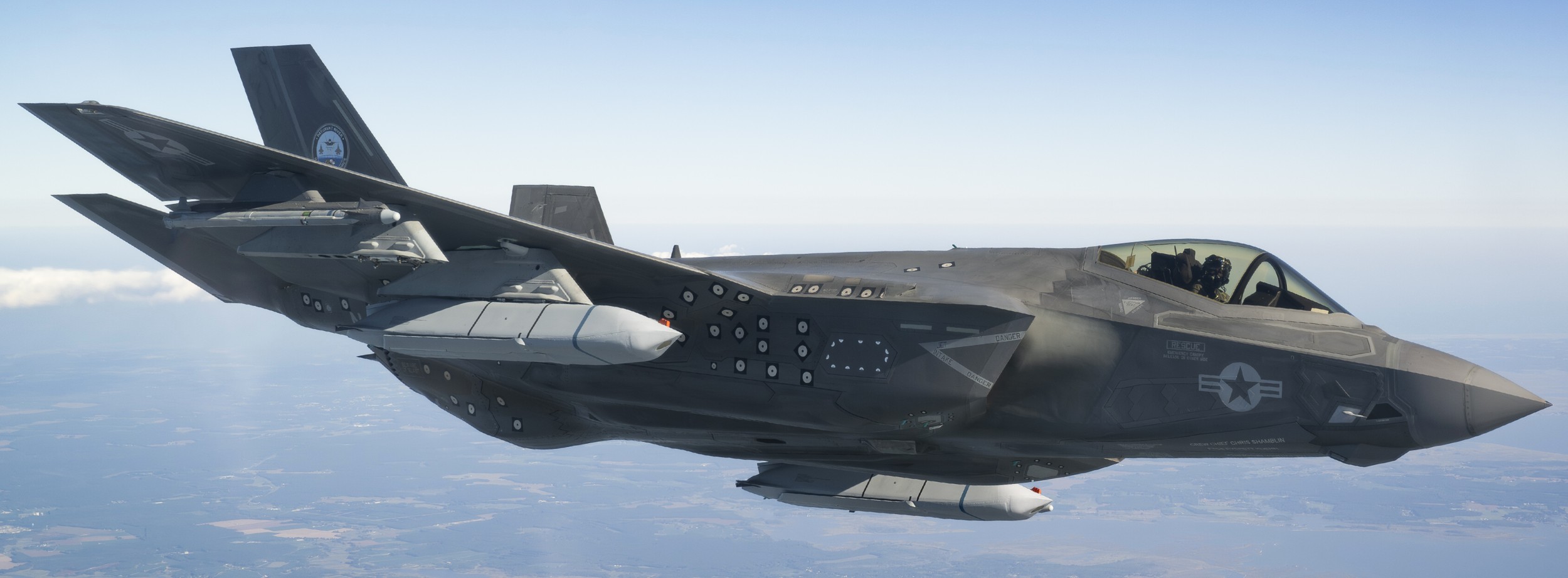  two AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) on an US Navy F-35B Lightning II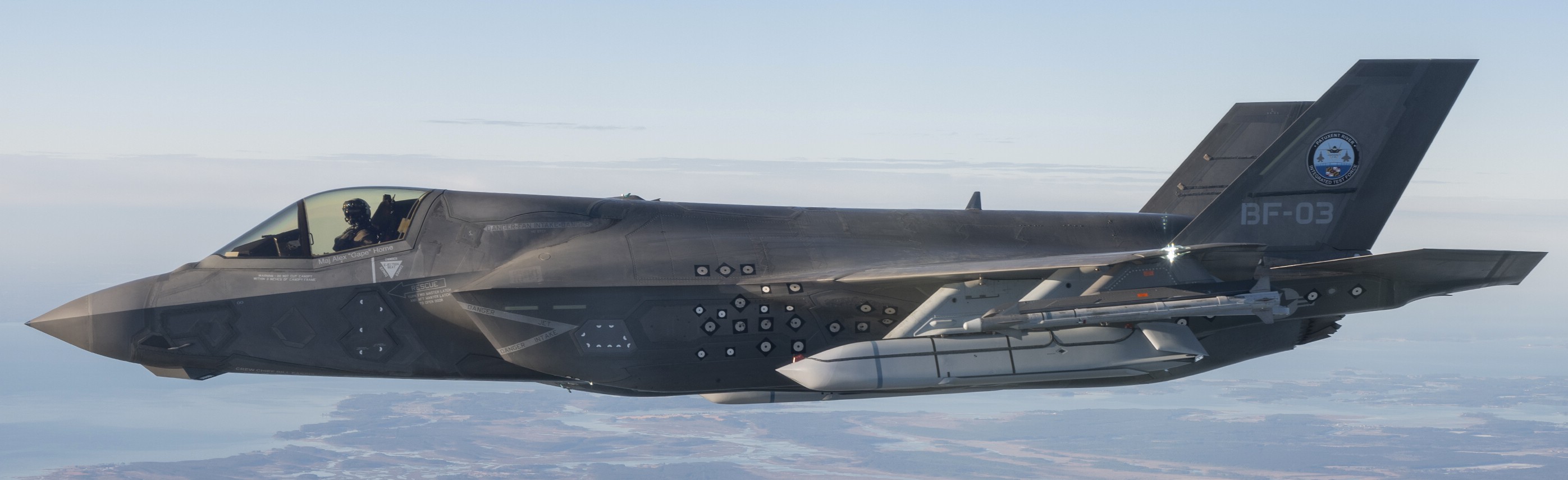  two AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) on an US Navy F-35B Lightning II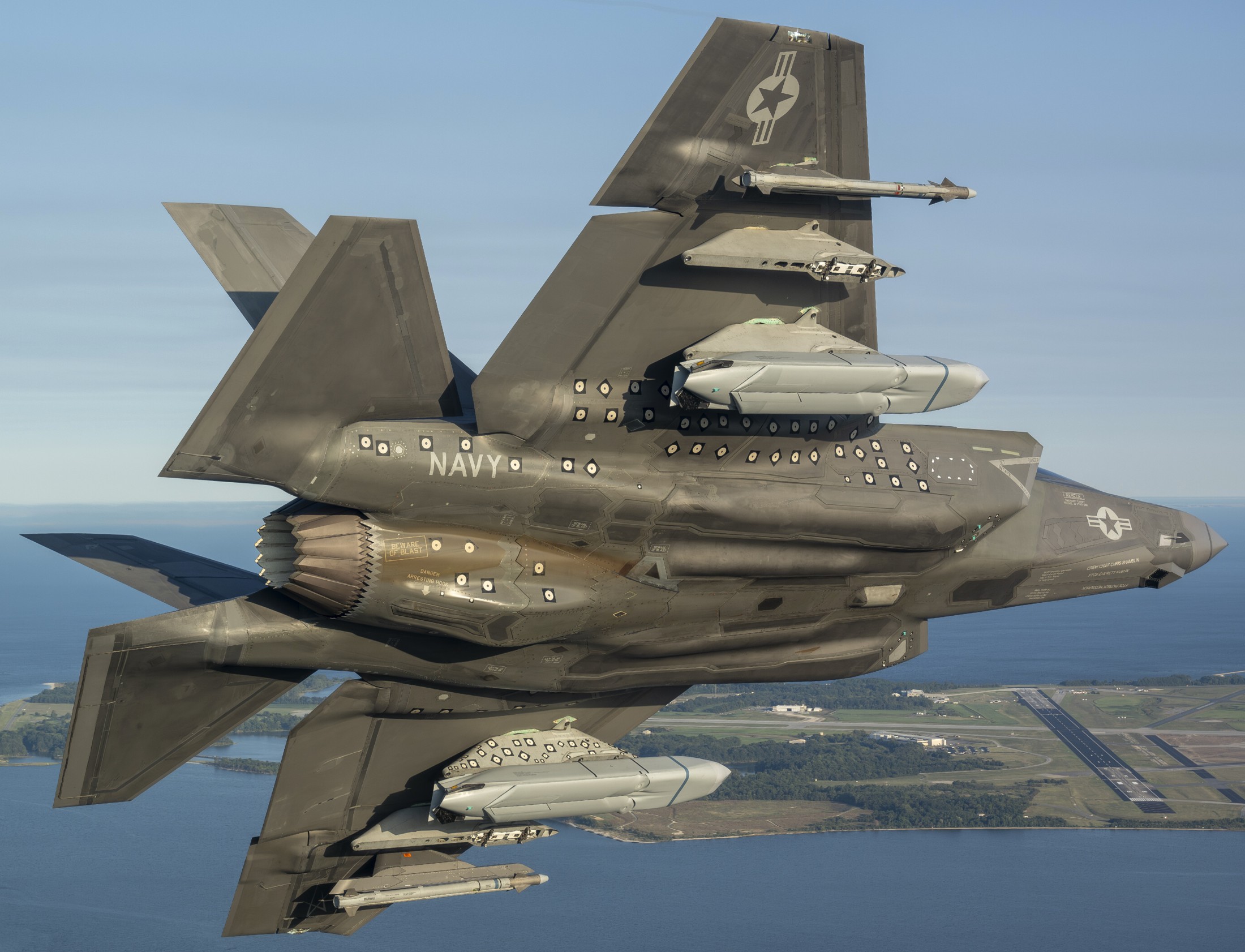  two AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) on an US Navy F-35C Lightning II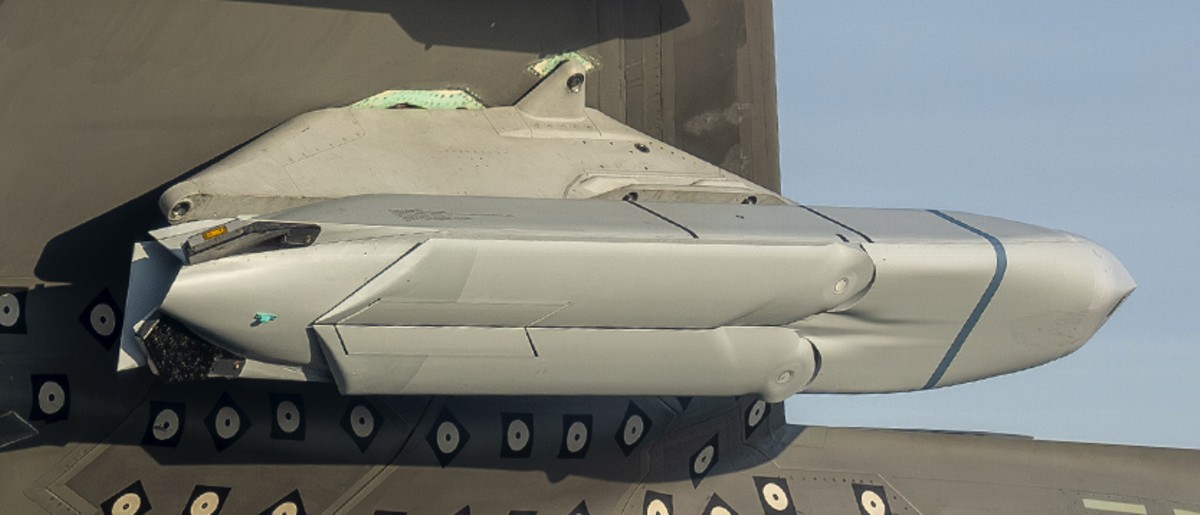  