 |
||
|
HOME
|
US Navy -
ships
|
US Navy - air
units
|
USMC - air
units
|
International
Navies
|
Weapon Systems
|
Special Reports |
||
|
US Navy - Ballistic / Guided Missile Submarine SSBN / SSGN 726 - USS Ohio |
||
|
||
| 12/25 | ||
|
Type,
class: Ballistic Missile Submarine, nuclear
propulsion - SSBN; Ohio class Builder: General Dynamics Electric Boat (GDEB), Groton, Connecticut, USA STATUS: Awarded: July 1, 1974 Laid down: April 10, 1976 Launched: April 7, 1979 Commissioned: November 11, 1981 converted to SSGN: 2002-2006 Re-commissioned SSGN 726: February 7, 2006 IN SERVICE Homeport: Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Naval Base Kitsap, Washington Namesake: State of Ohio Ships Motto: FIRST AND FINEST / ALWAYS FIRST Technical Data: see: INFO > Ohio class Ballistic Missile Submarine - SSBN |
||
| images | ||
|
SSGN 726 - USS Ohio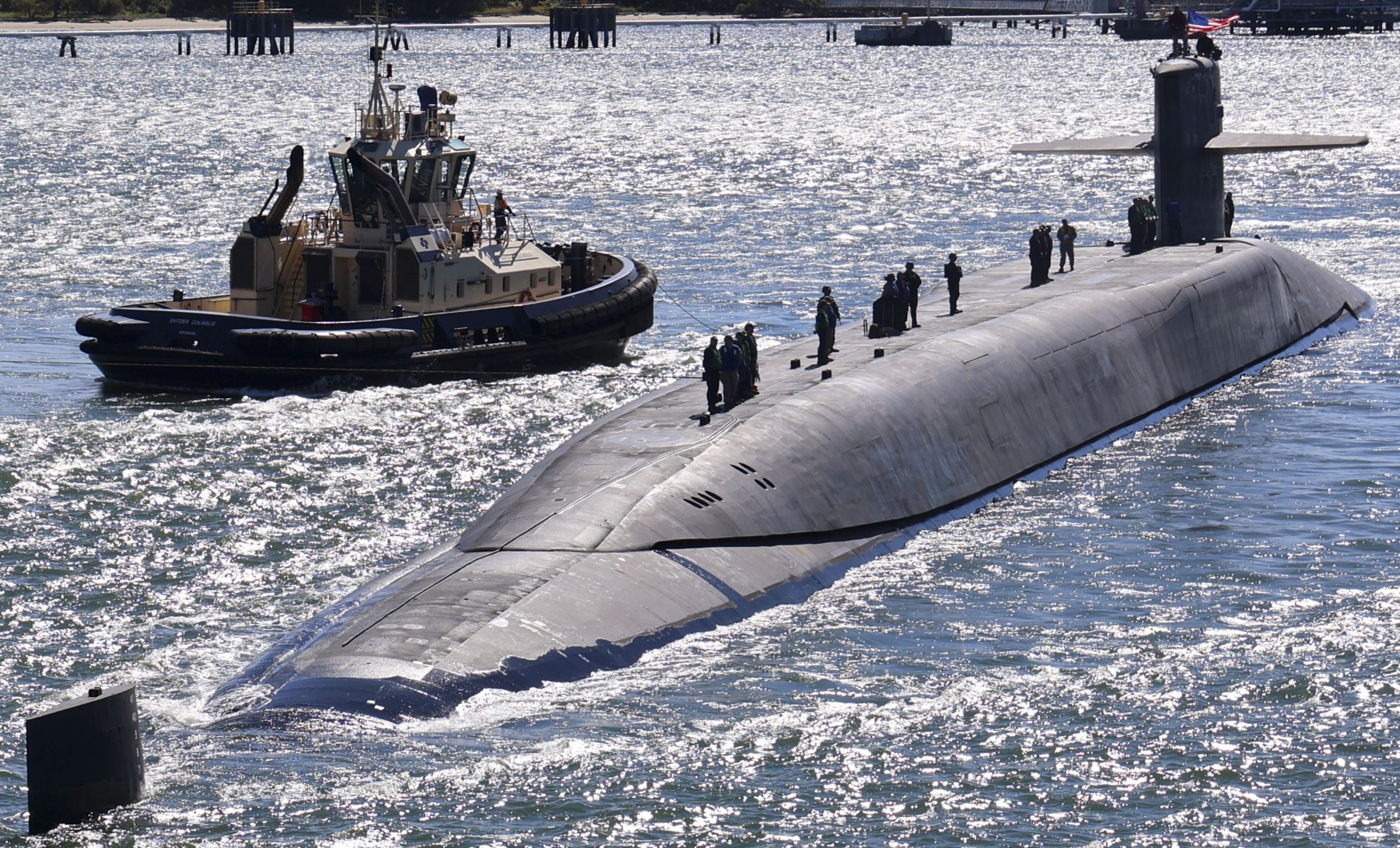  Brisbane, Australia - July 2025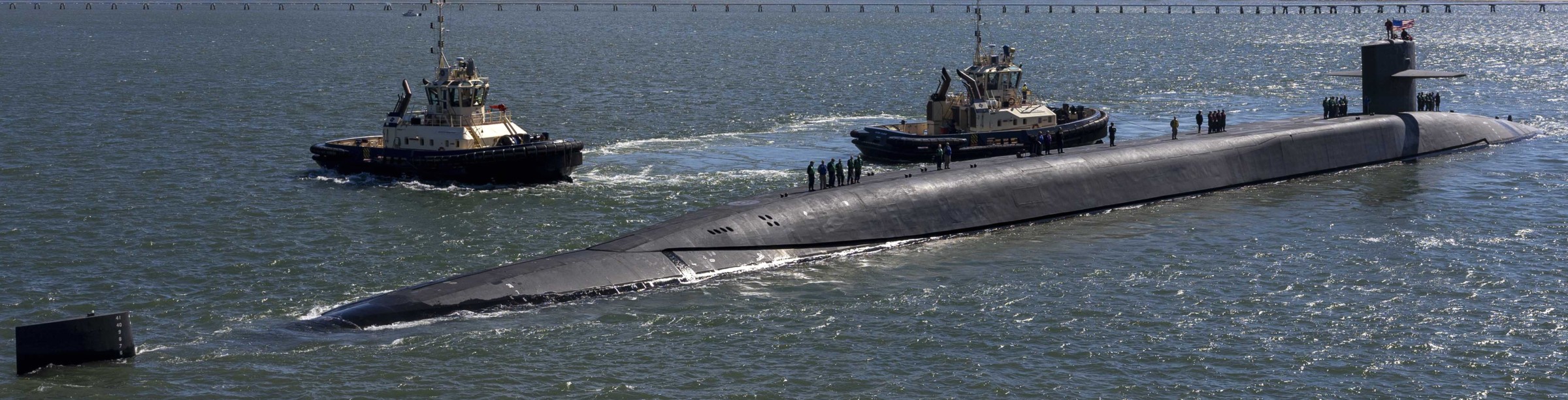  Brisbane, Australia - July 2025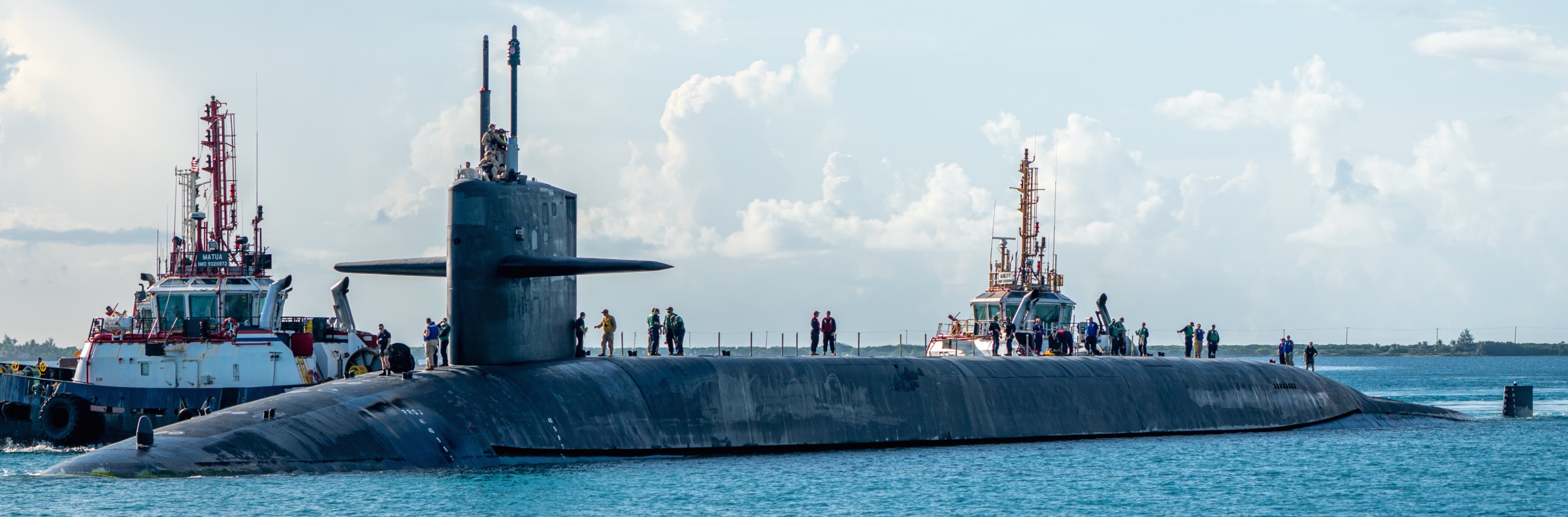  Naval Base Guam - June 