cutout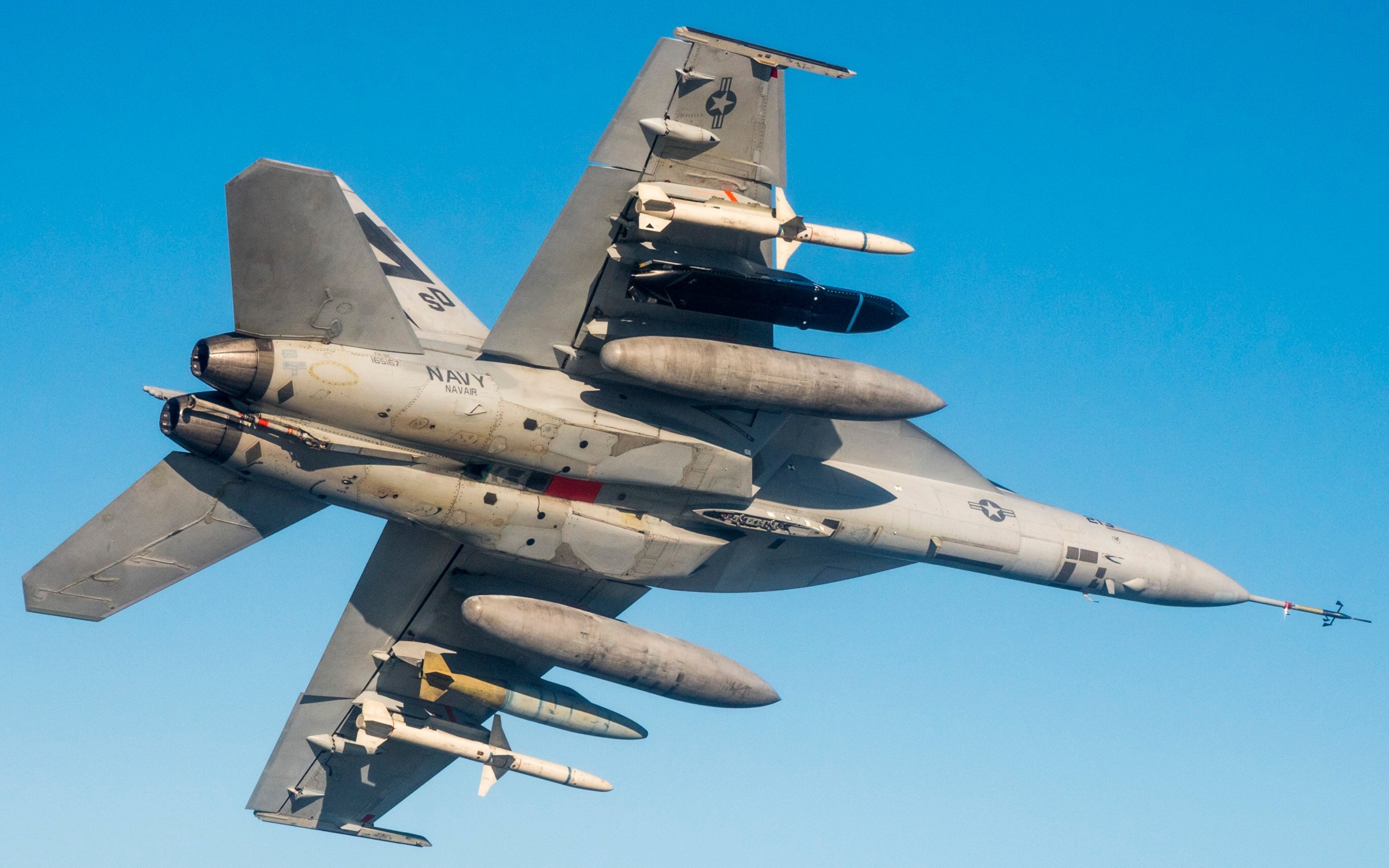  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) on an US Navy F/A-18E Super Hornet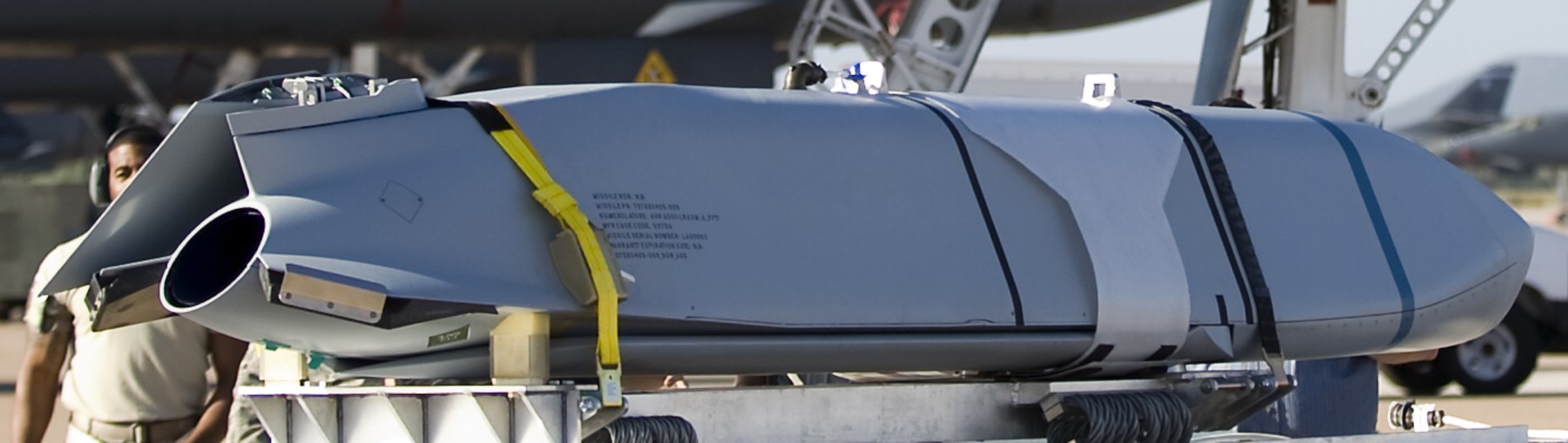  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)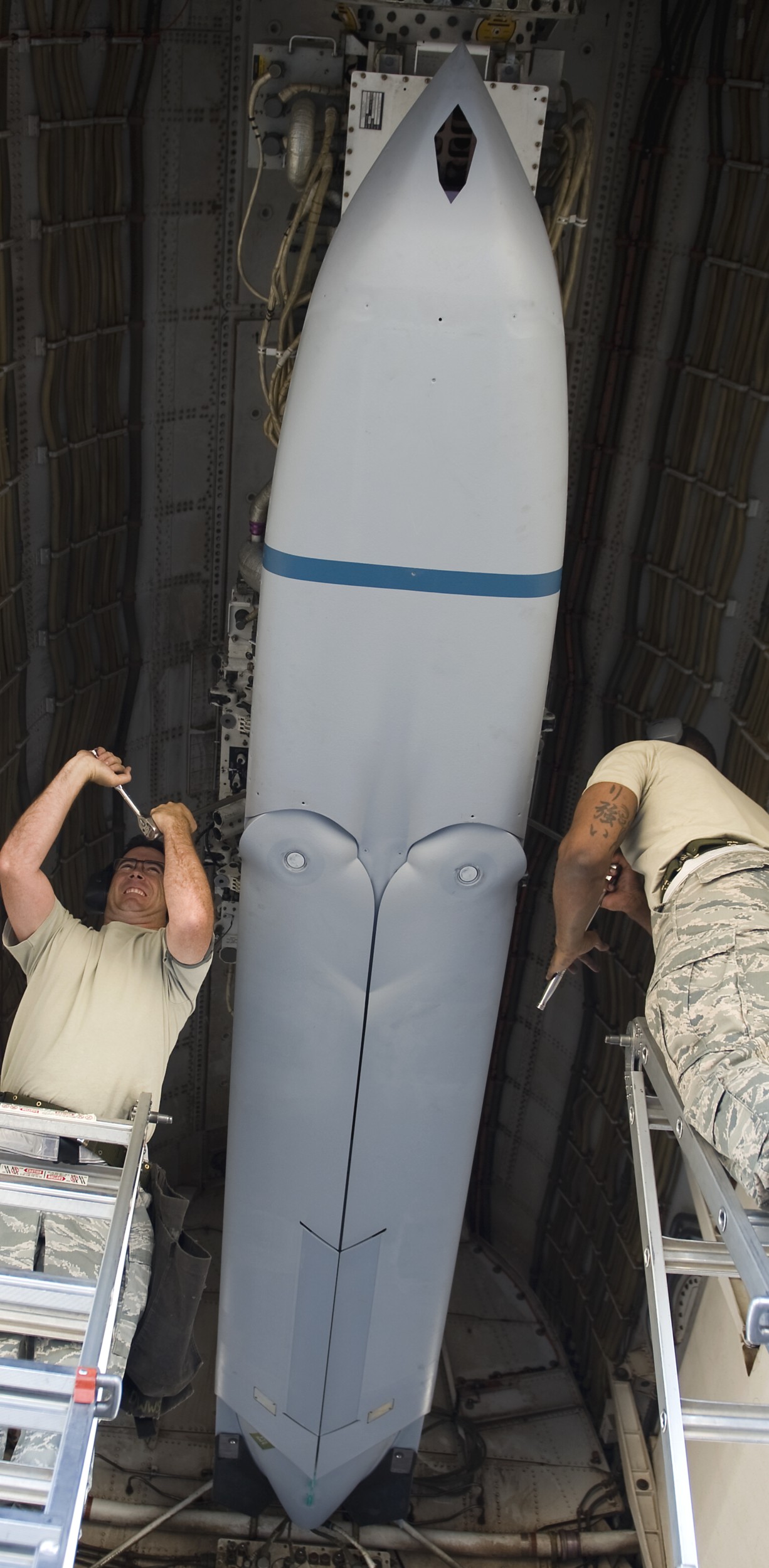  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) in an USAF B-1B lancer bomber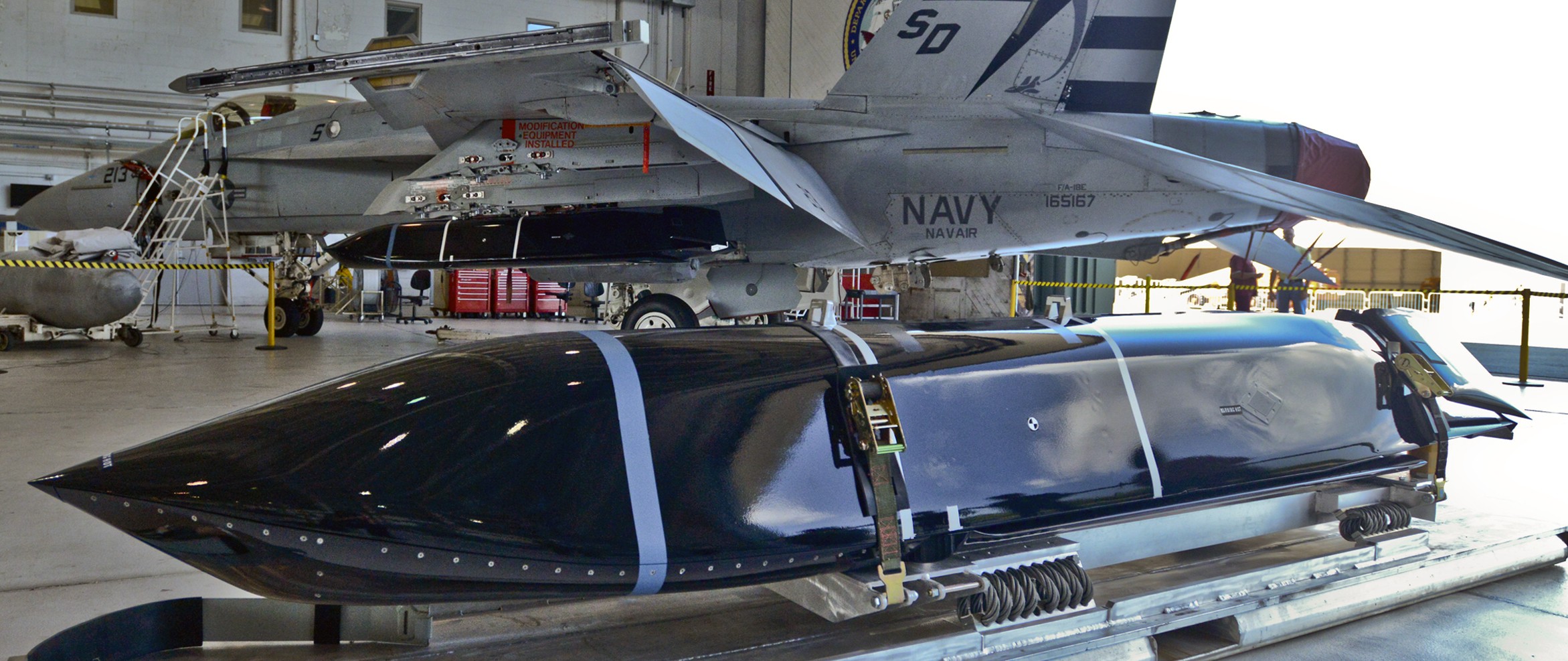  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)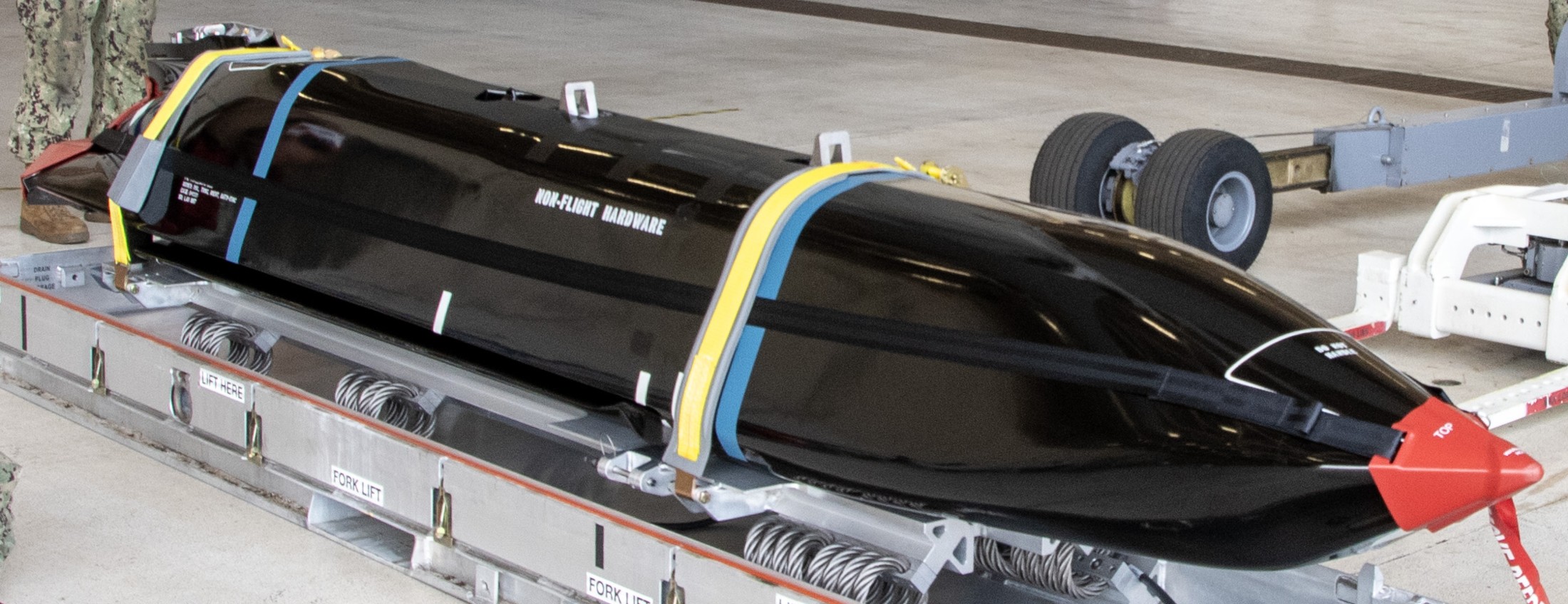  