2025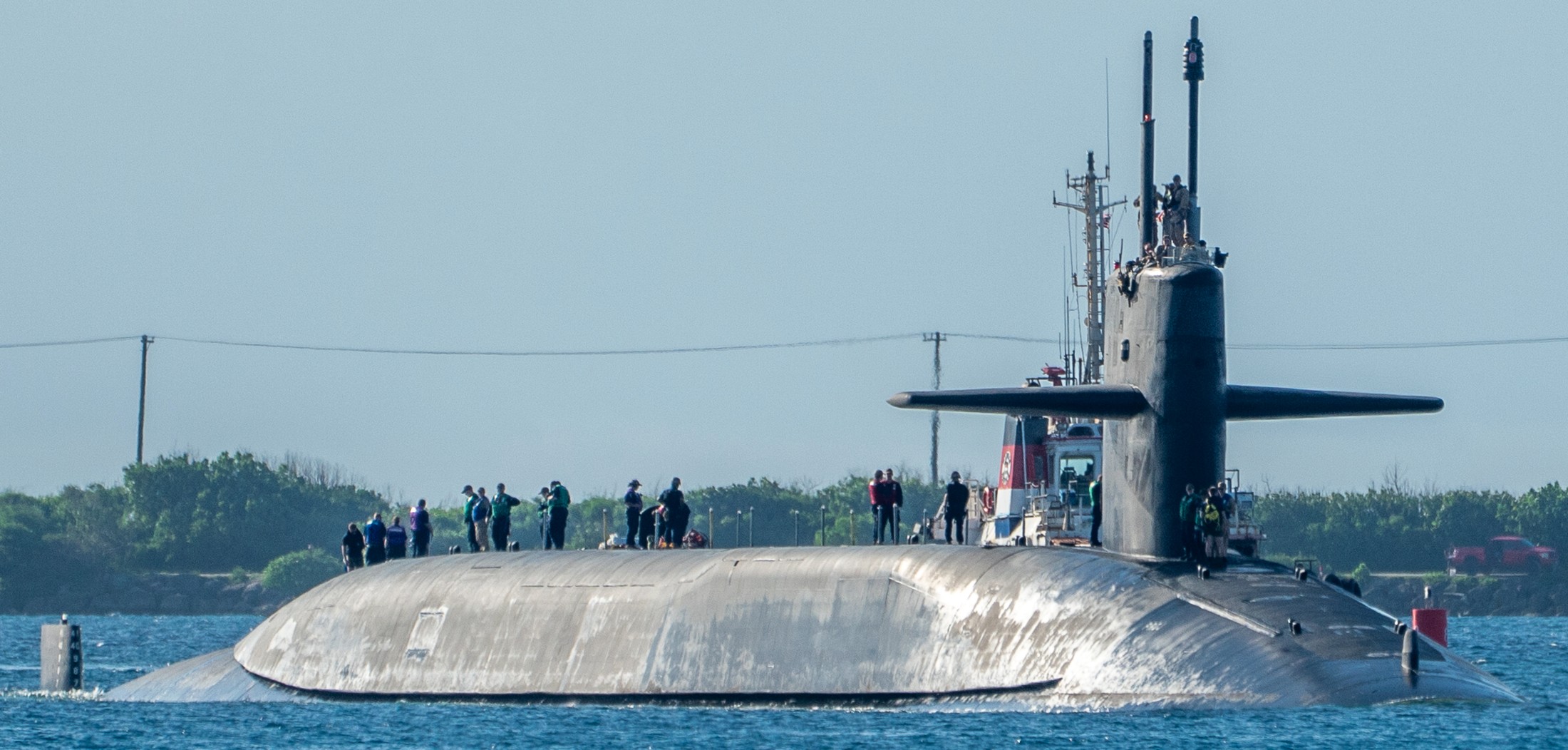  Naval Base Guam - June 2025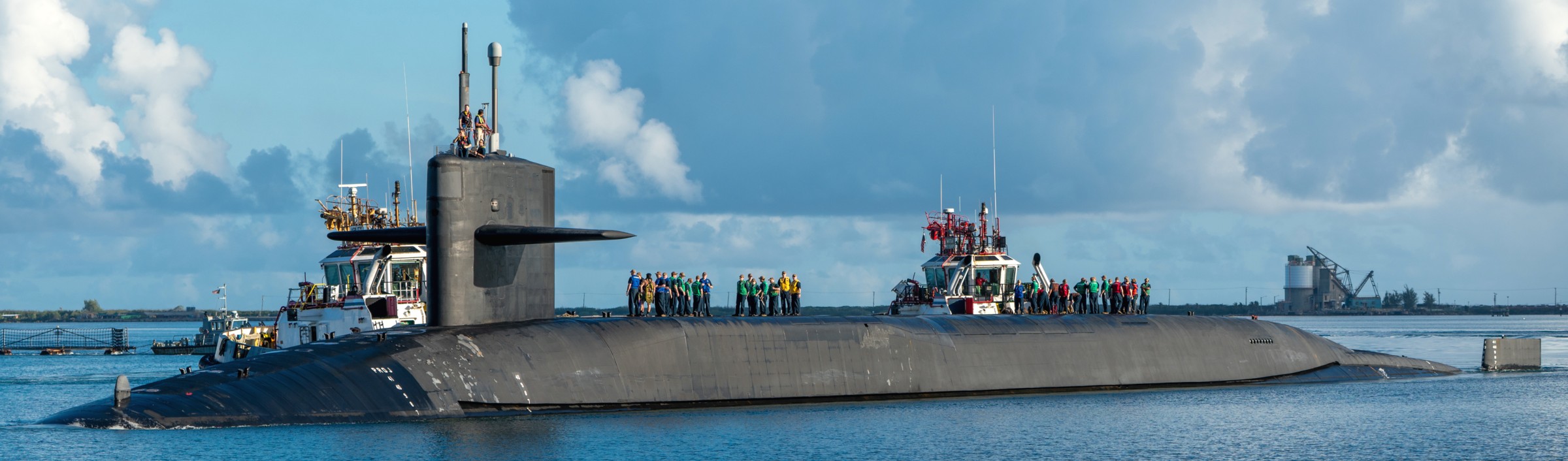  Naval Base Guam - April 2025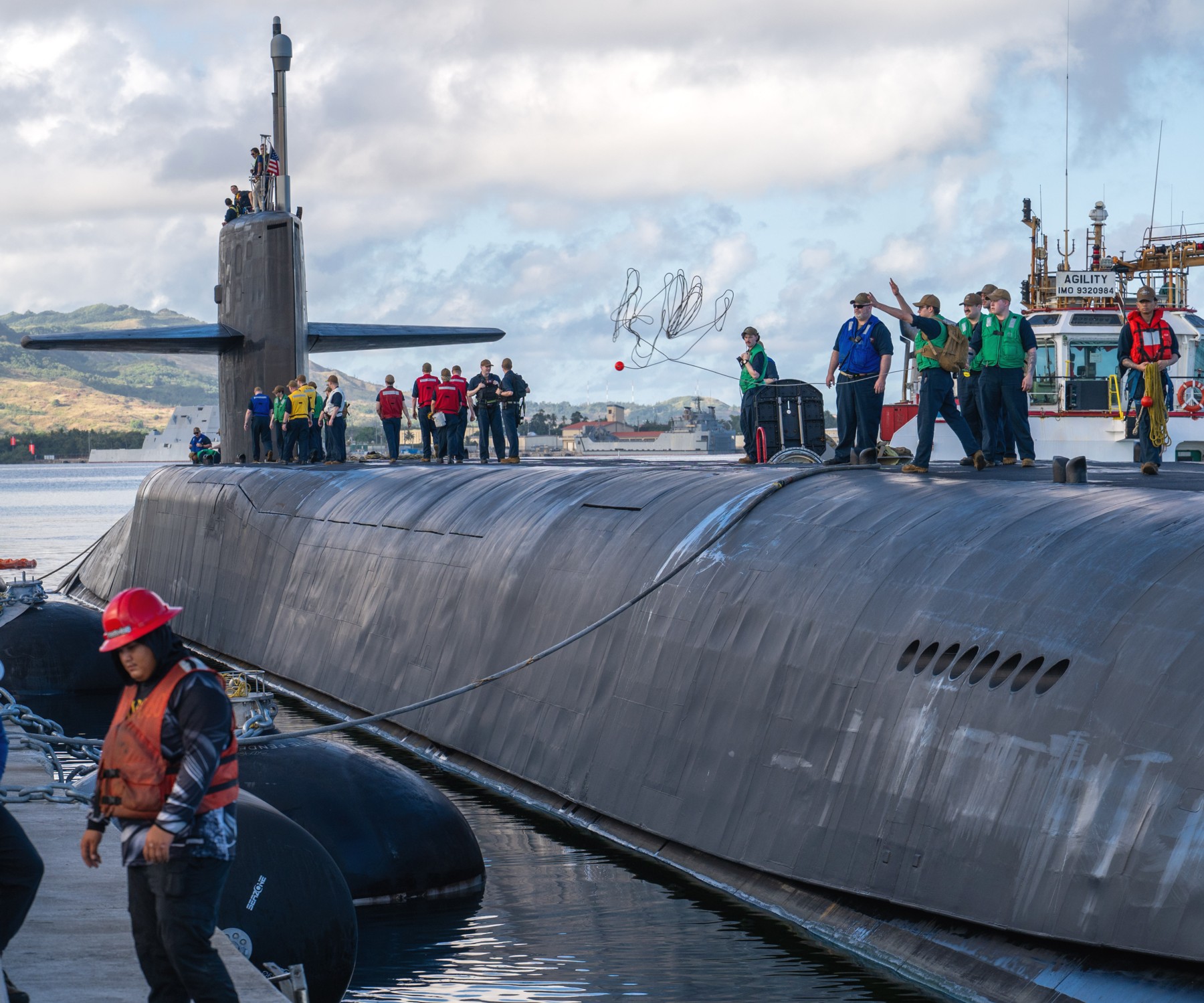  Naval Base Guam - April 2025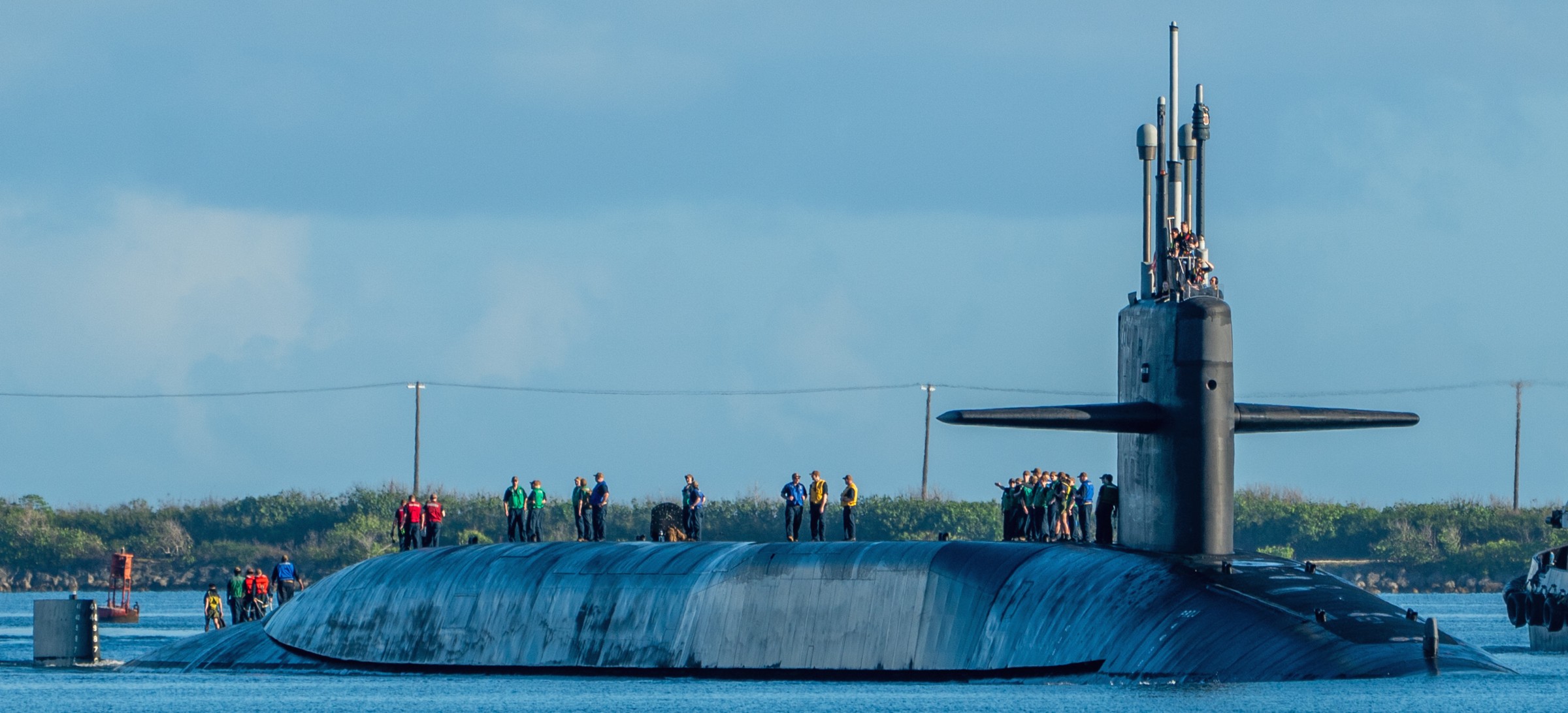  Naval Base Guam - April 2025 USS Ohio (SSGN 726) returned to the fleet after completing a three-year Major Maintenance Period availability at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard & Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNSY&IMF) in Bremerton, Washington on February 24, 