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)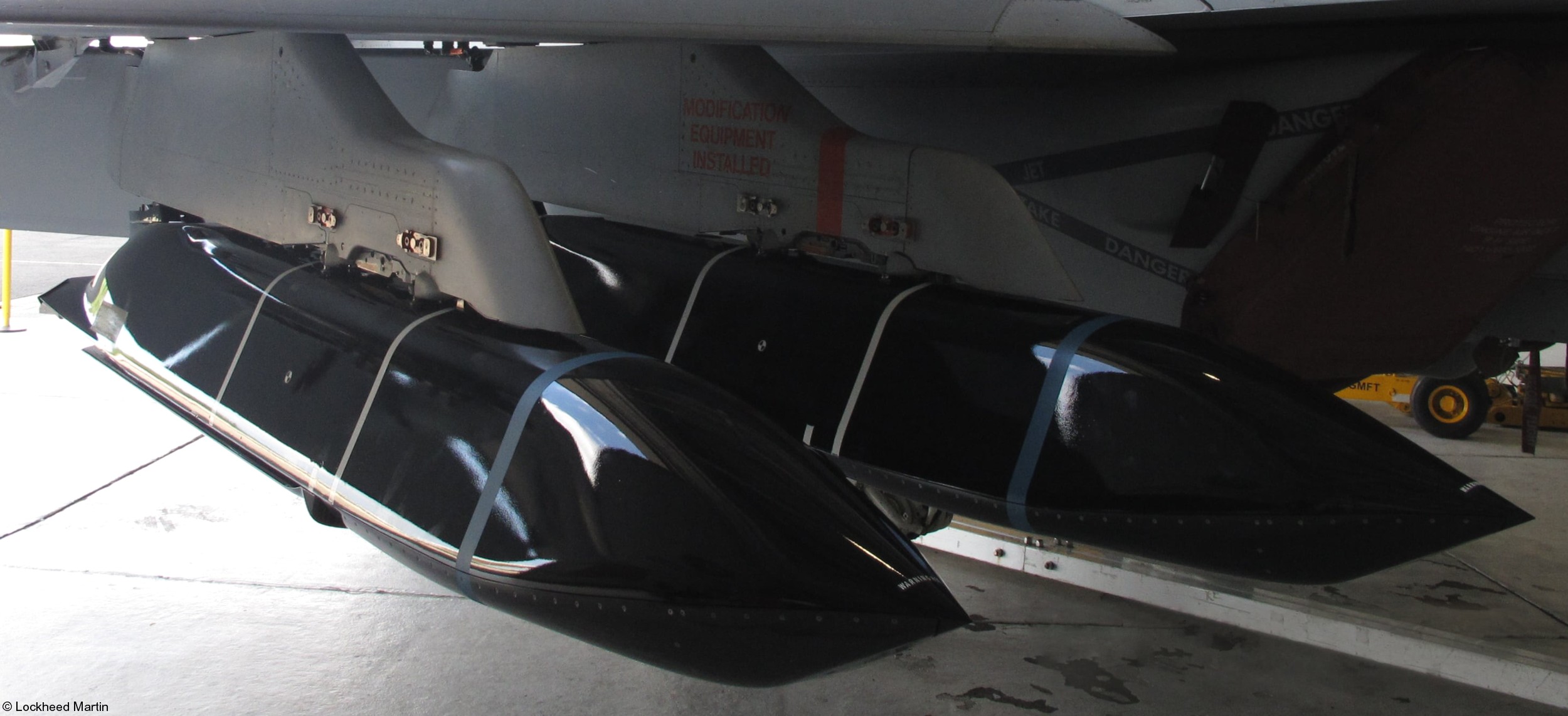  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)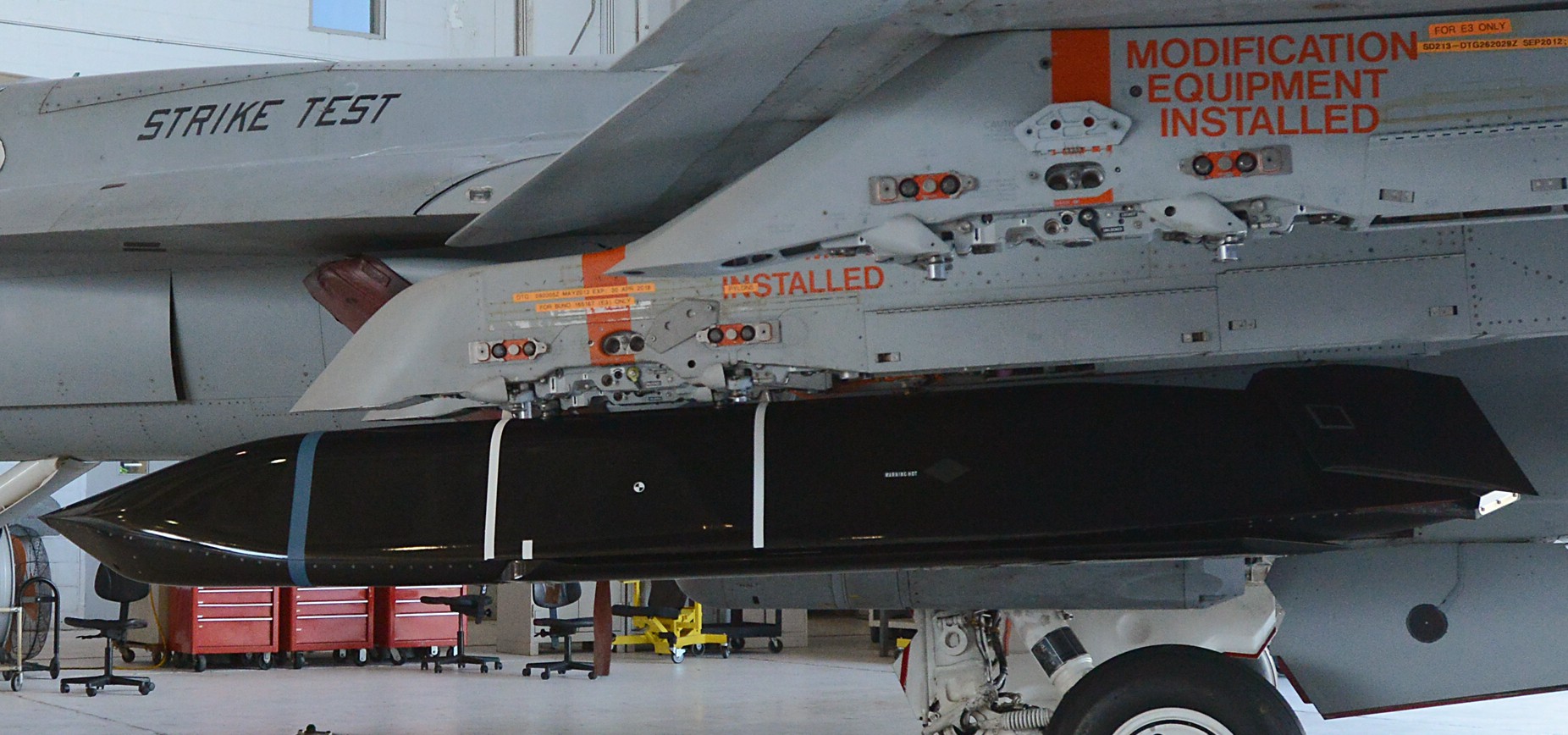  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)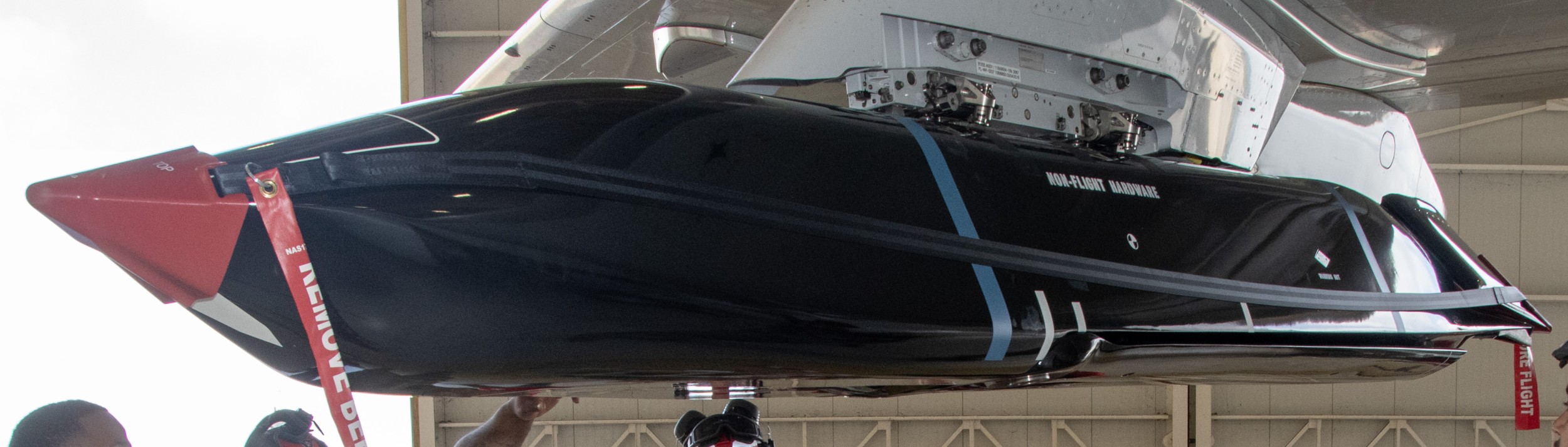  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)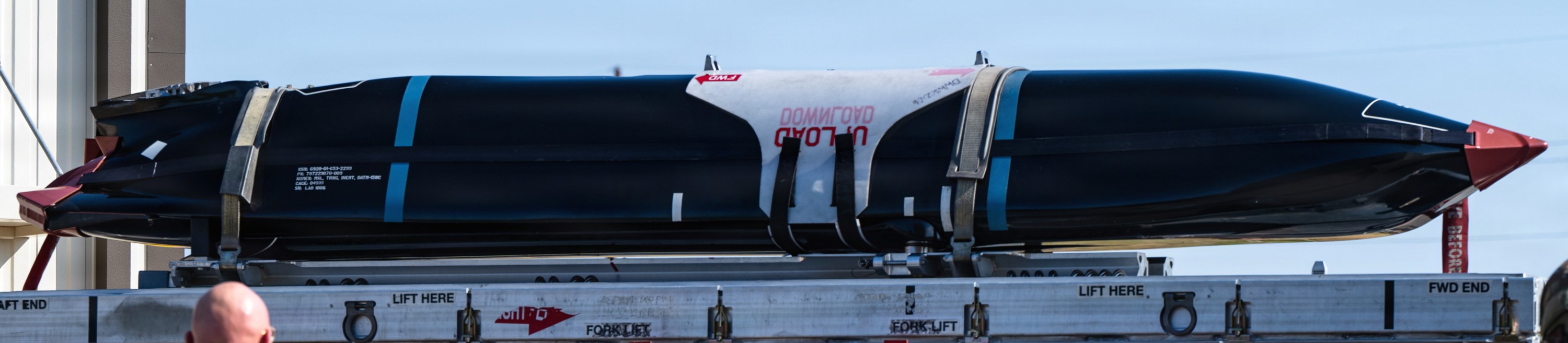  