2025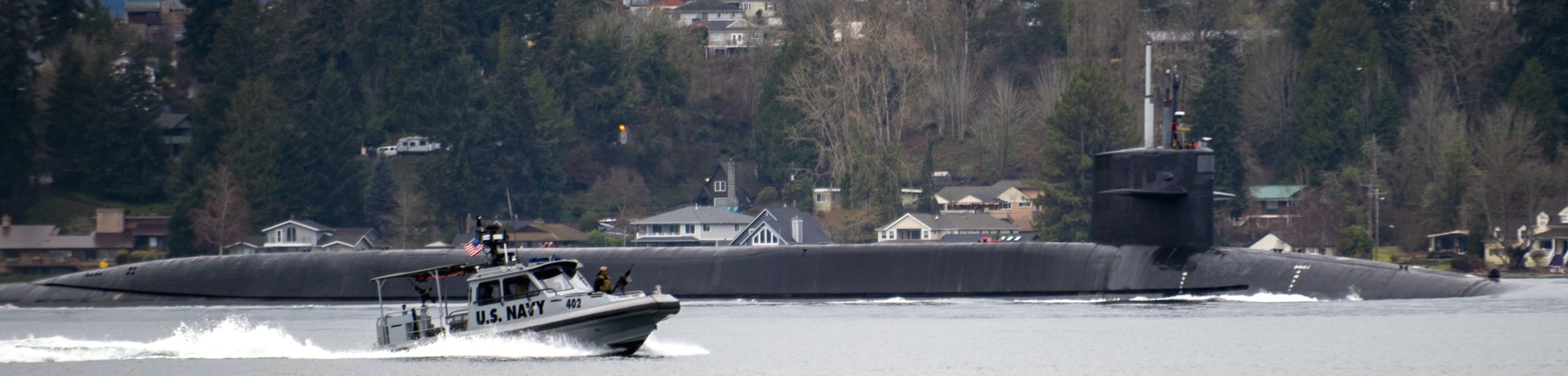  Puget Sound, Washington - December 2024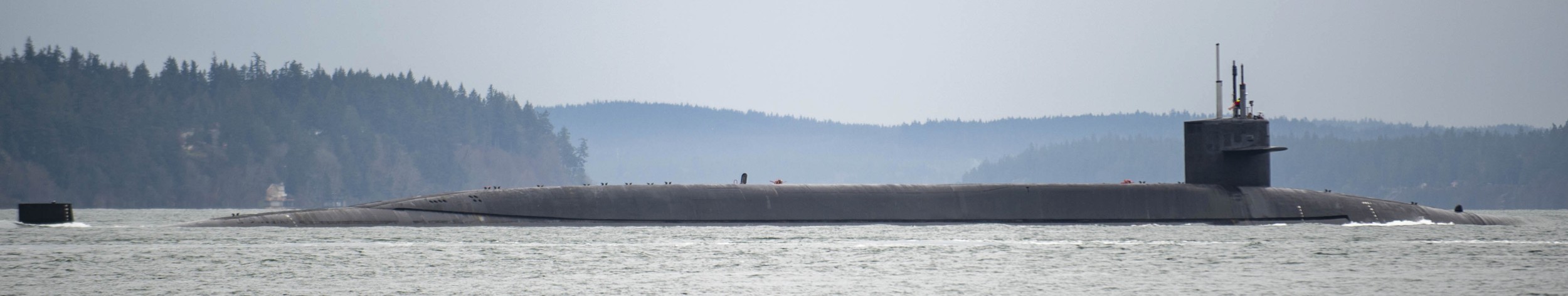  Puget Sound, Washington - December 2024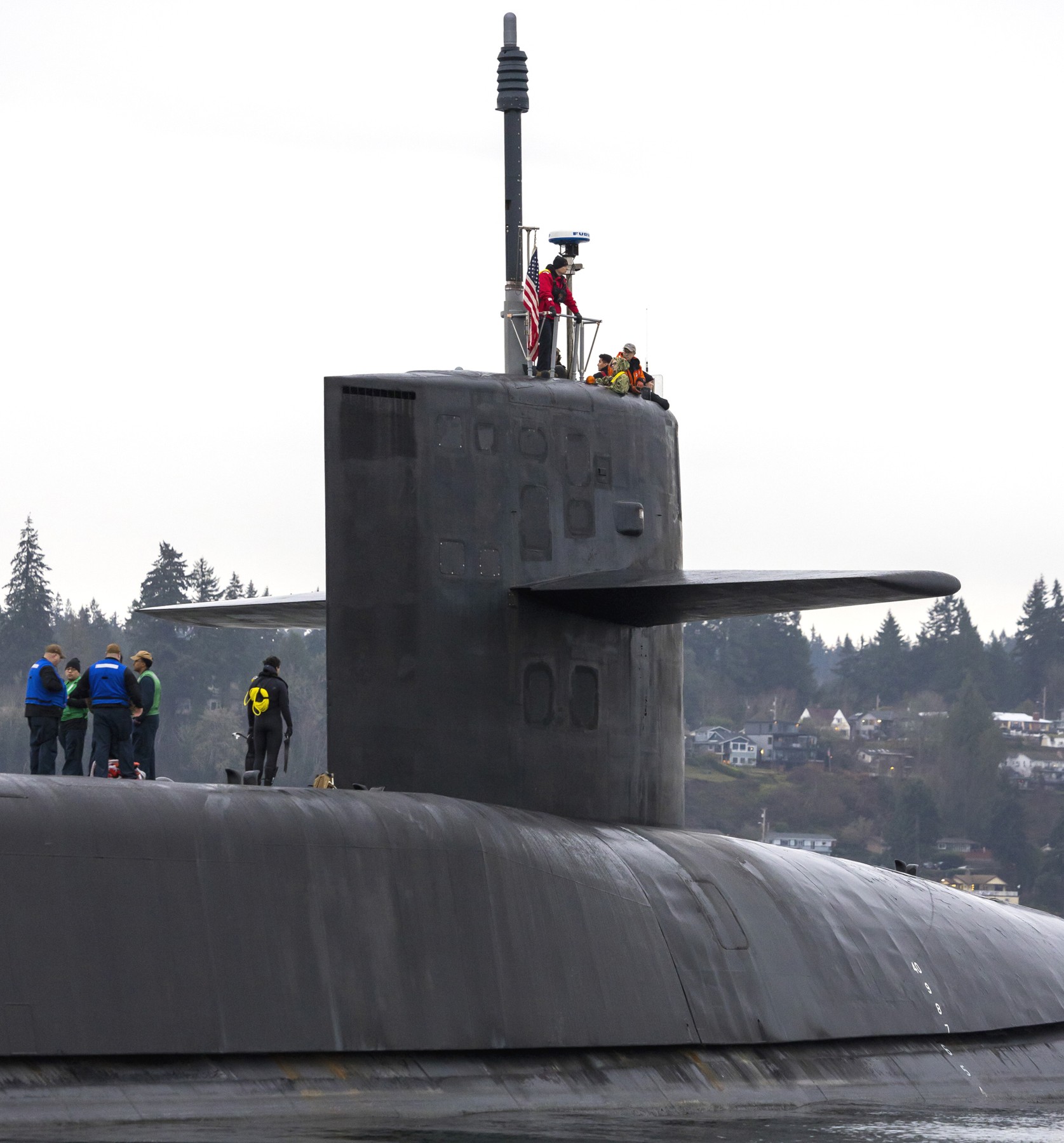  departing Puget Sound Naval Shipyard & Intermediate Maintenance Facility, Bremerton, Washington - December 2024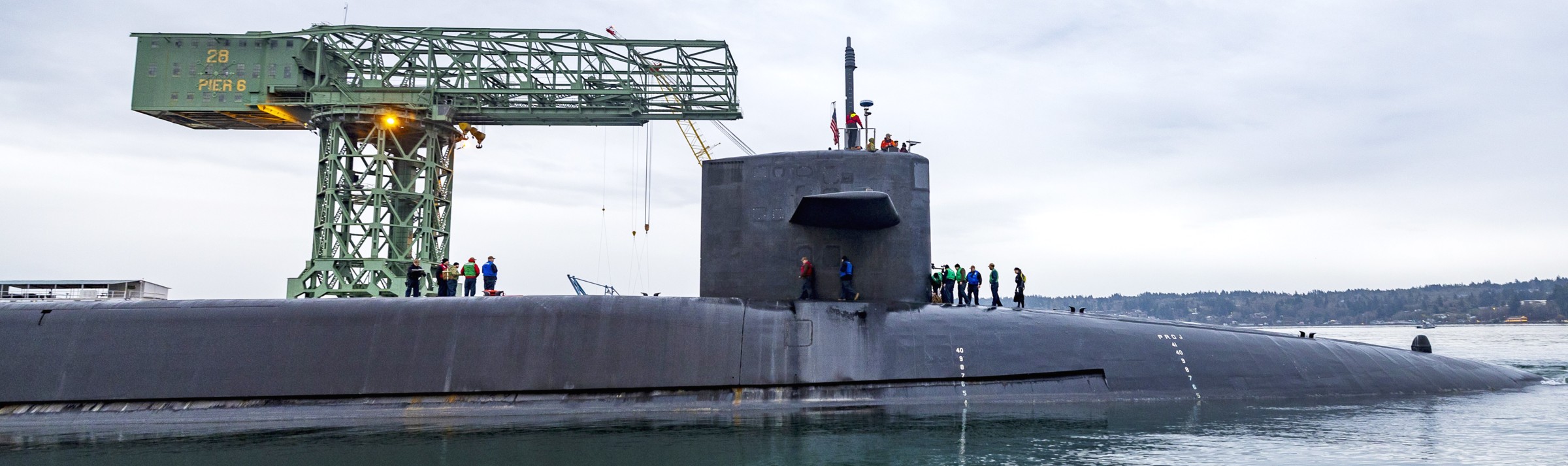  departing Puget Sound Naval Shipyard & Intermediate Maintenance Facility, Bremerton, Washington - December 2024 January 2022 - December 2024: Major Maintenance Period at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility, Washington  Pacific Ocean - February 2021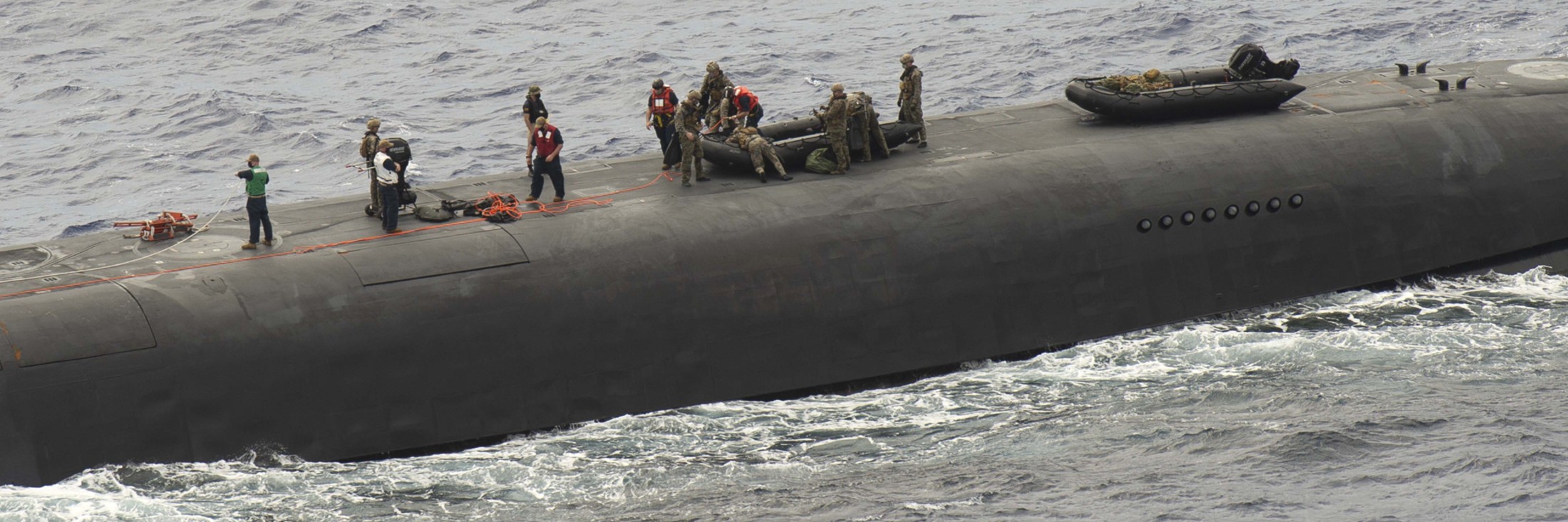  Pacific Ocean - February 2021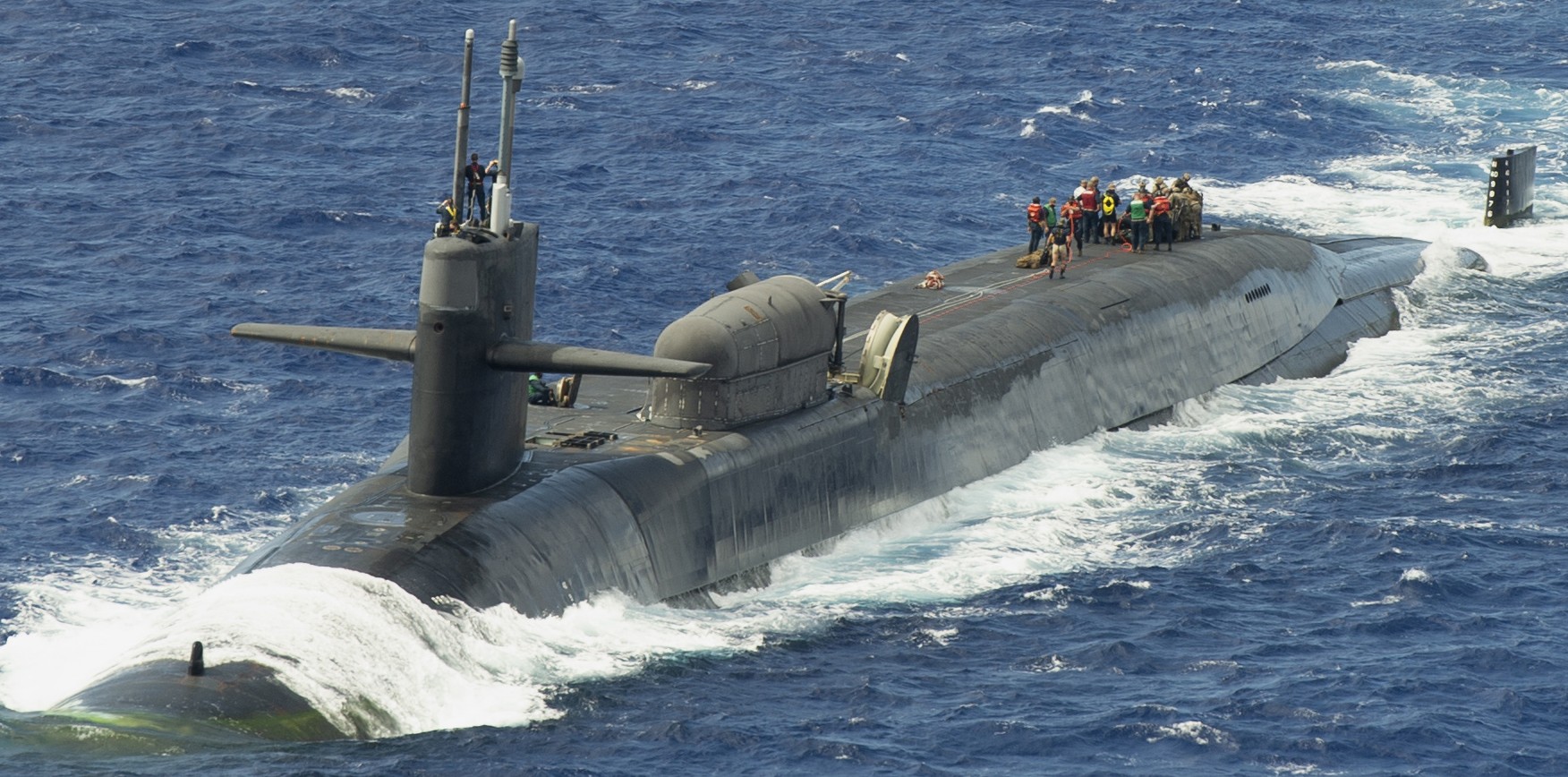  Pacific Ocean - February 2021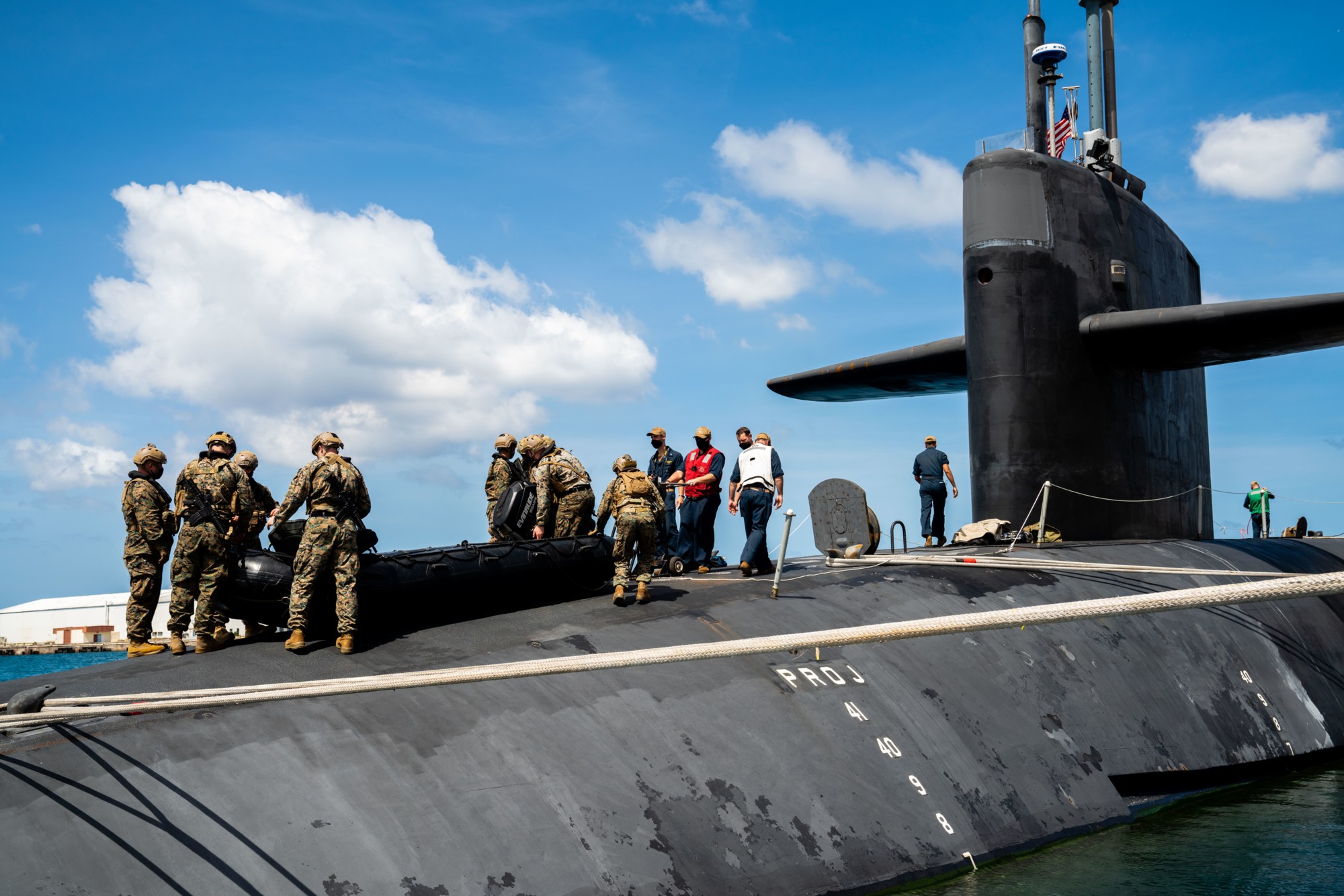  Naval Base Guam - February 2021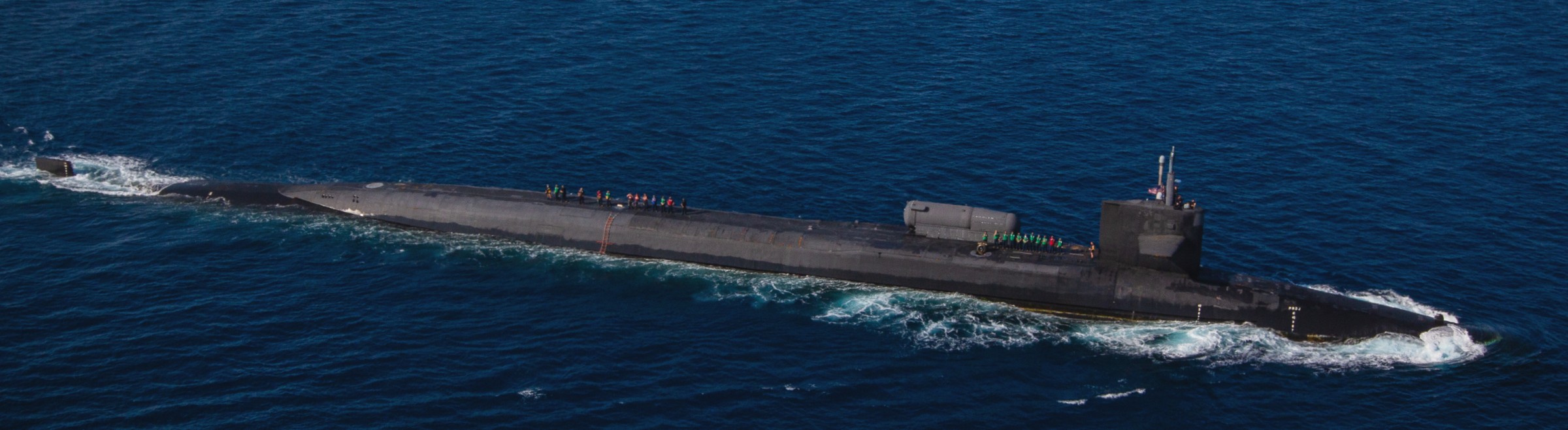  Philippine Sea - February 2021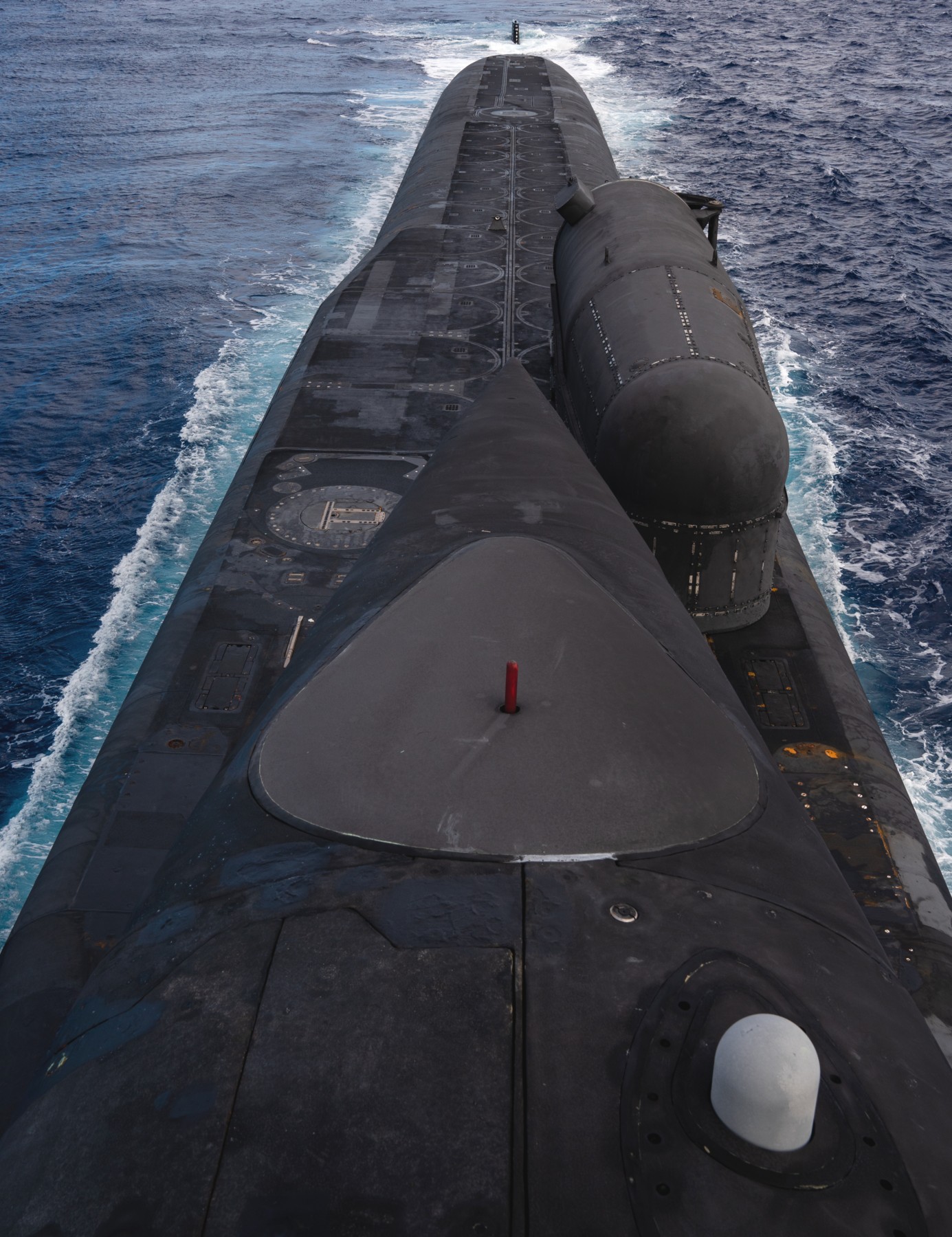  Pacific Ocean - January 2021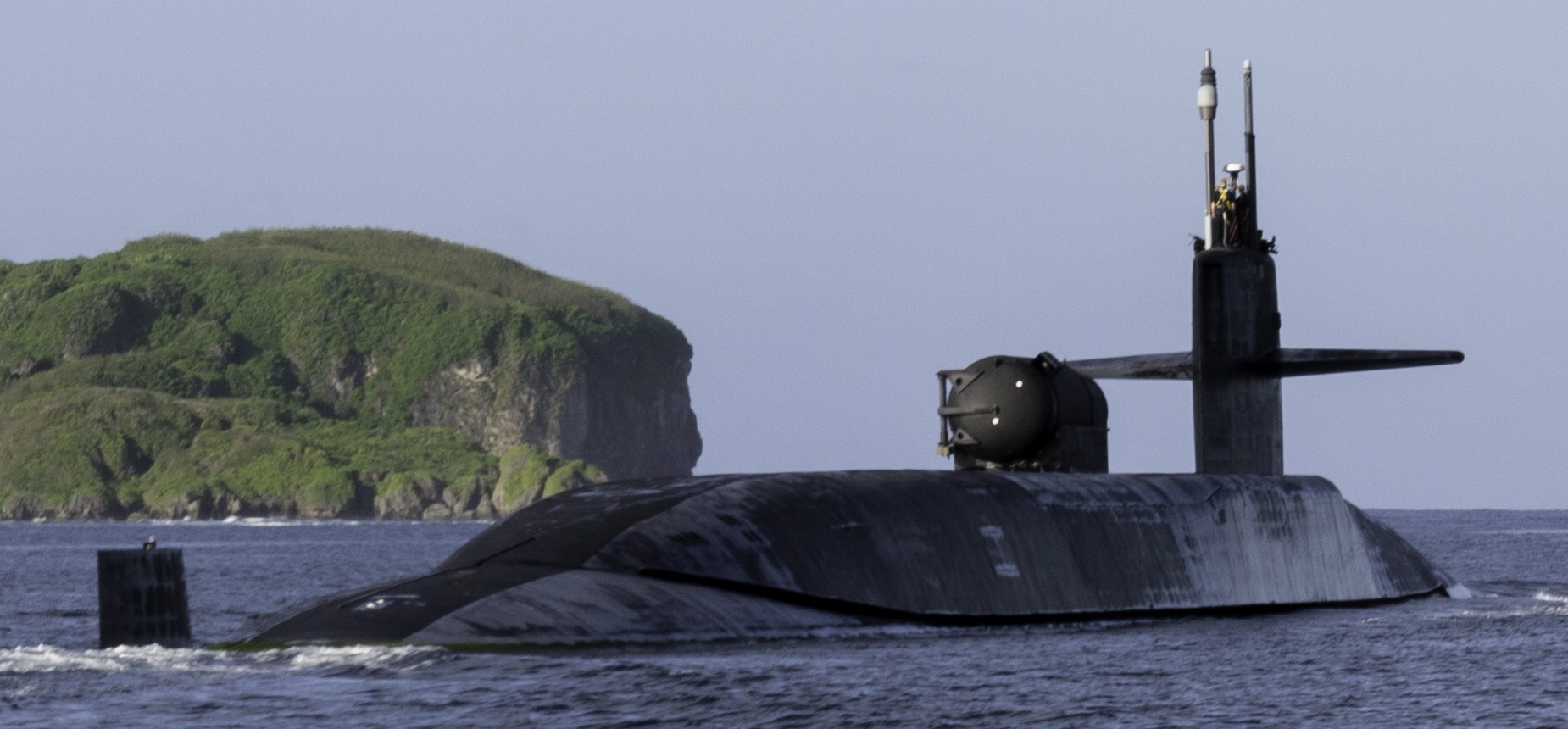  departing Naval Base Guam - January 2021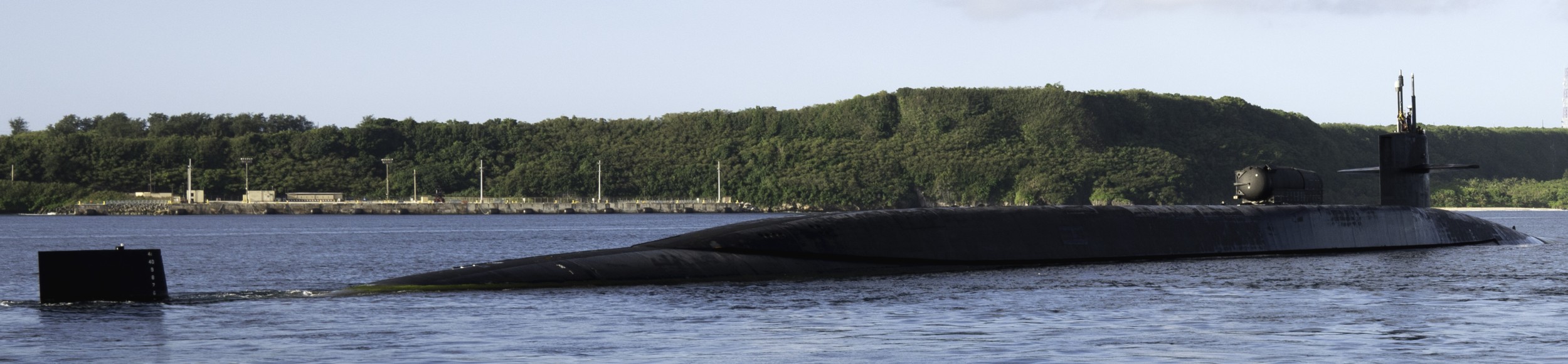  