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM)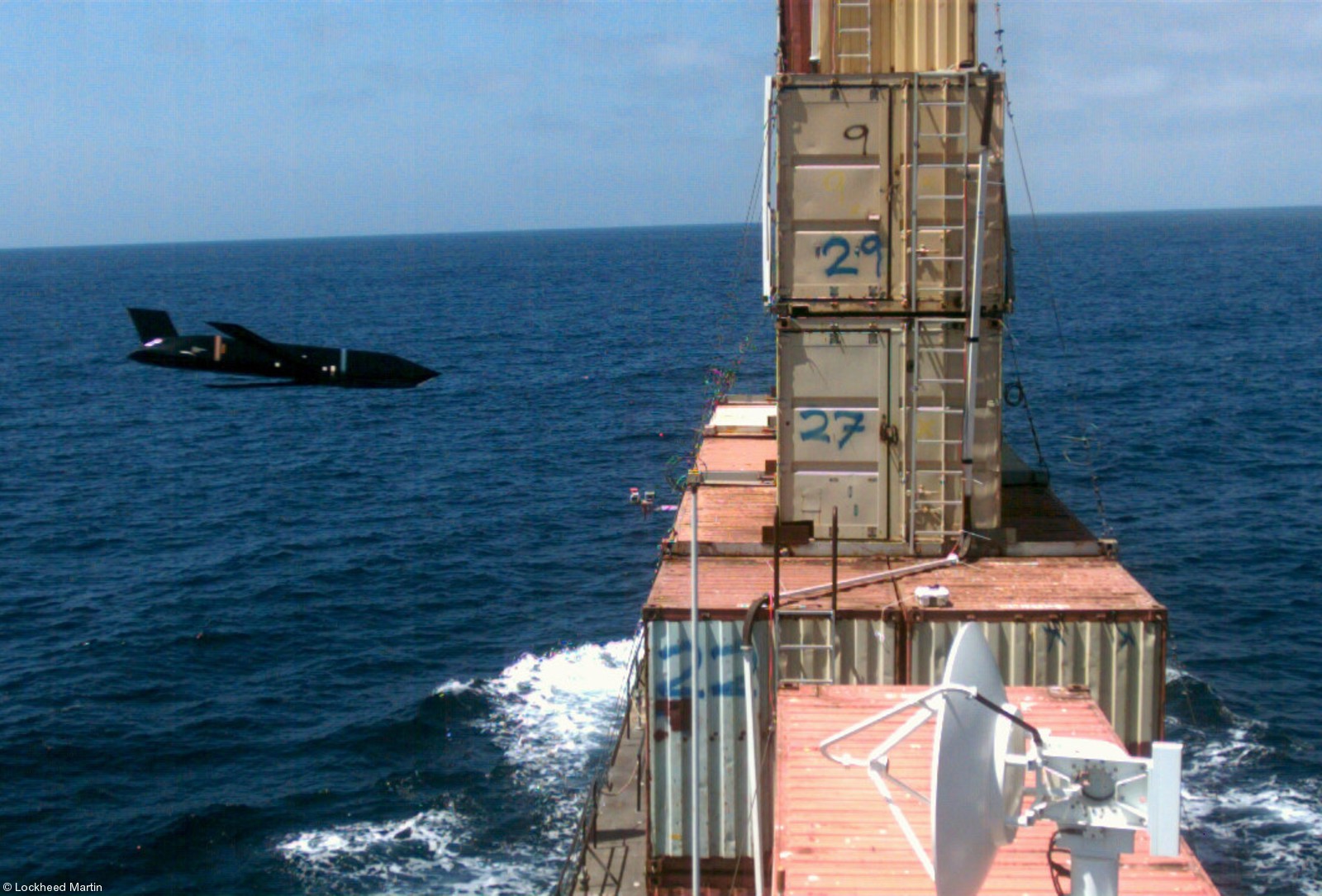  AGM-158C Long Range Anti Ship Missile (LRASM) - target tests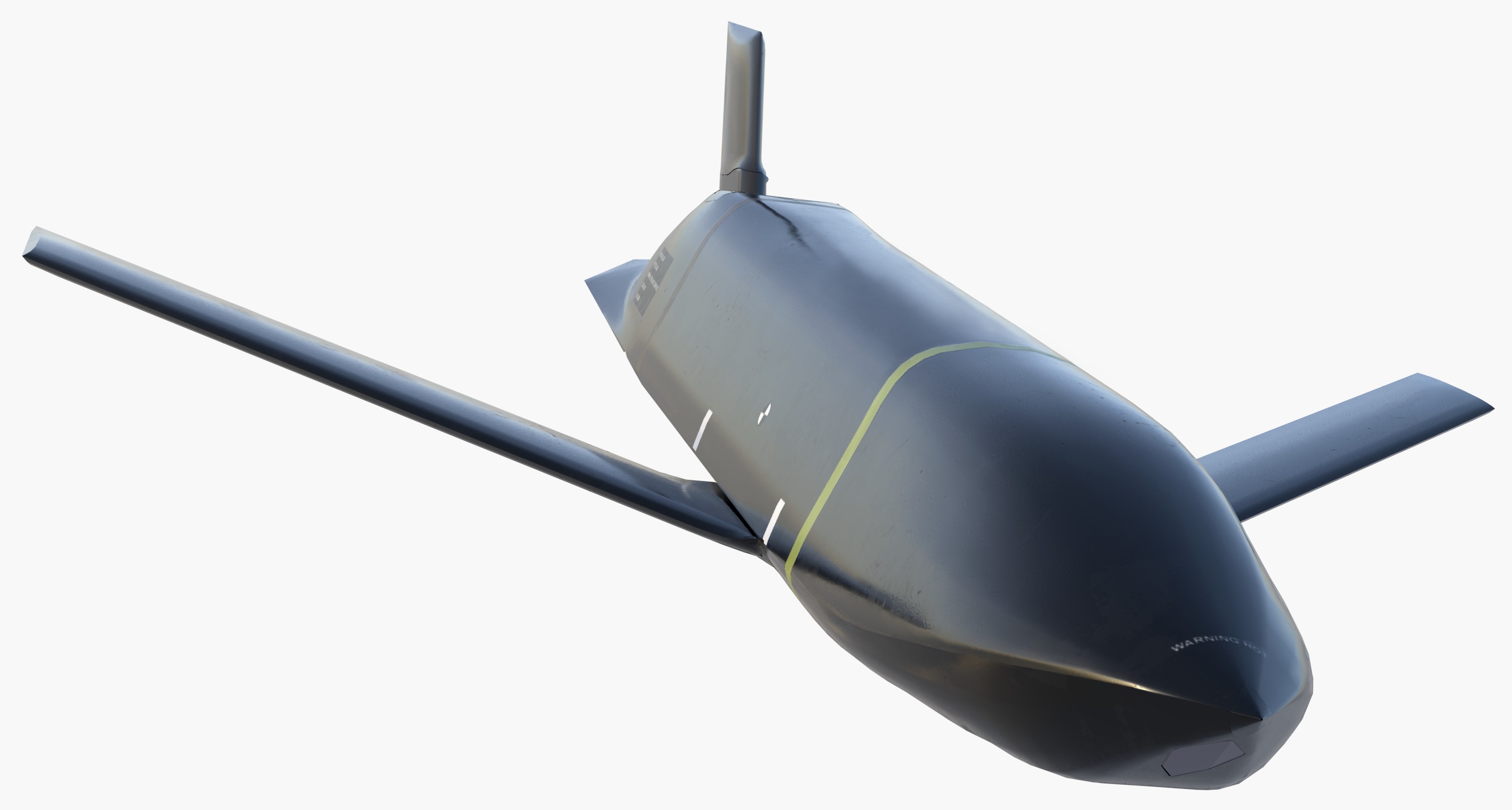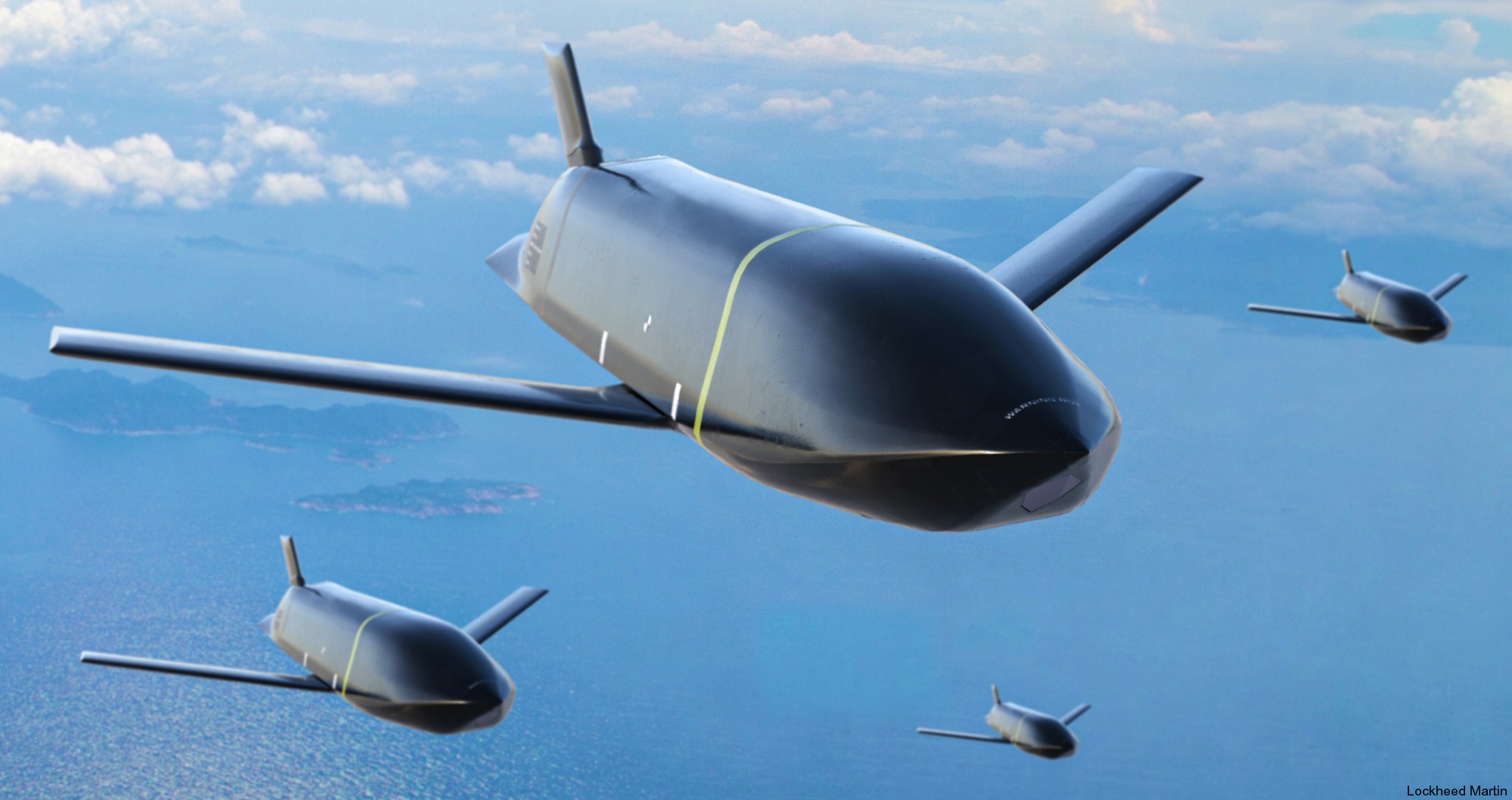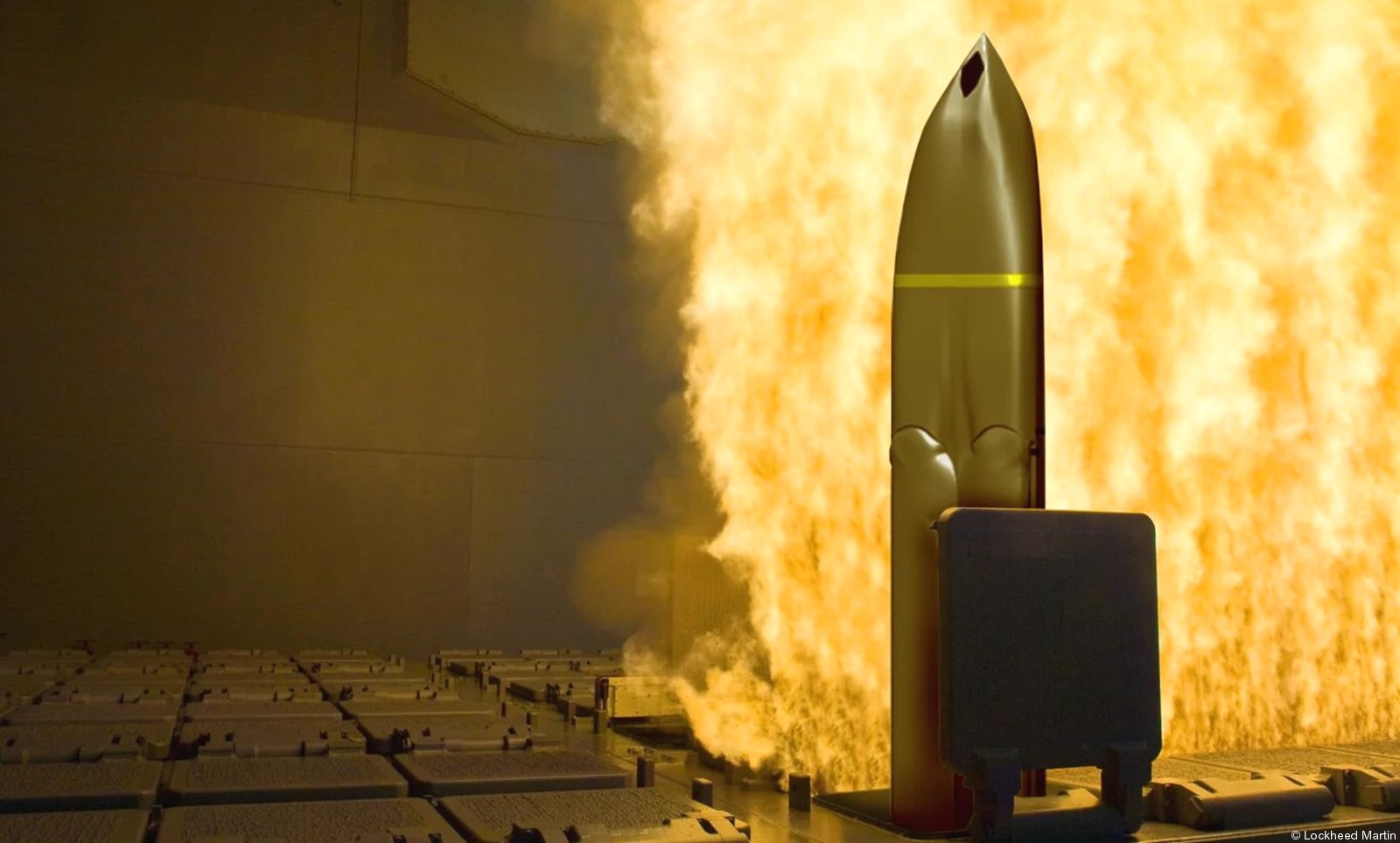    vertical launch LRASM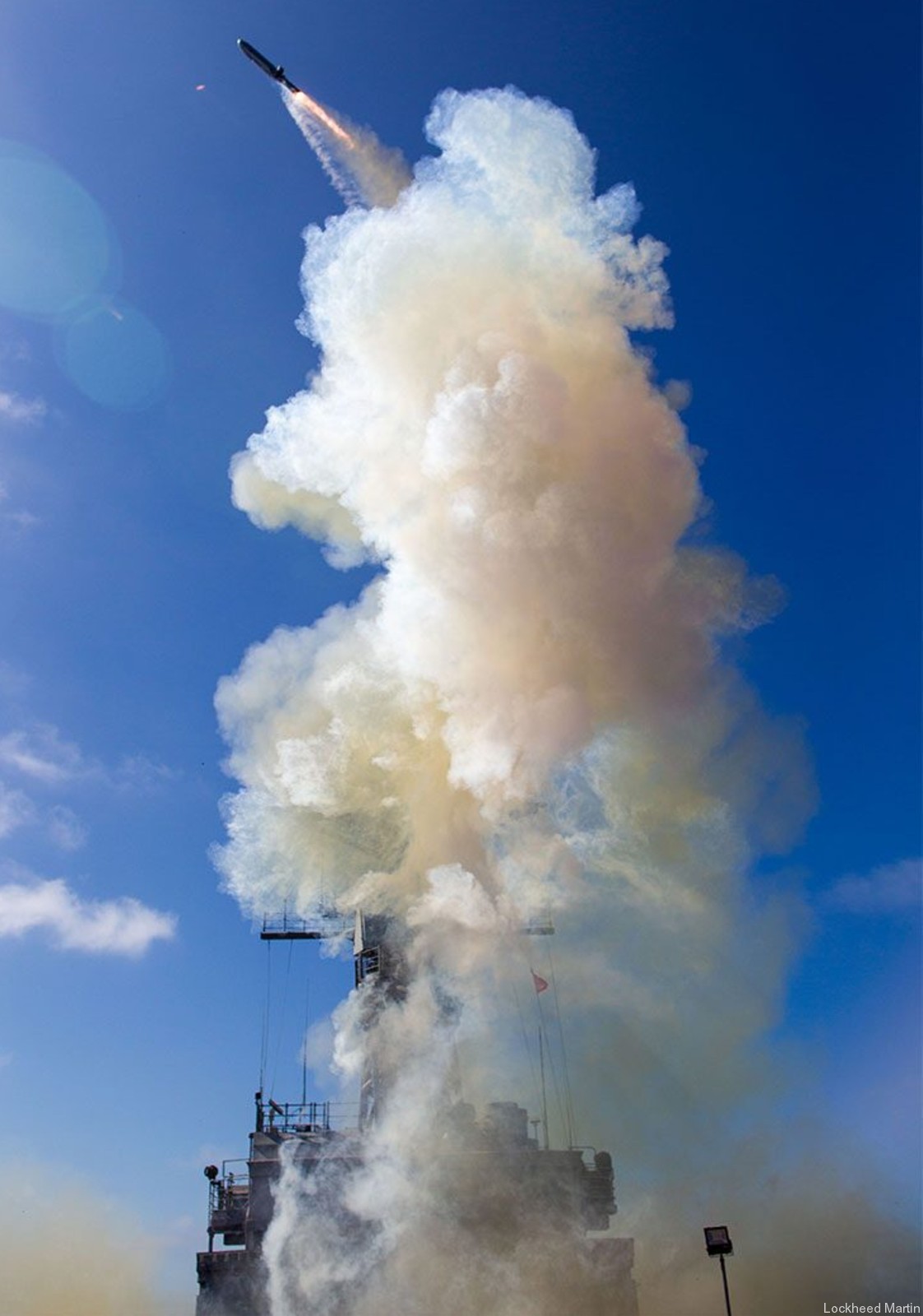  Mk.41 Vertical Launching System (VLS) test firing AGM-158A JASSM (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile) AGM-158B JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile-Extended Range)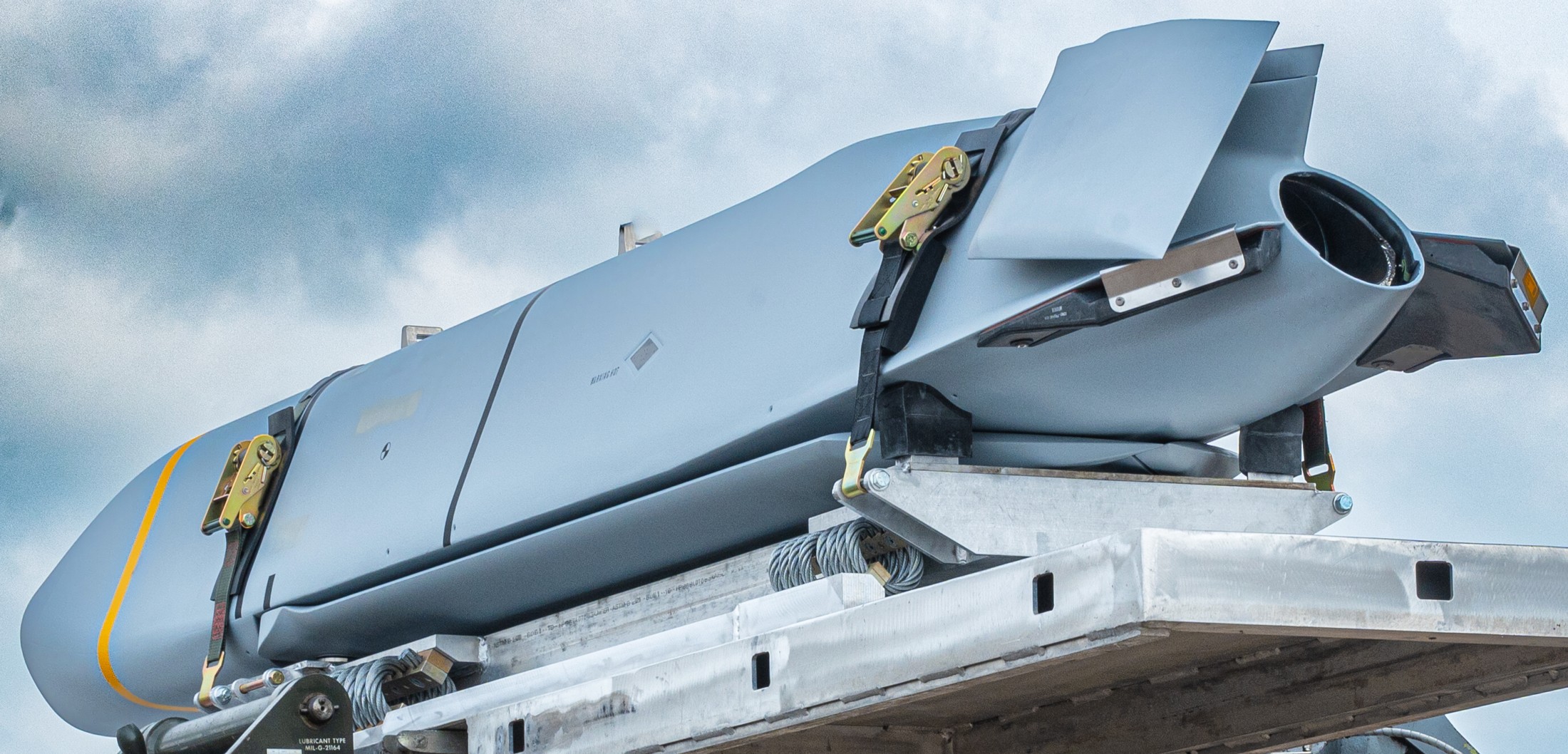  AGM-158A JASSM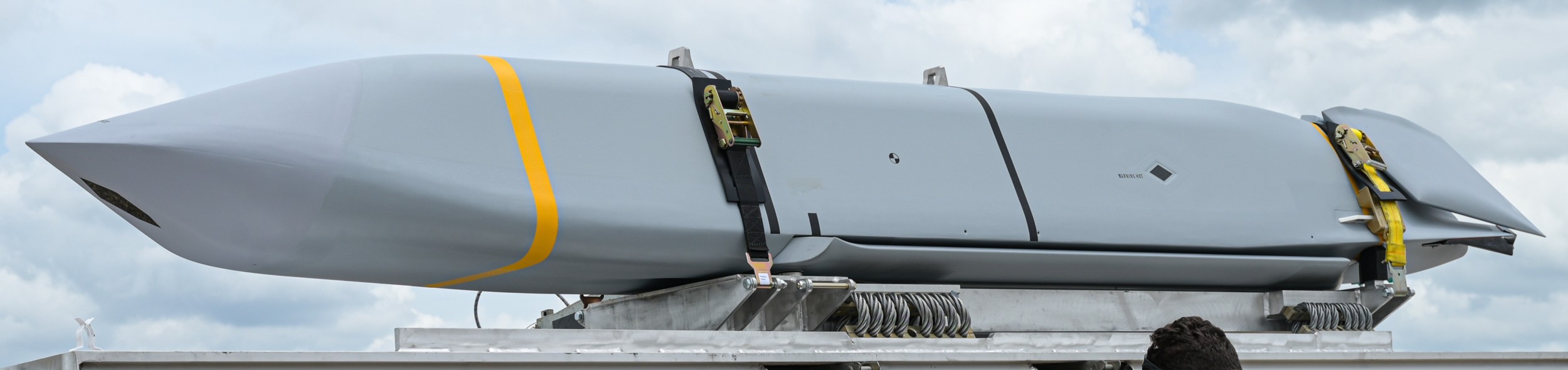  AGM-158A JASSM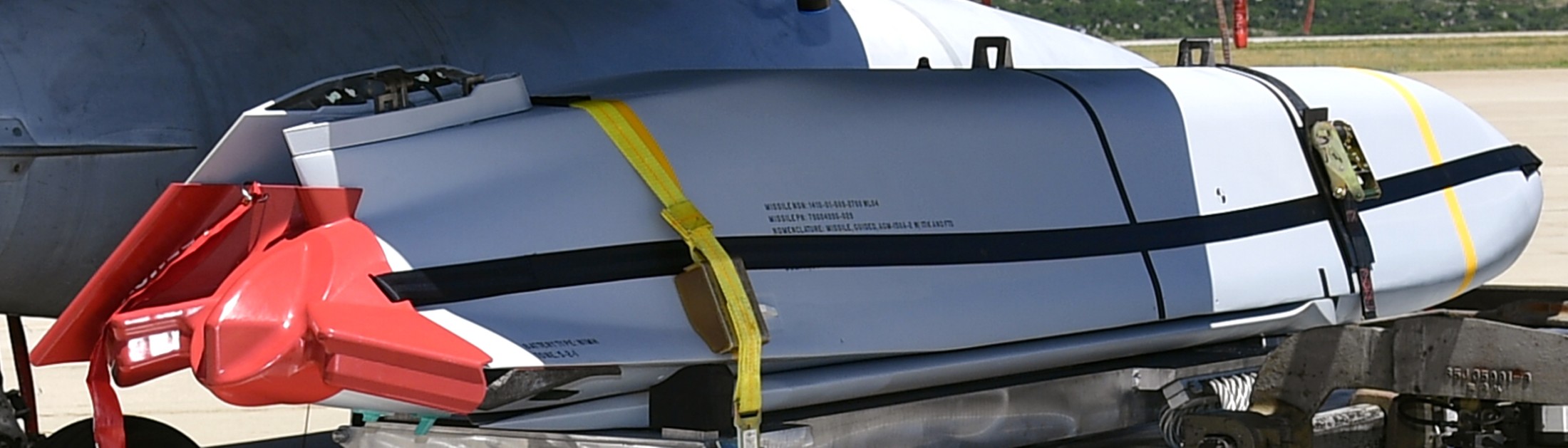  AGM-158A JASSM  AGM-158A JASSM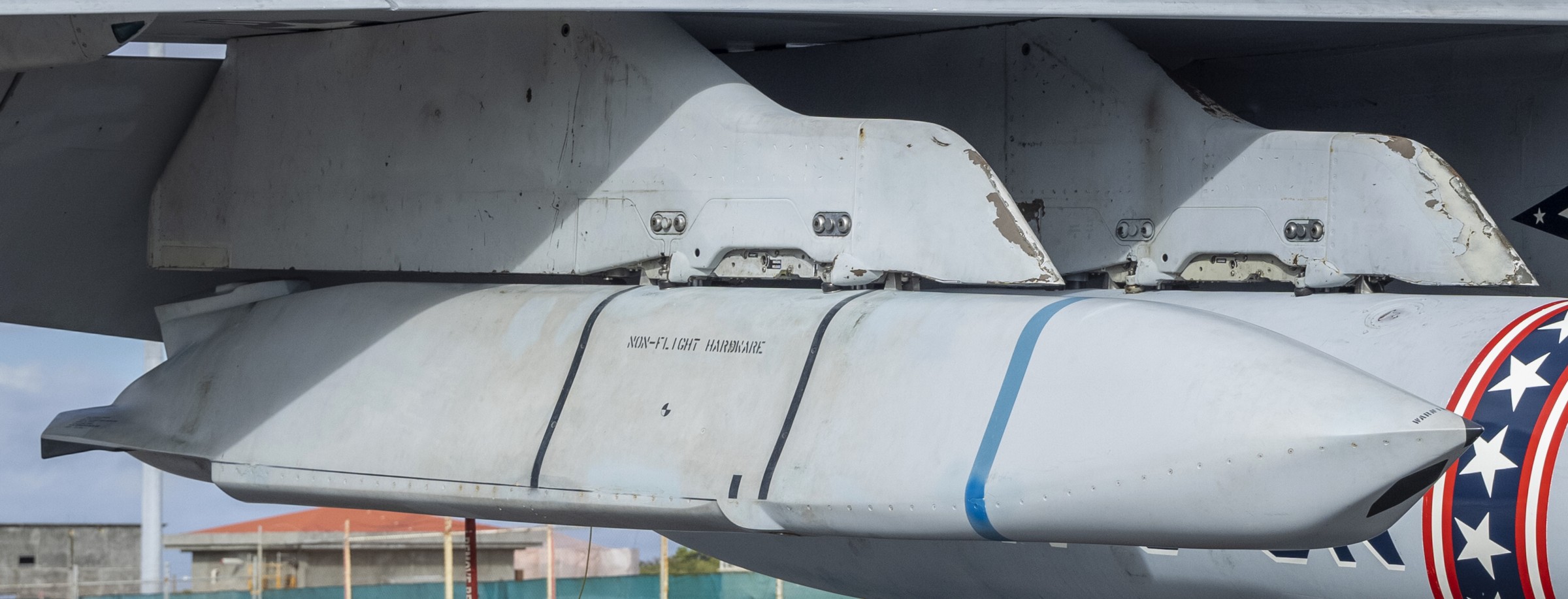  AGM-158A JASSM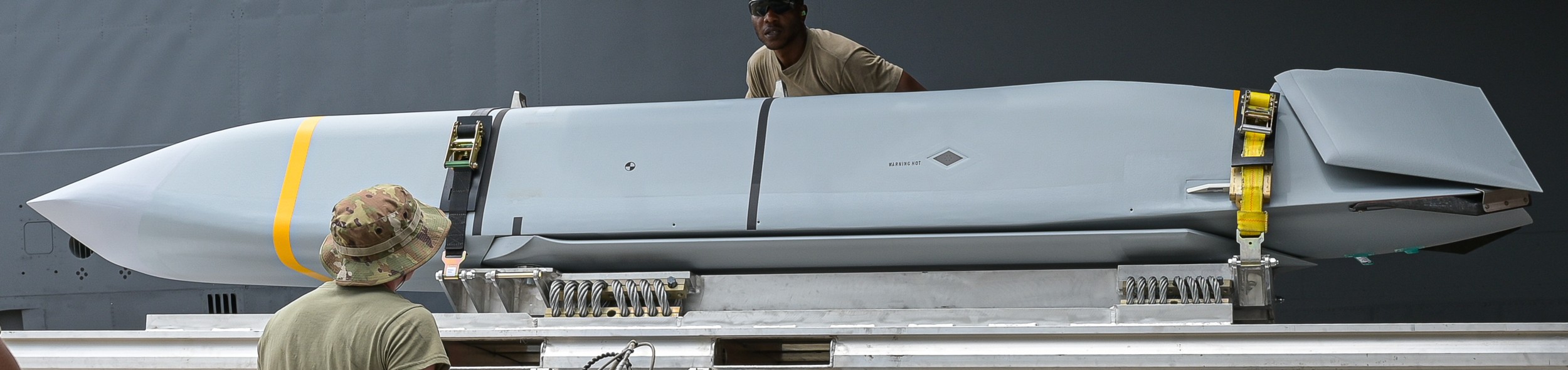  AGM-158A JASSM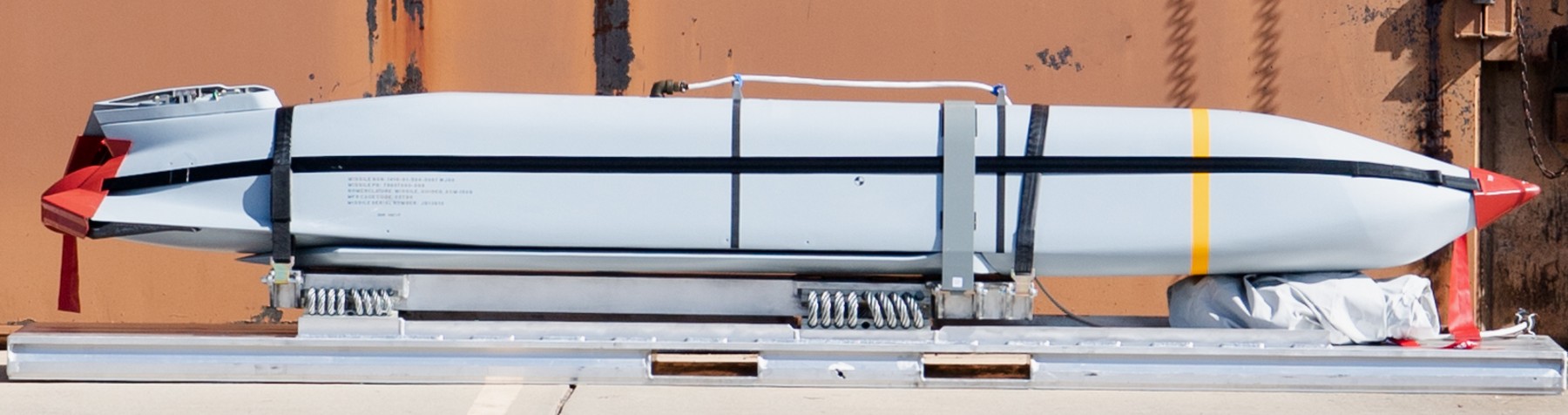  AGM-158A JASSM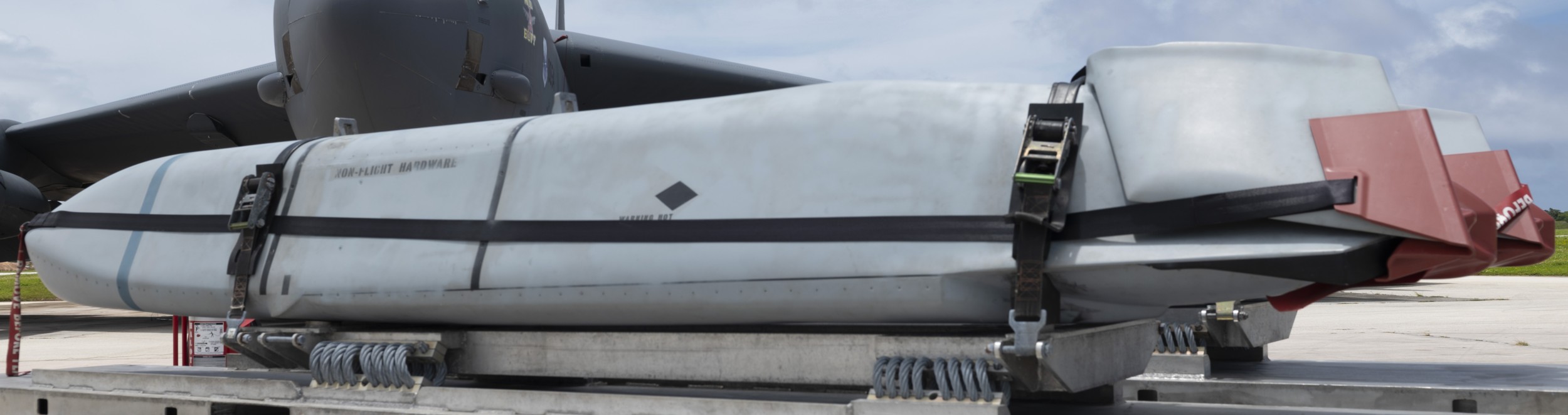  AGM-158A