departing Naval Base Guam - January 2021  inport Naval Base Kitsap, Washington - June 2018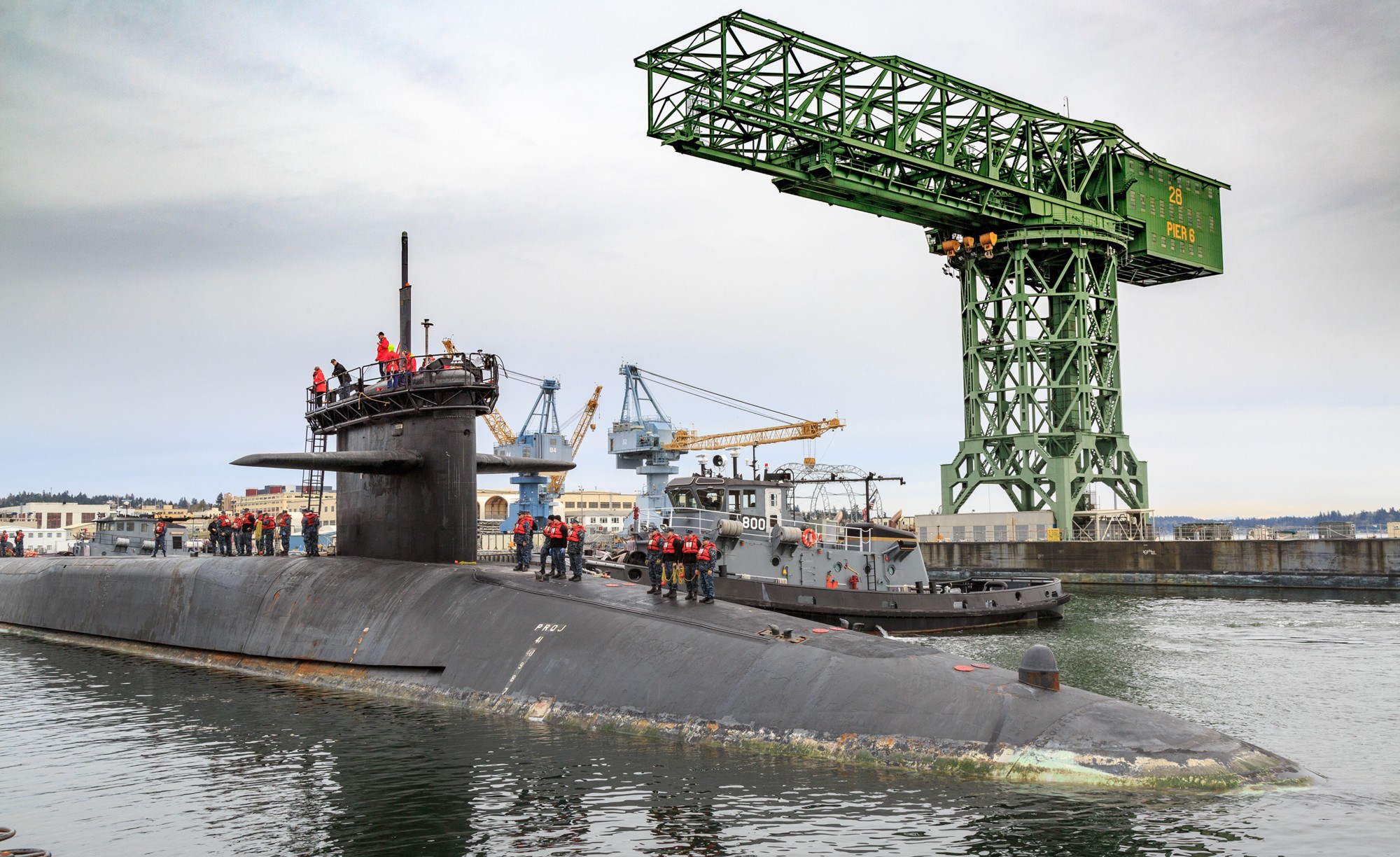  arriving at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), Washington - April 4, 2017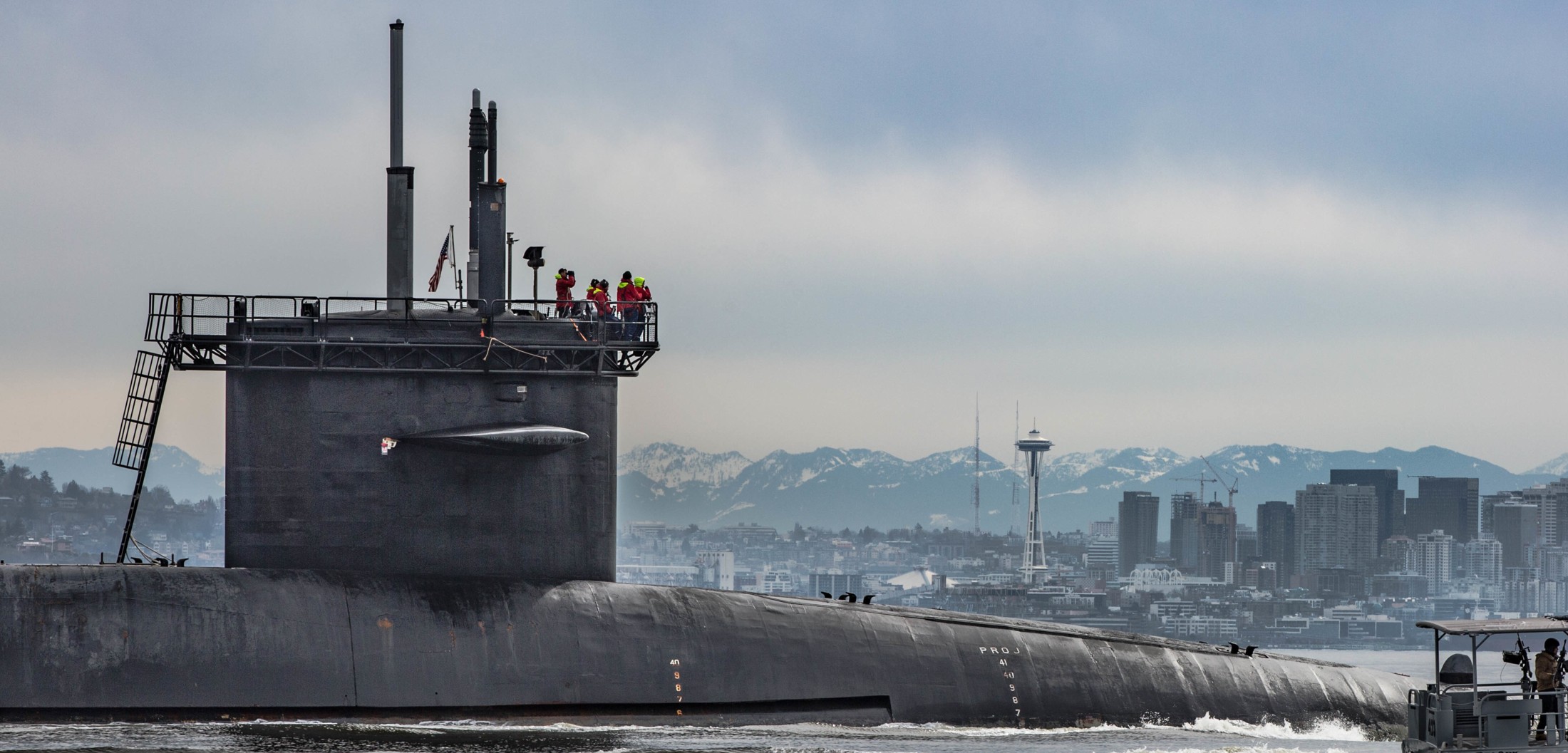  arriving at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), Washington - April 4, 2017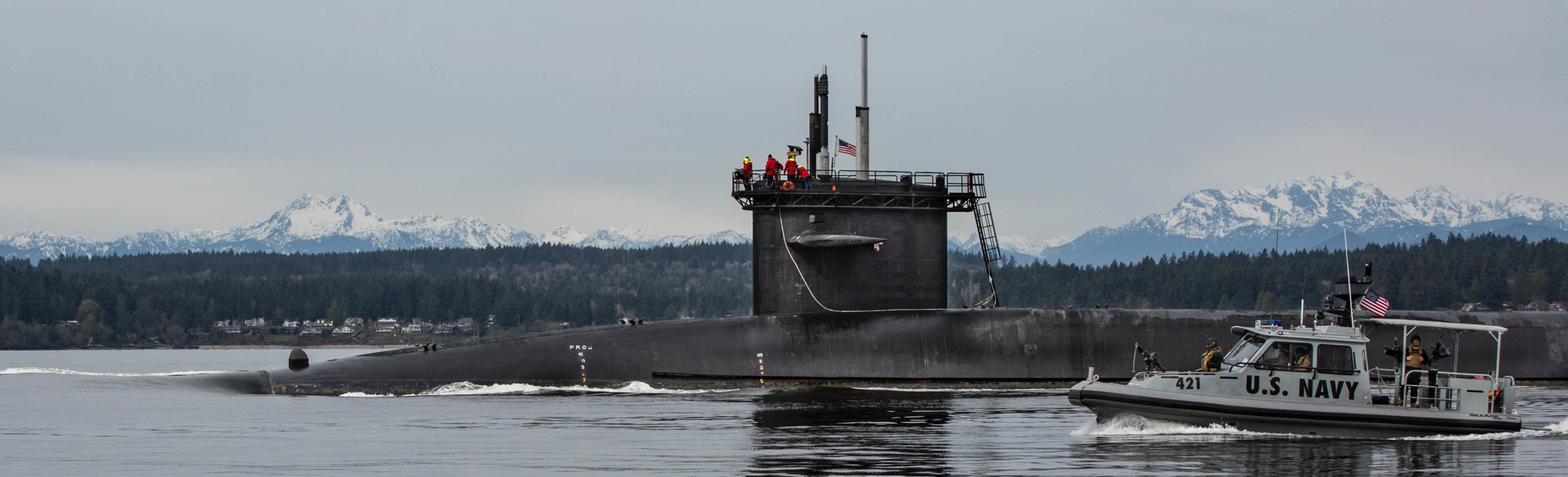  arriving at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), Washington - April 4, 2017  arriving