JASSM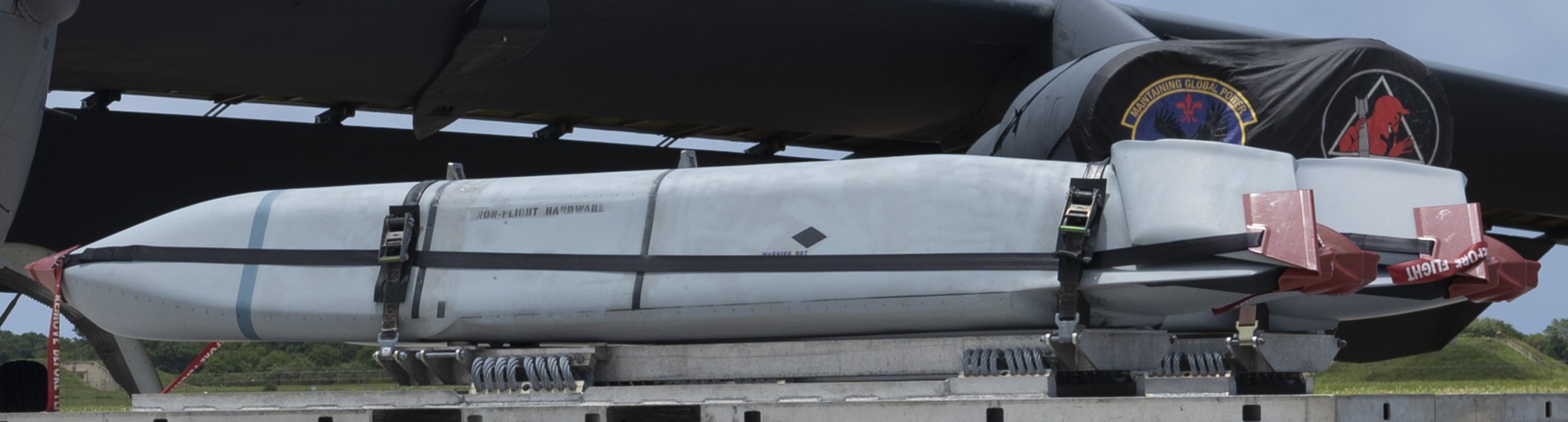  AGM-158A JASSM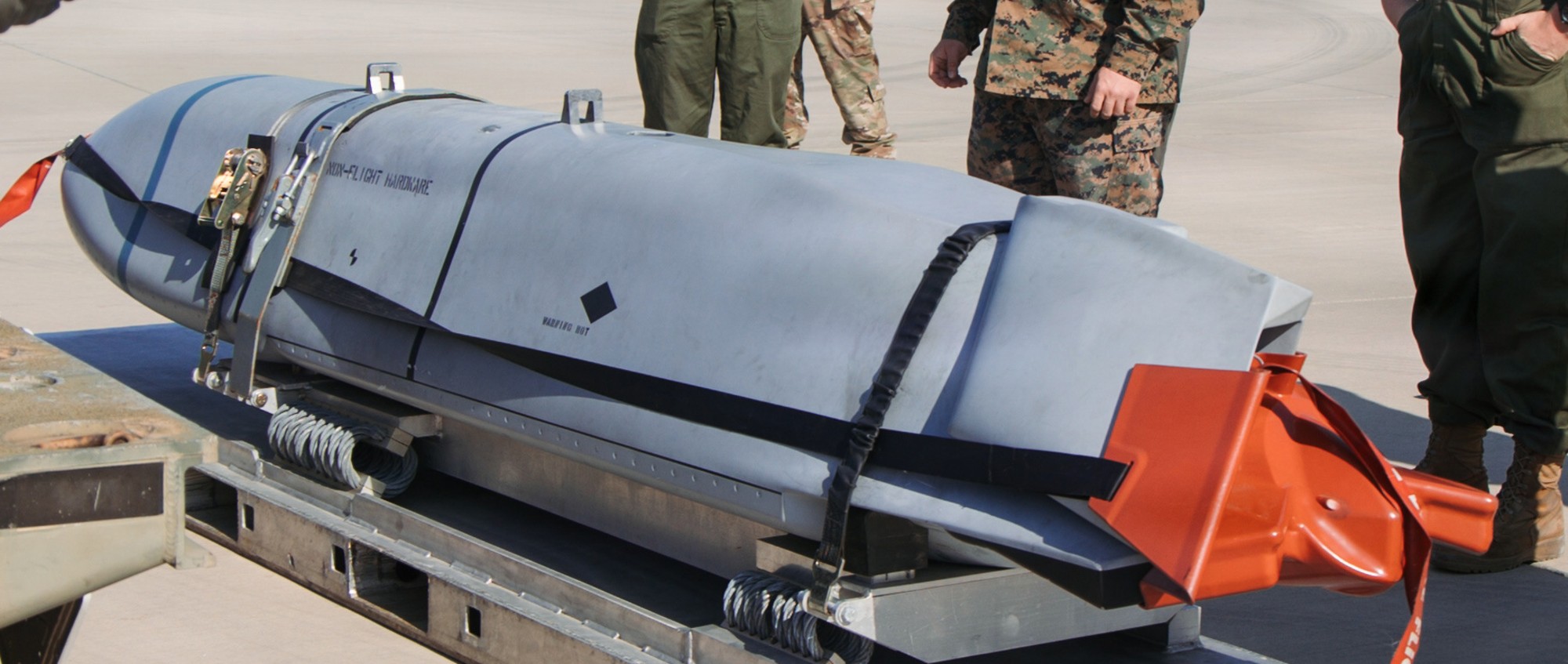  AGM-158A JASSM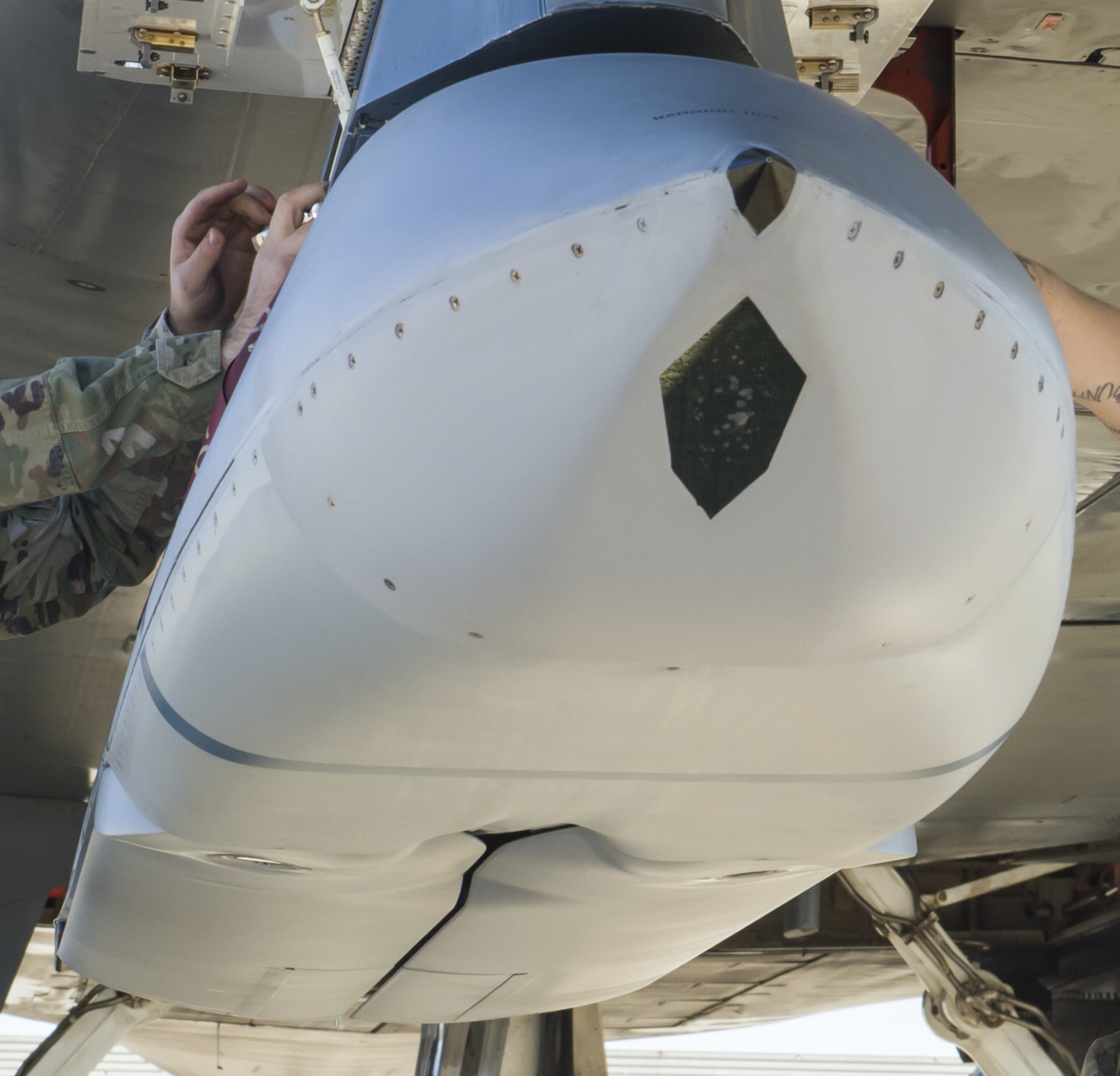  AGM-158A JASSM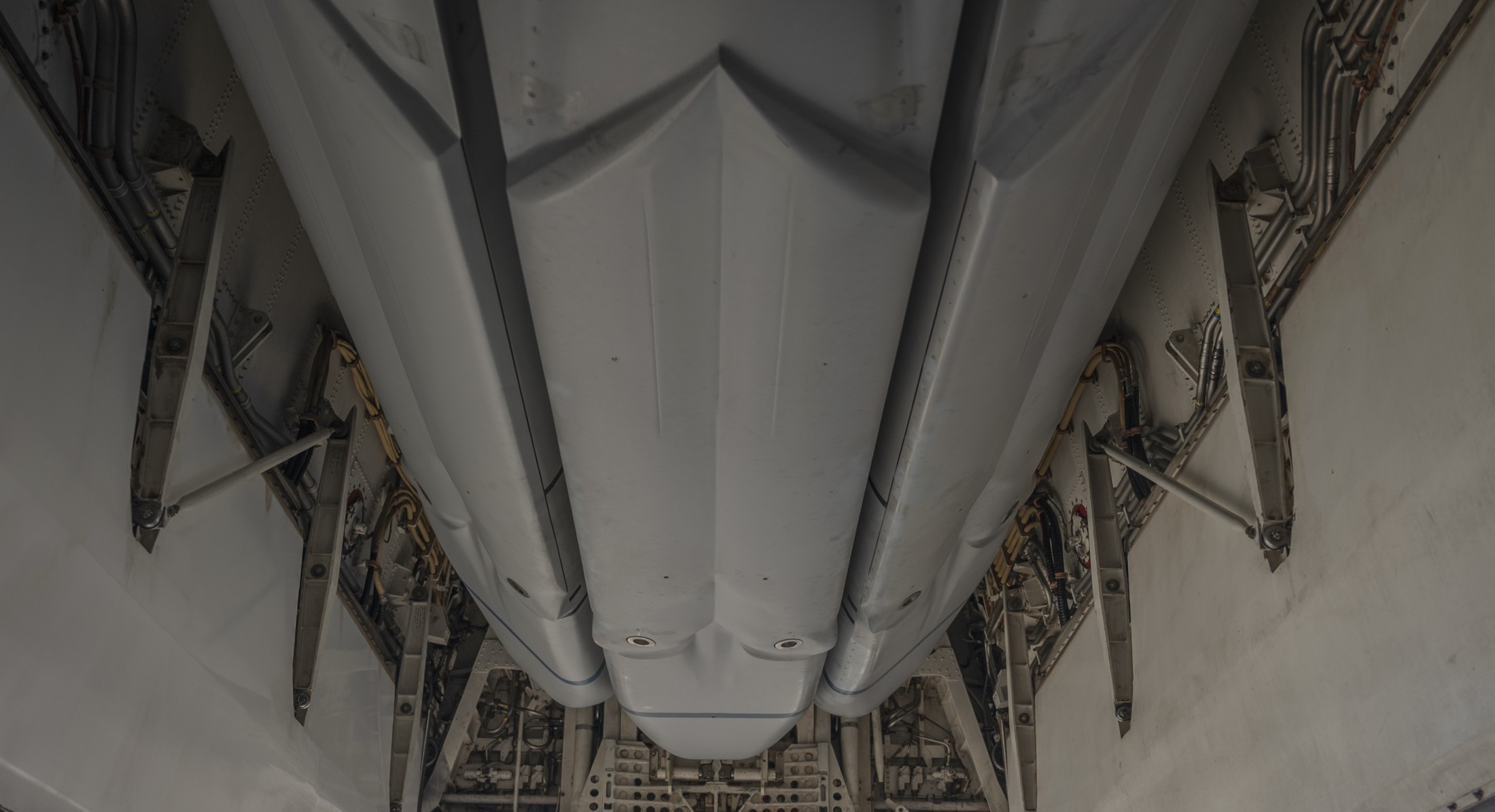  AGM-158A JASSM in an USAF B-1B Lancer bomber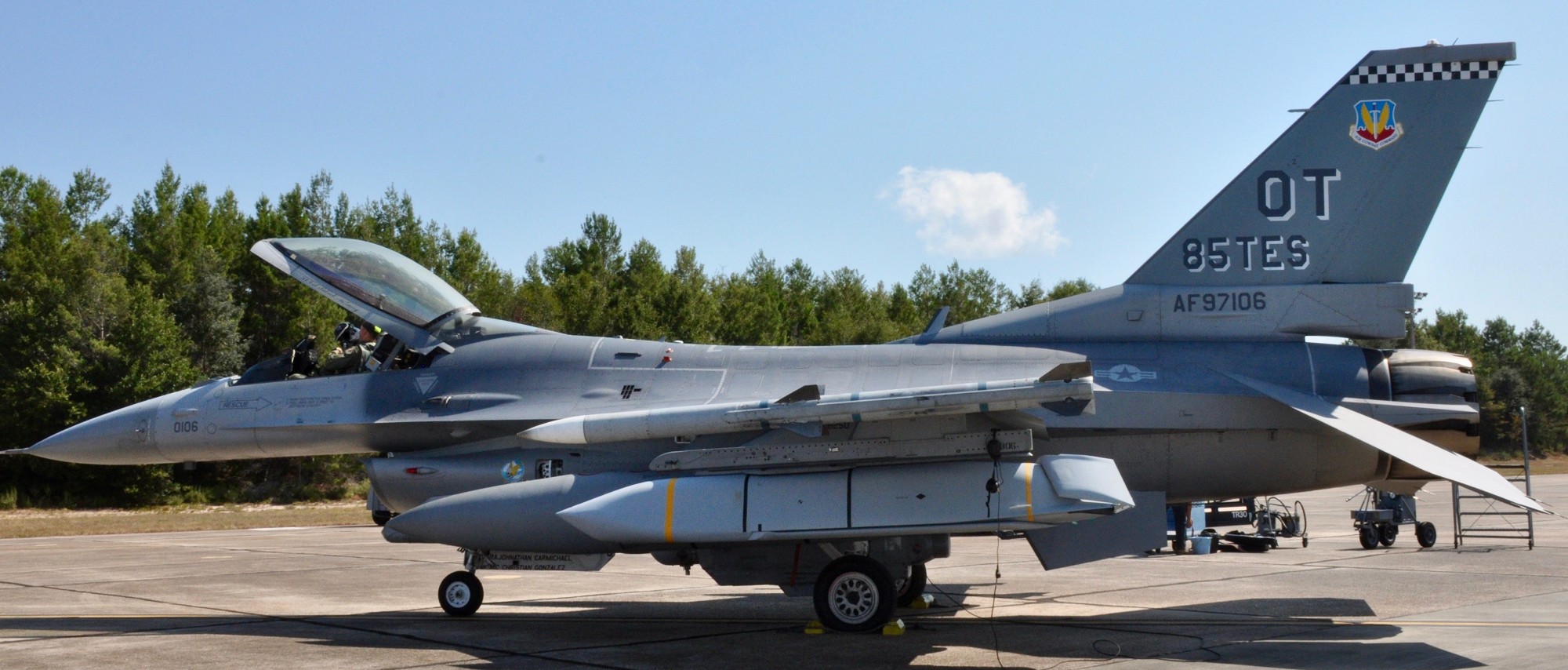  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) on an USAF F-16C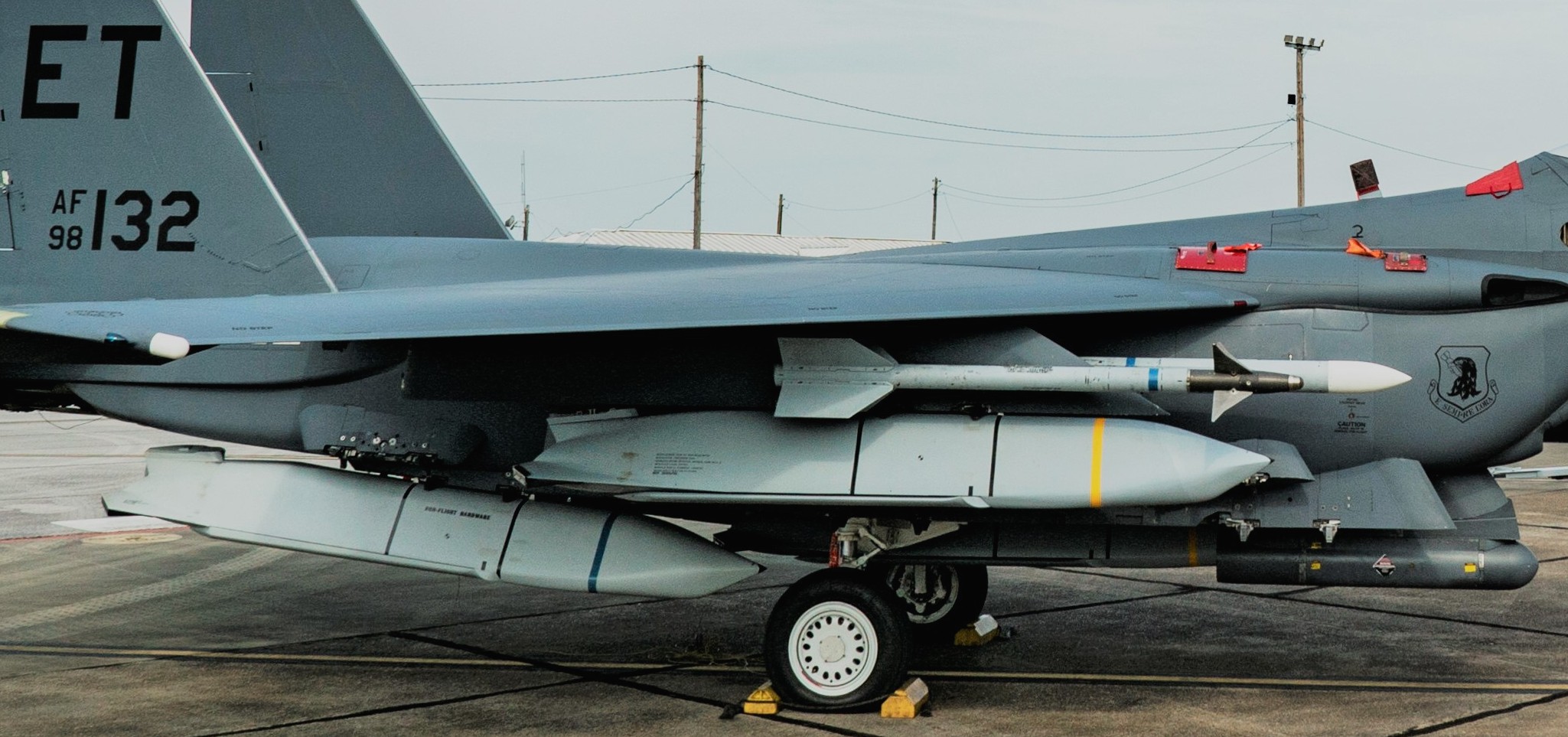  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) on