at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), Washington - April 4, 2017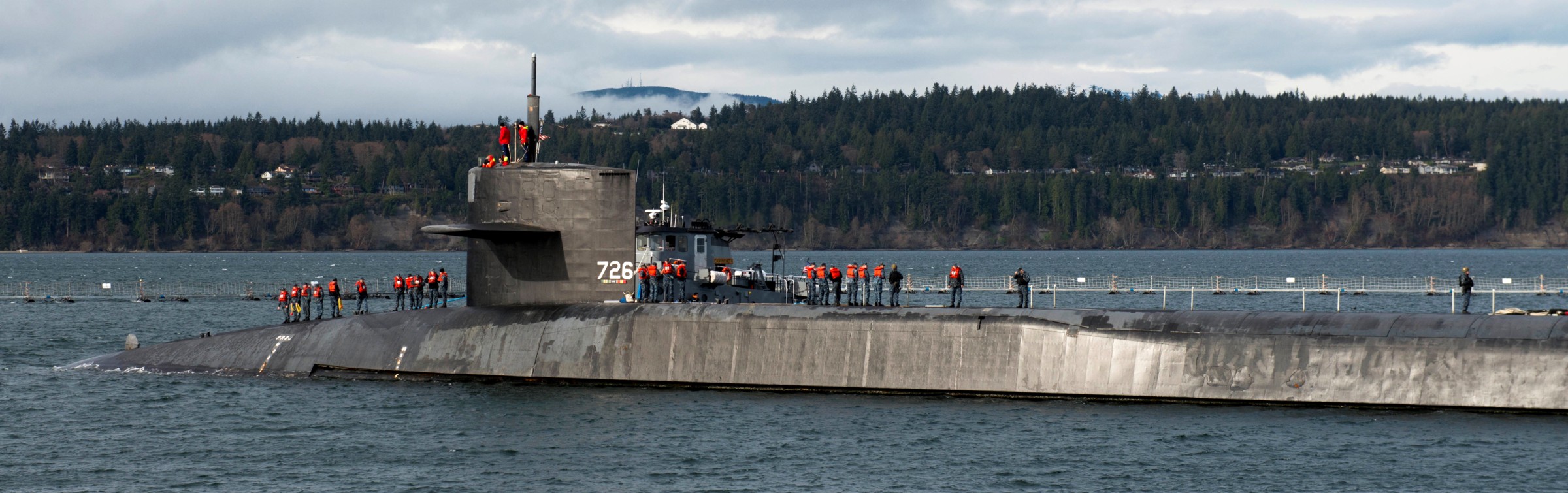  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 20-month forward deployment to Guam - March 2017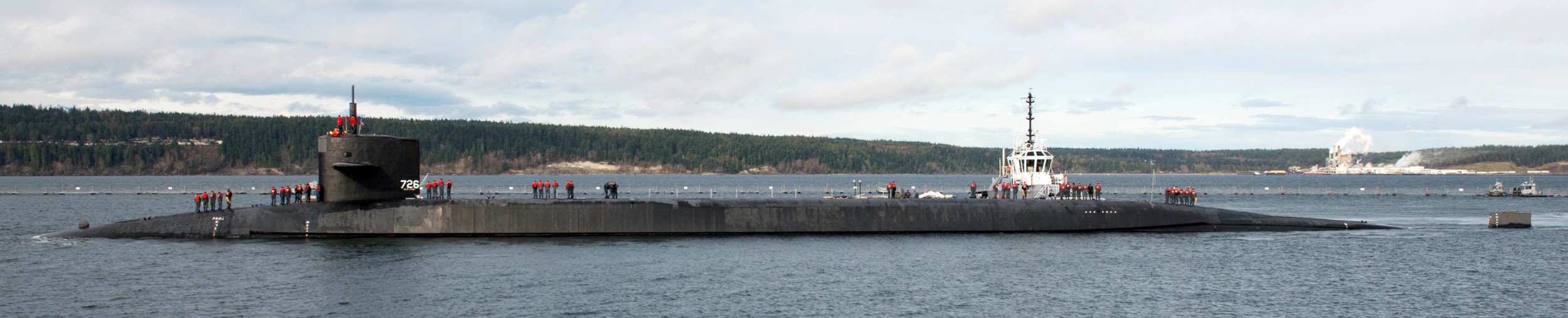  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 20-month forward deployment to Guam - March 2017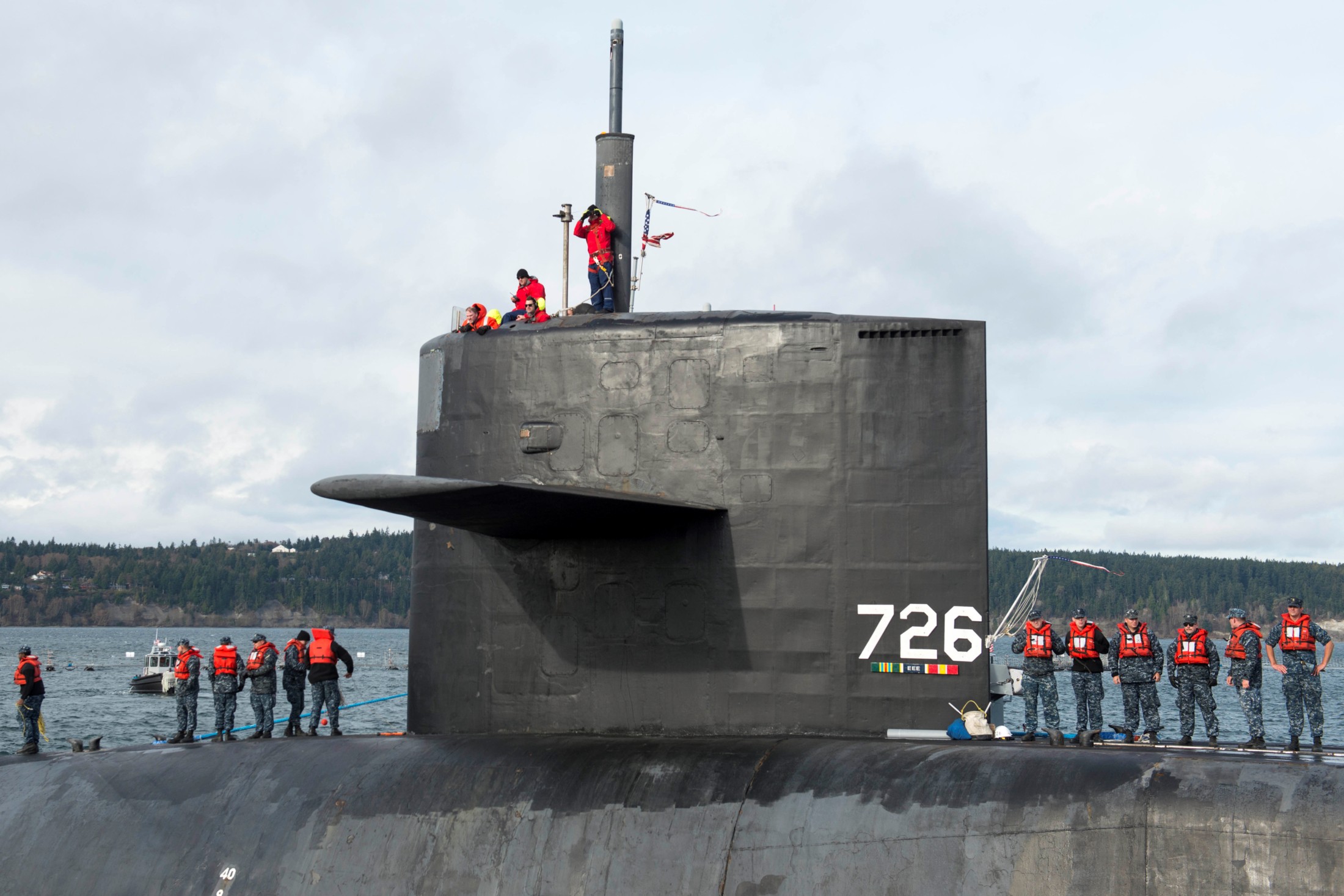  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 20-month forward deployment to Guam - March 2017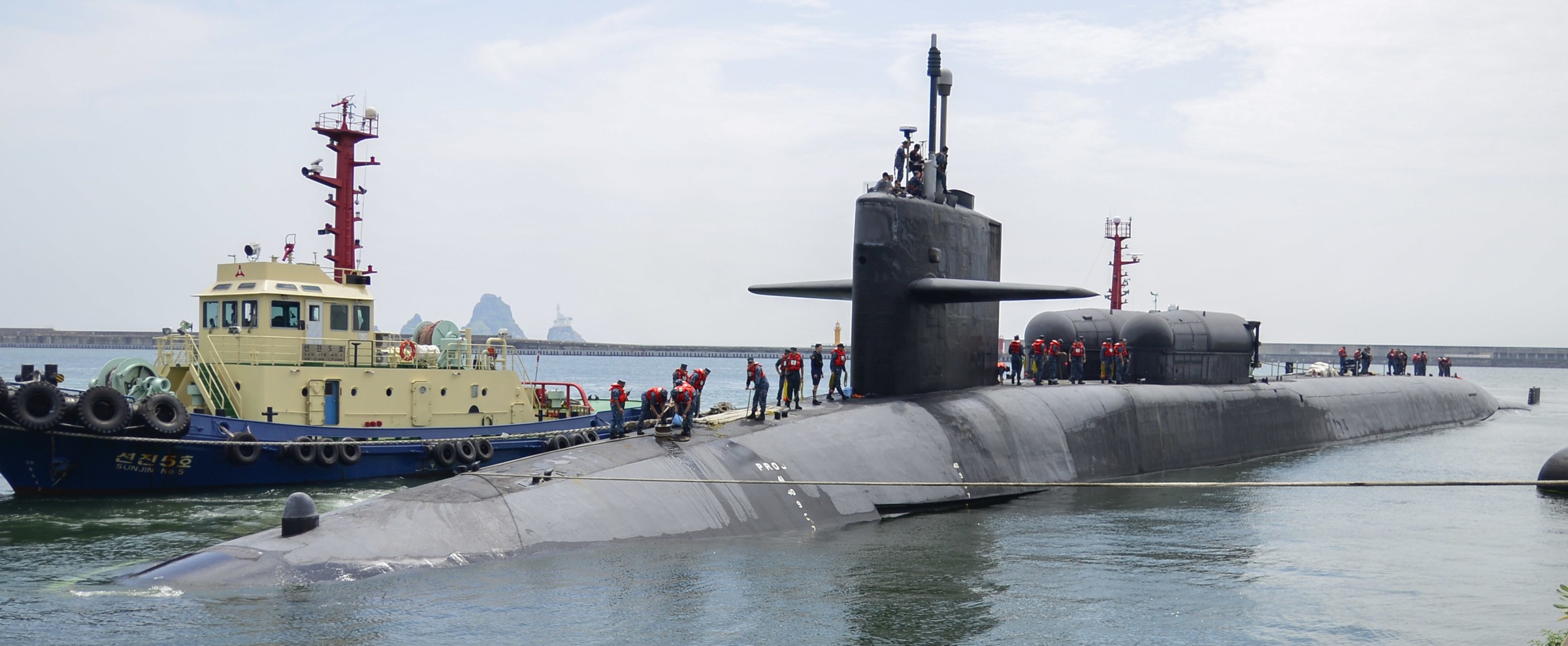  