an USAF F-15E Strike Eagle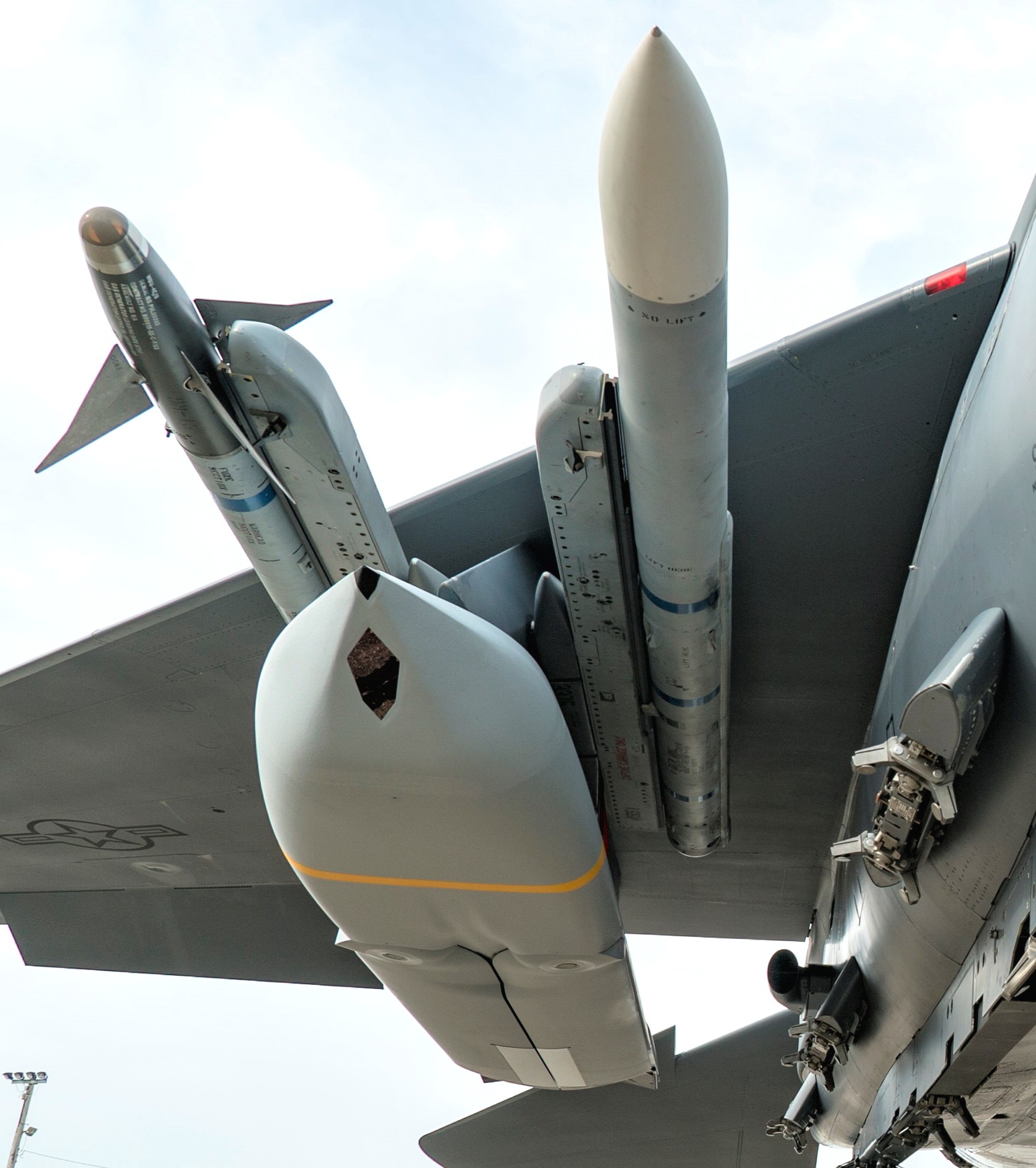  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) on an USAF F-15E Strike Eagle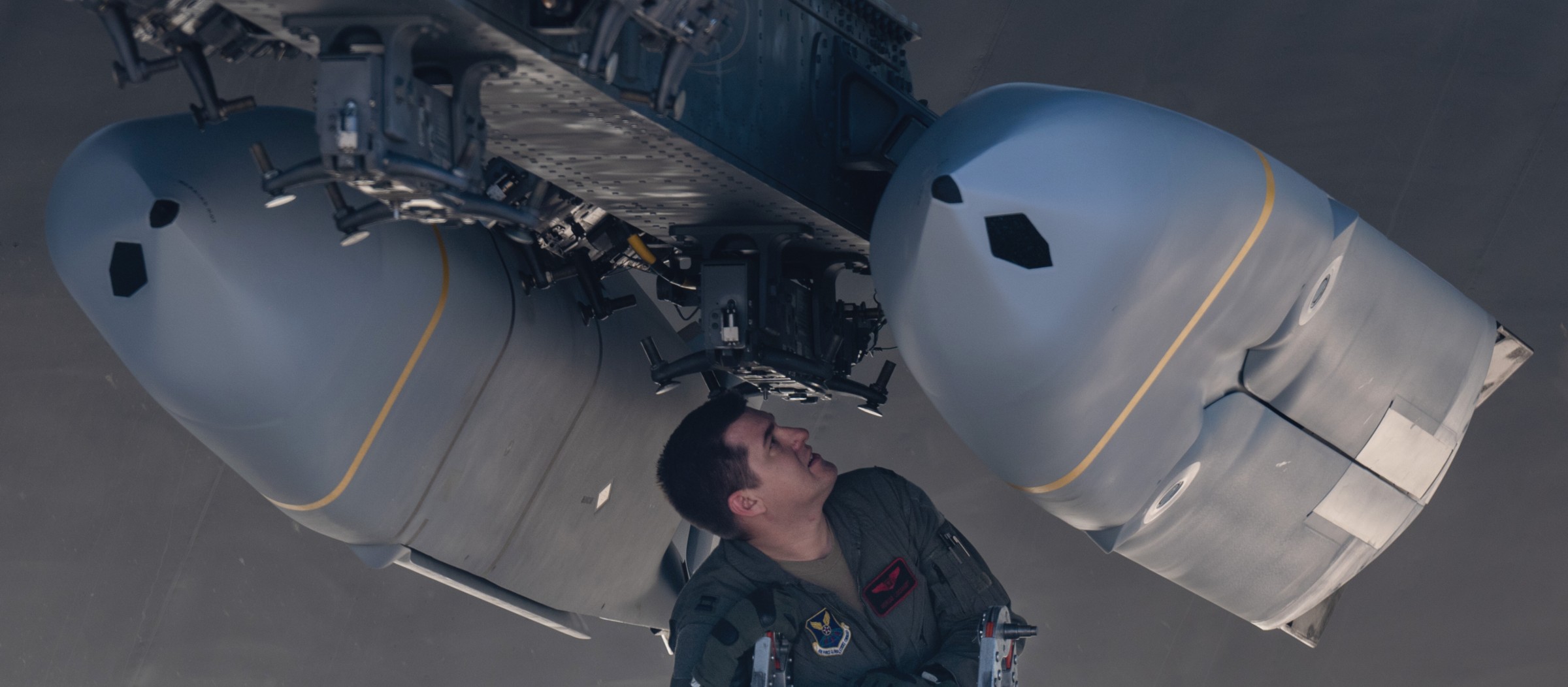  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) on an USAF B-52H Stratofortress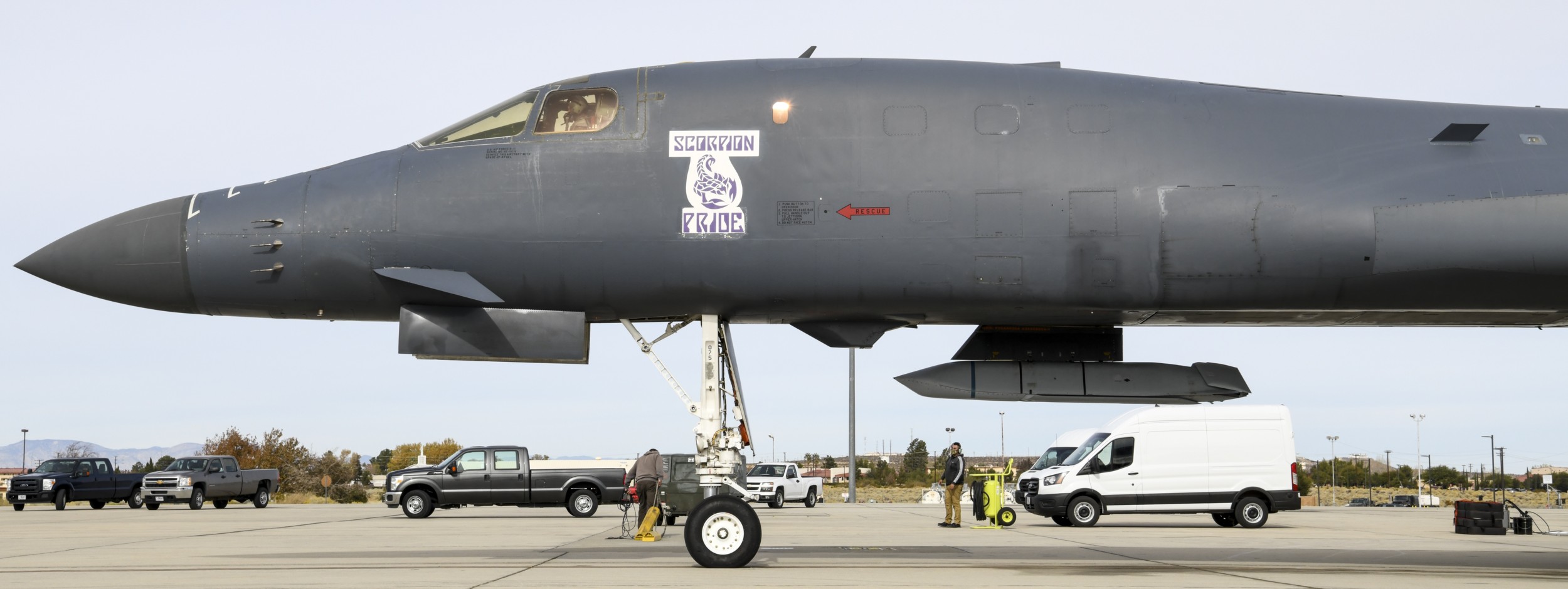  AGM-158A JASSM on an USAF B-1B Lancer bomber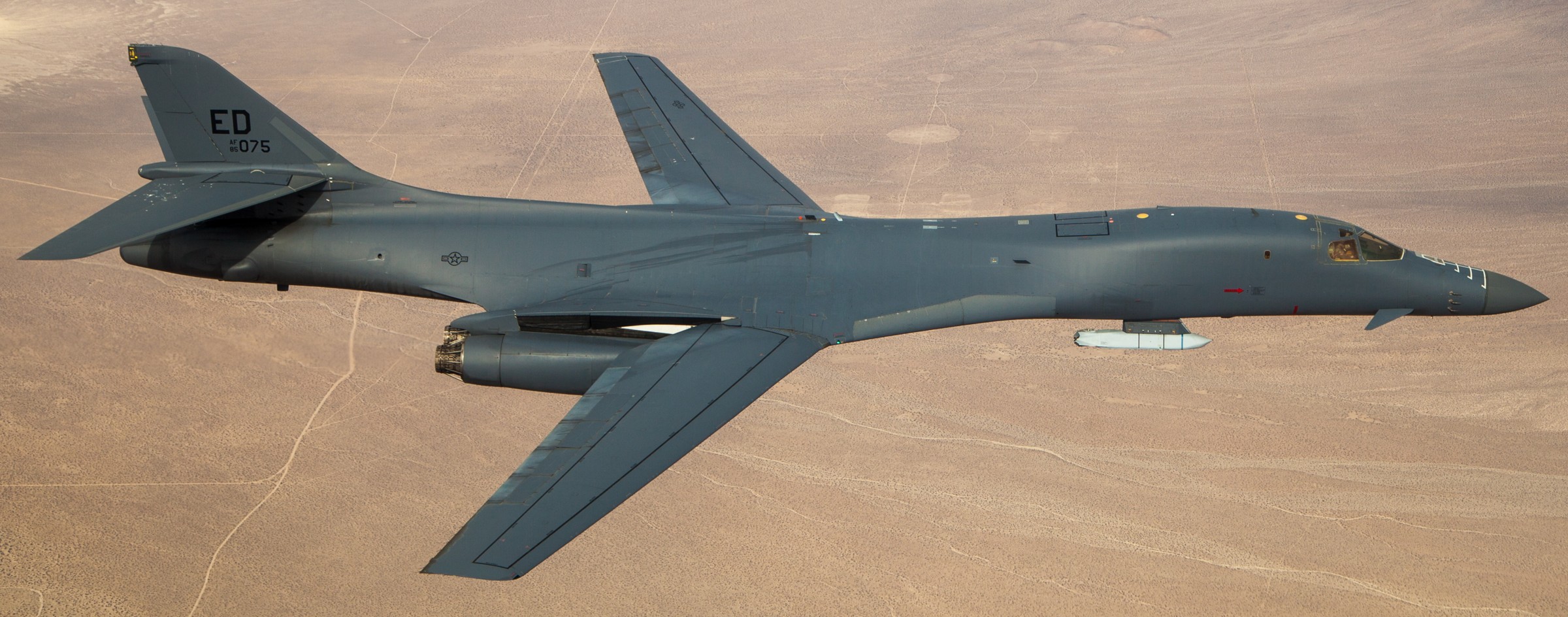  AGM-158A JASSM on an USAF B-1B Lancer bomber  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) on an USMC F/A-18C Hornet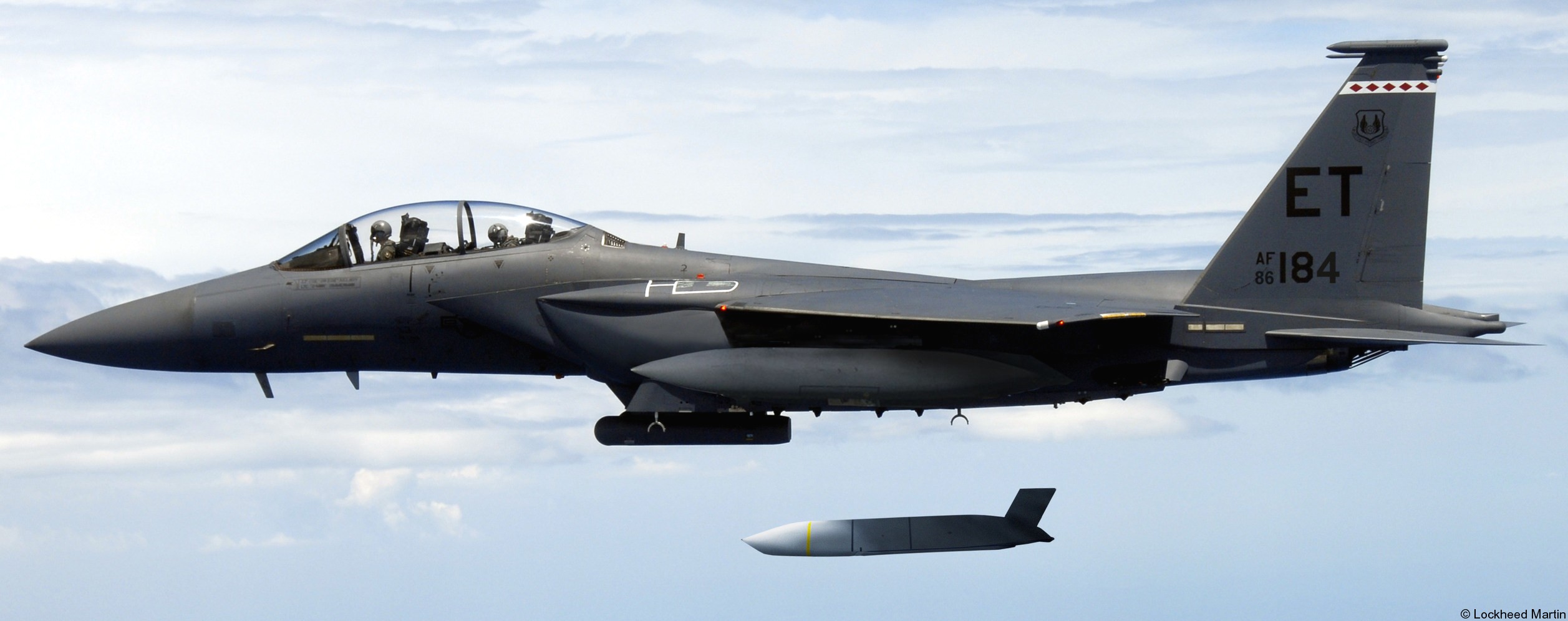  AGM-158A Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) was launched from an USAF F-15E Strike Eagle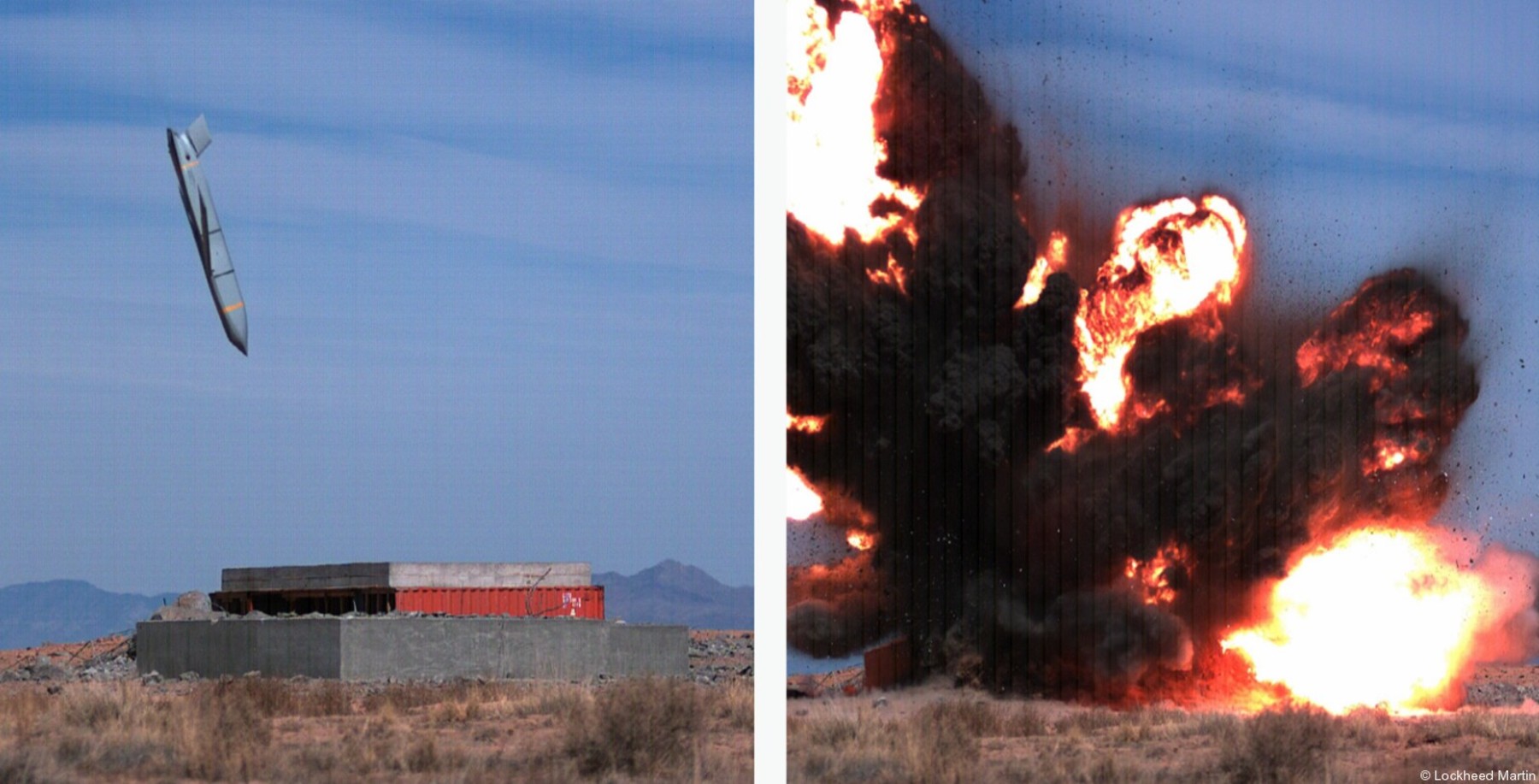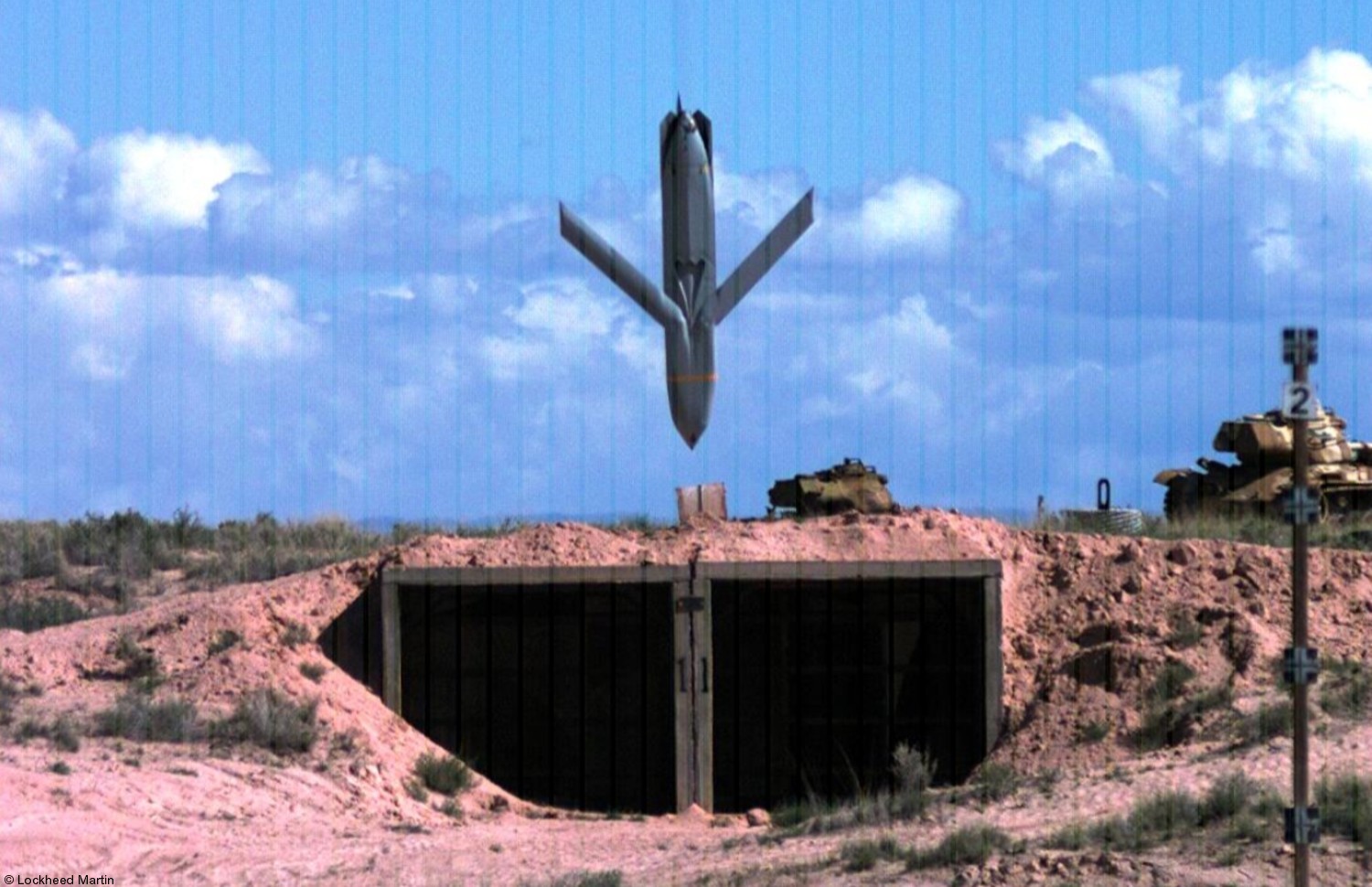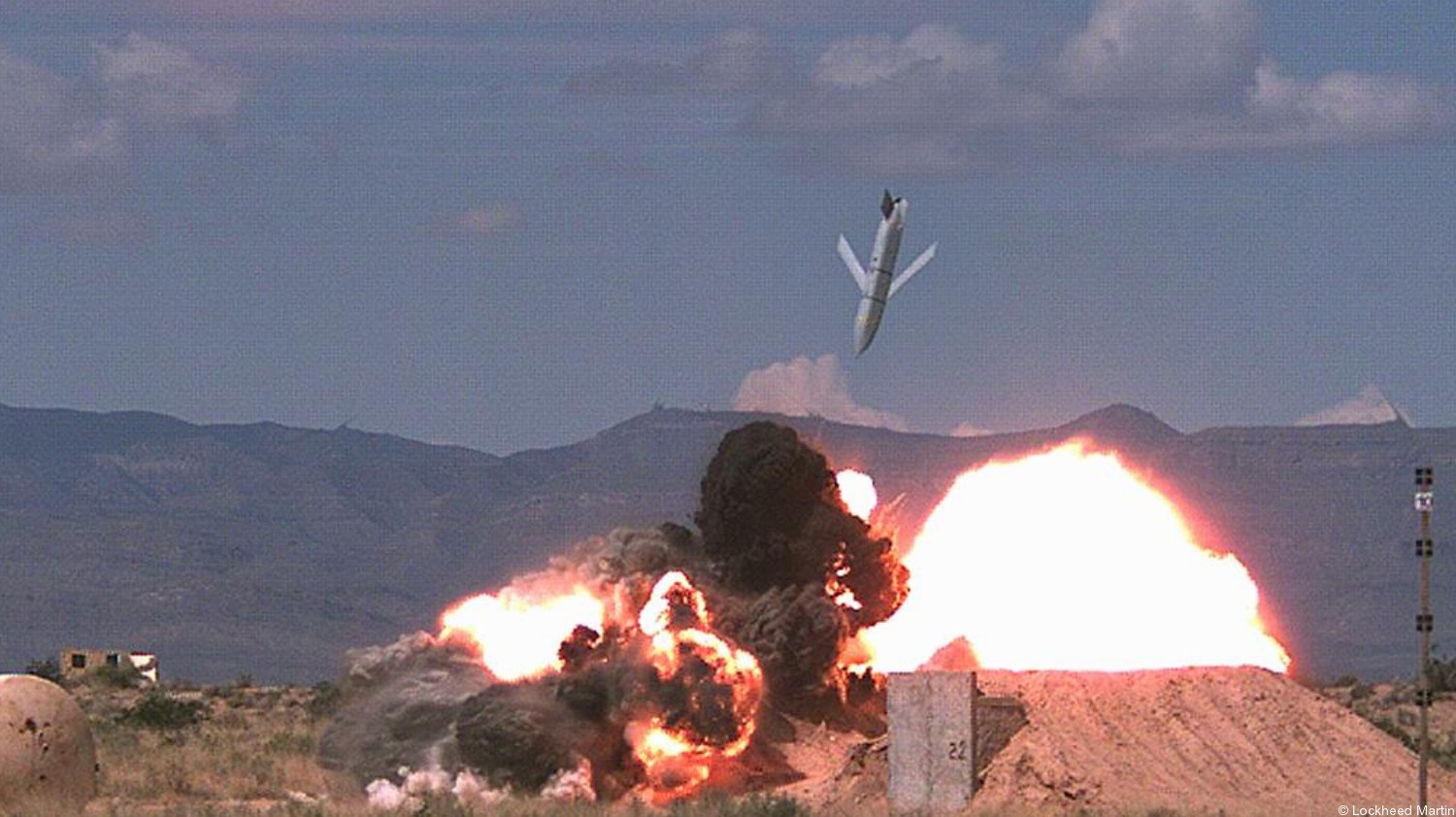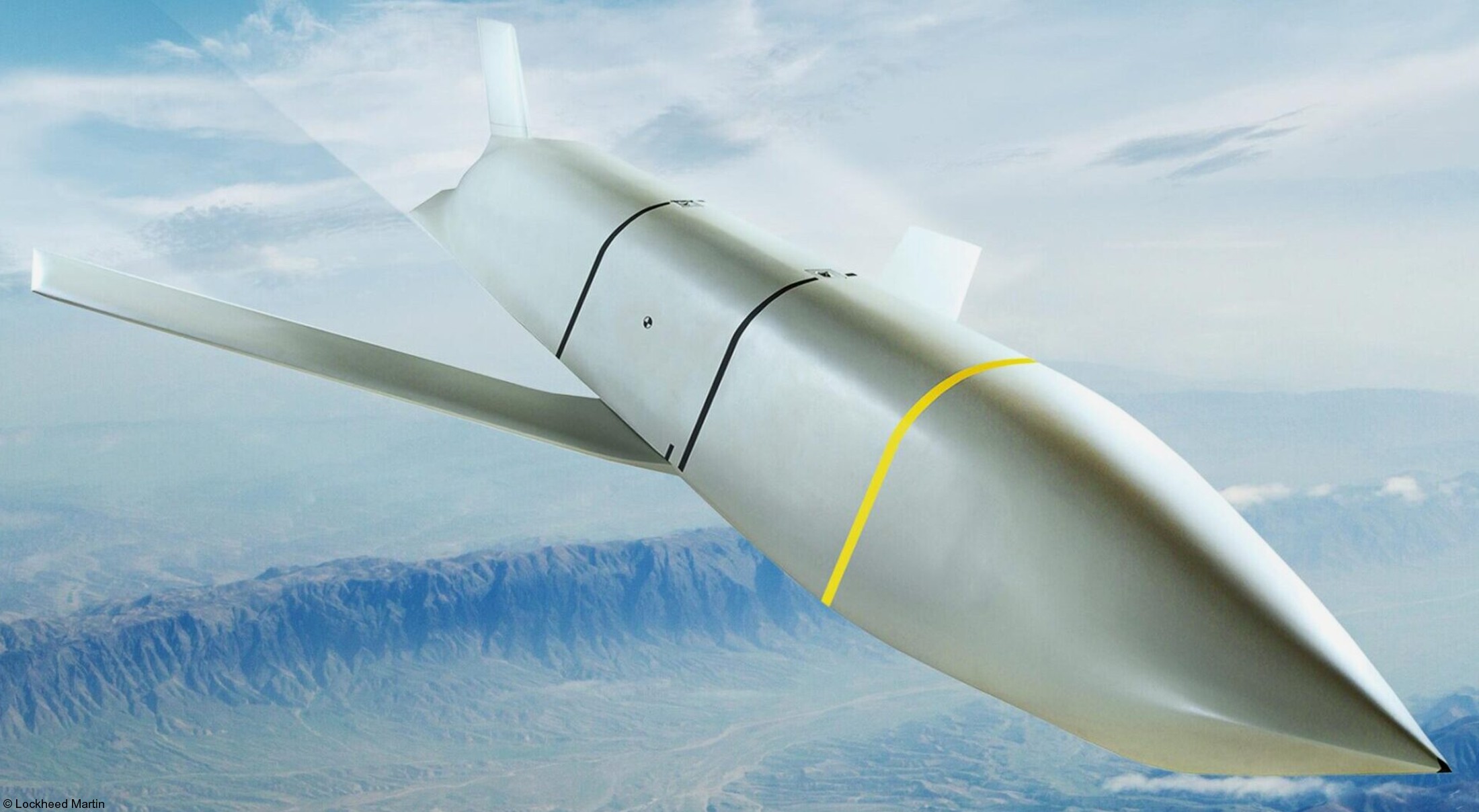     |
|
|
seaforces.org
|
Weapon Systems
start page
| |