Busan, Republic of Korea - July 2016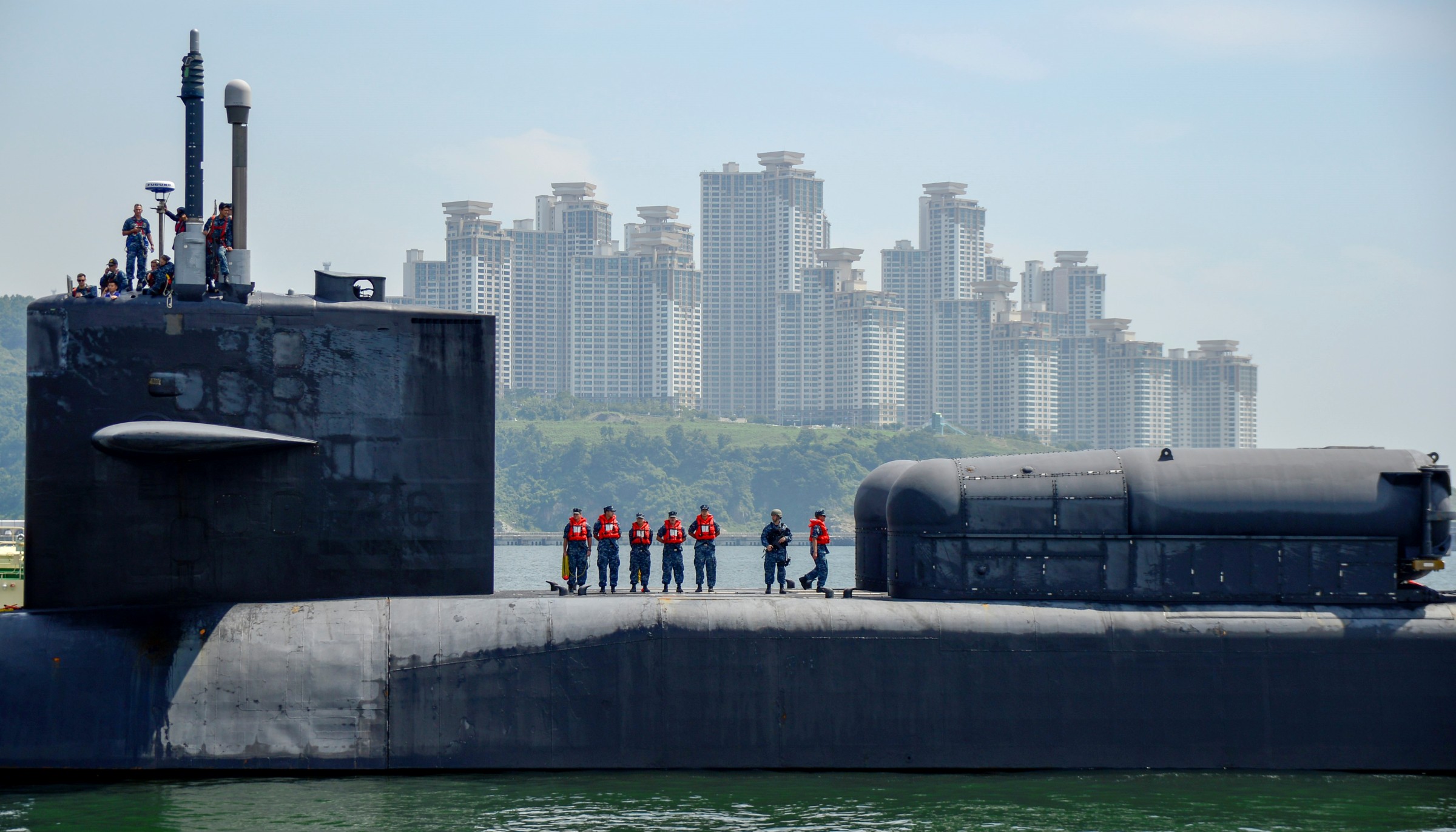  Busan, Republic of Korea - July 2016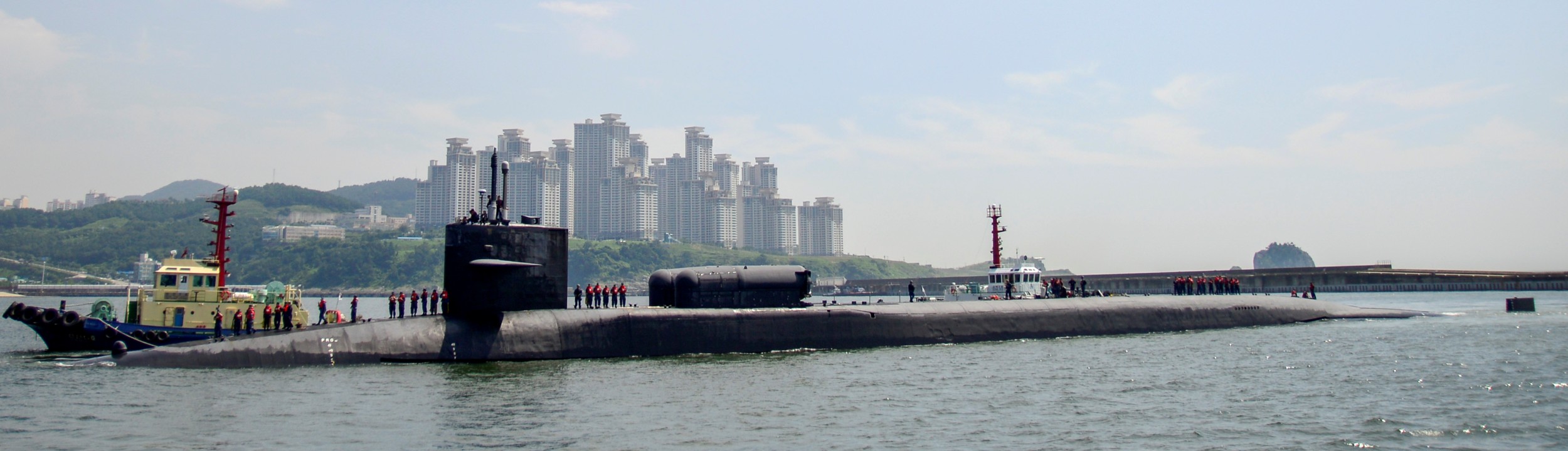  Busan, Republic of Korea - July 2016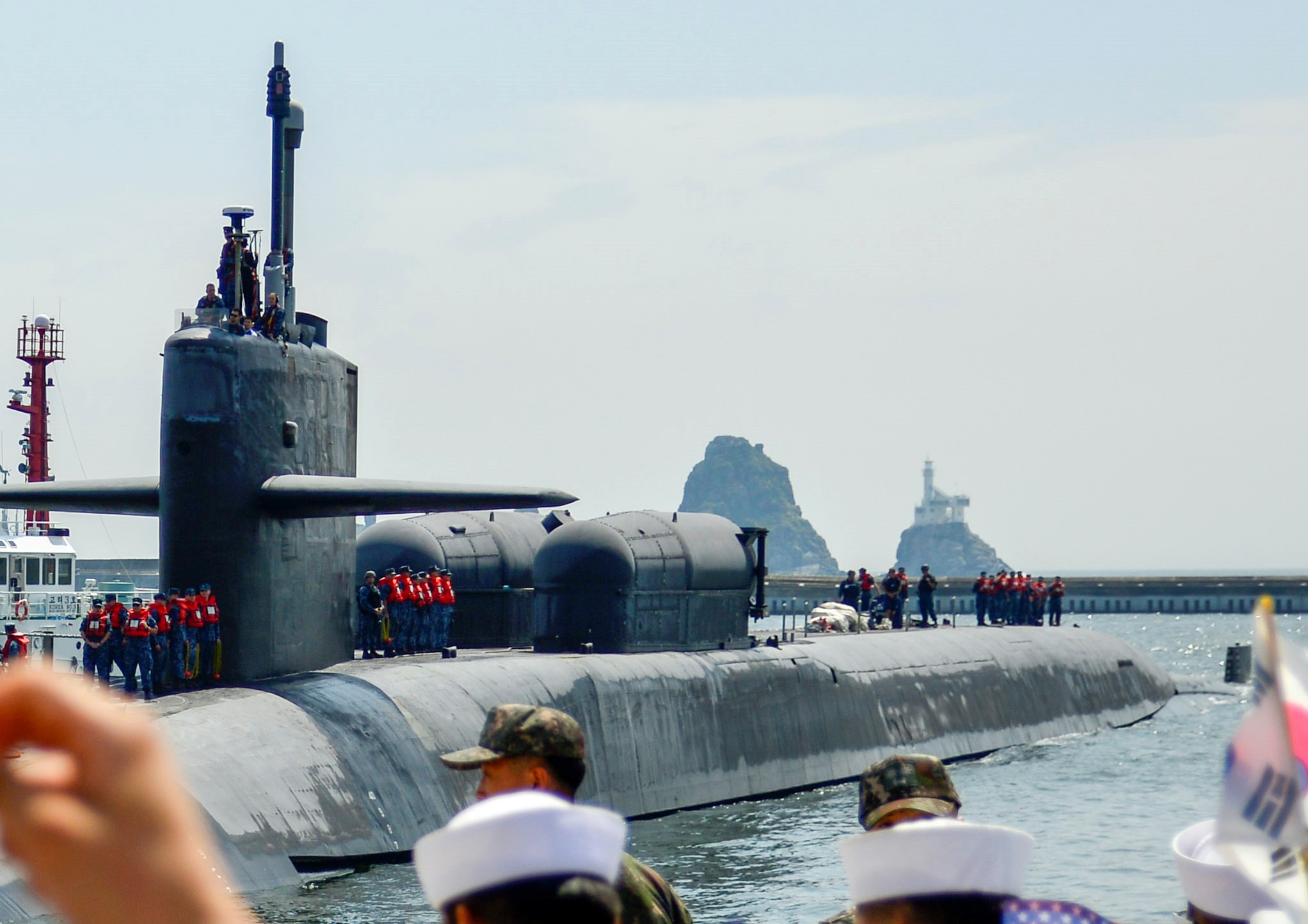  Busan, Republic of Korea - July 2016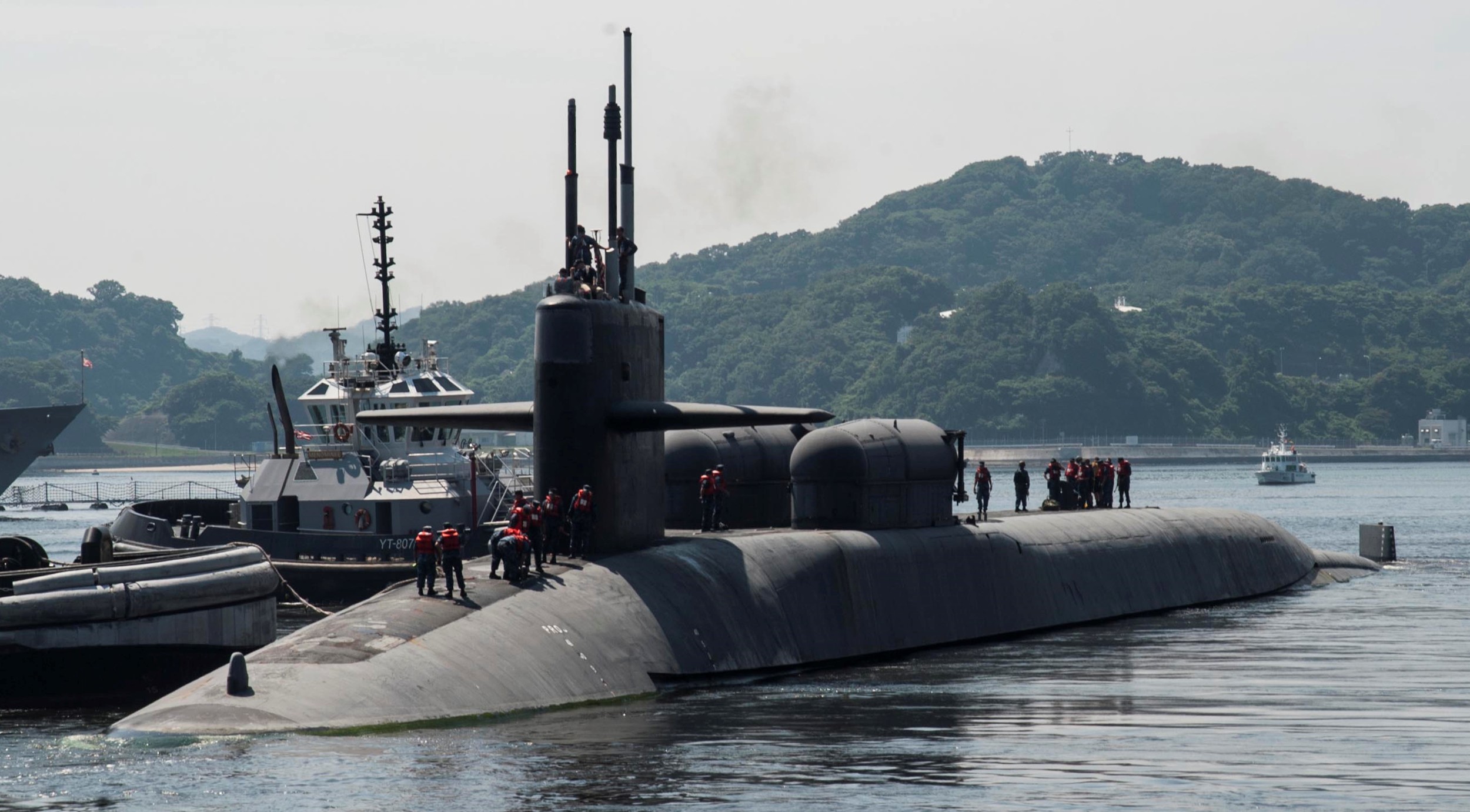  departing Fleet Activities Yokosuka, Japan - July 2016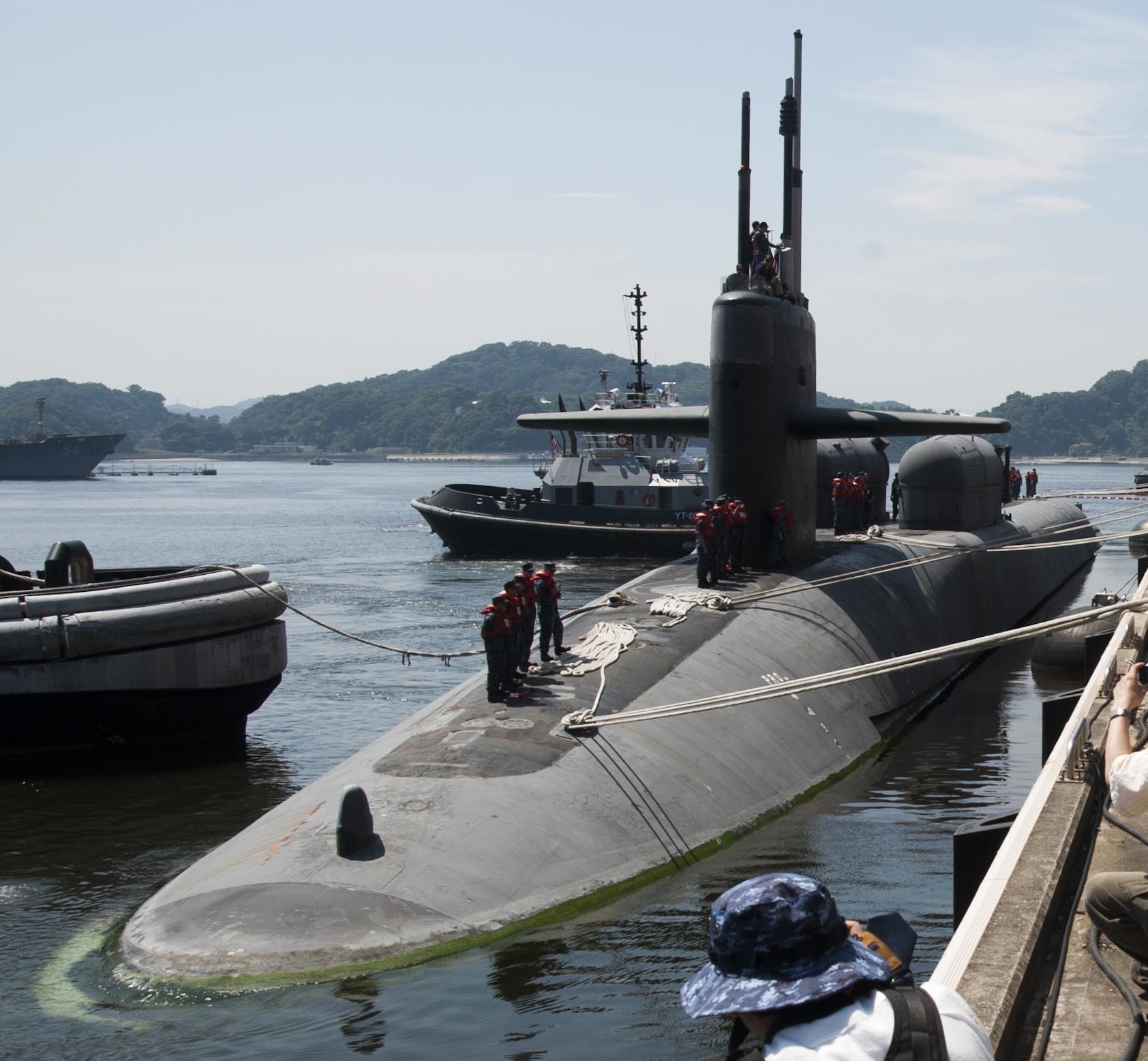  departing Fleet Activities Yokosuka, Japan - July 2016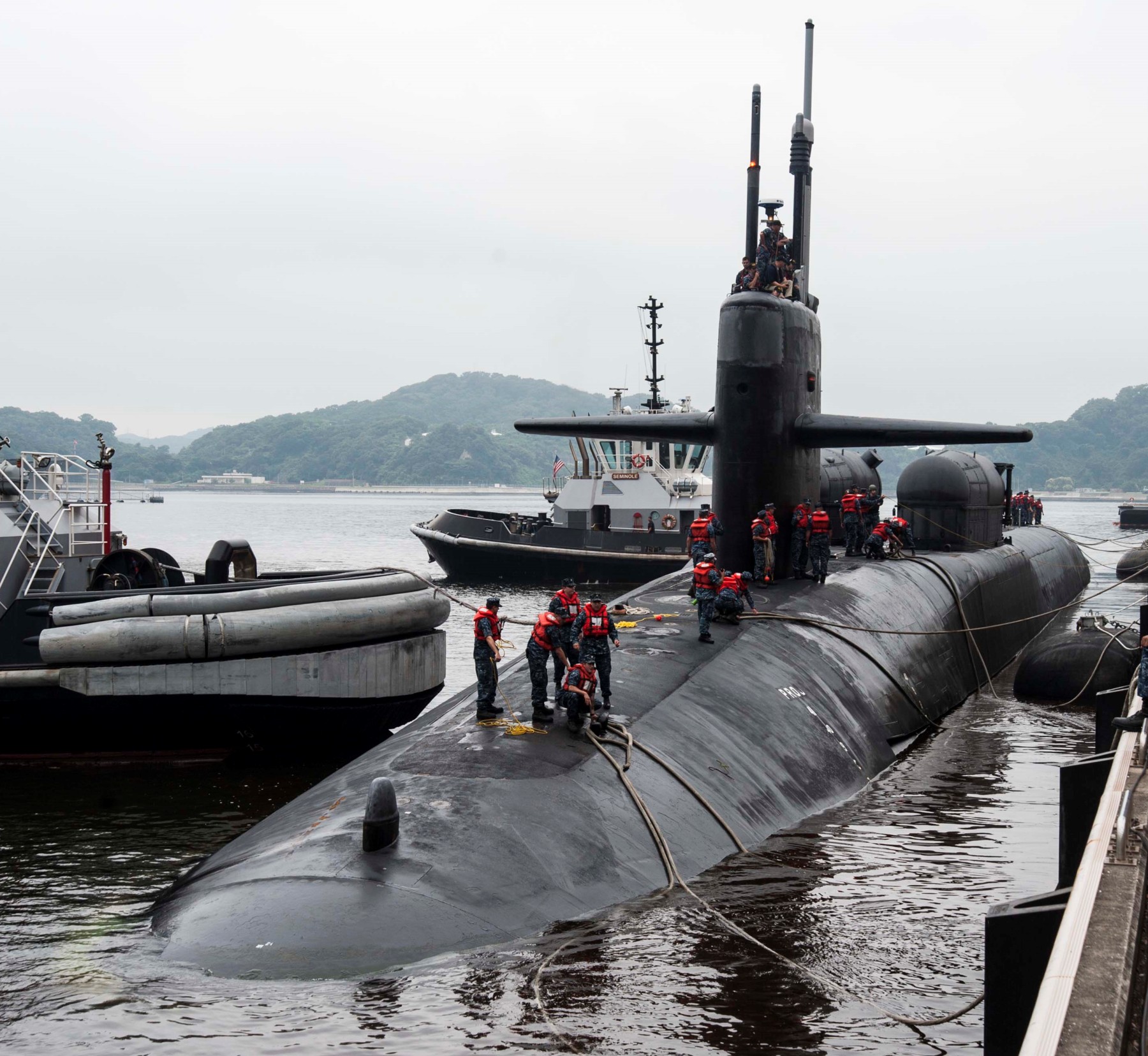  Fleet Activities Yokosuka, Japan - June 2016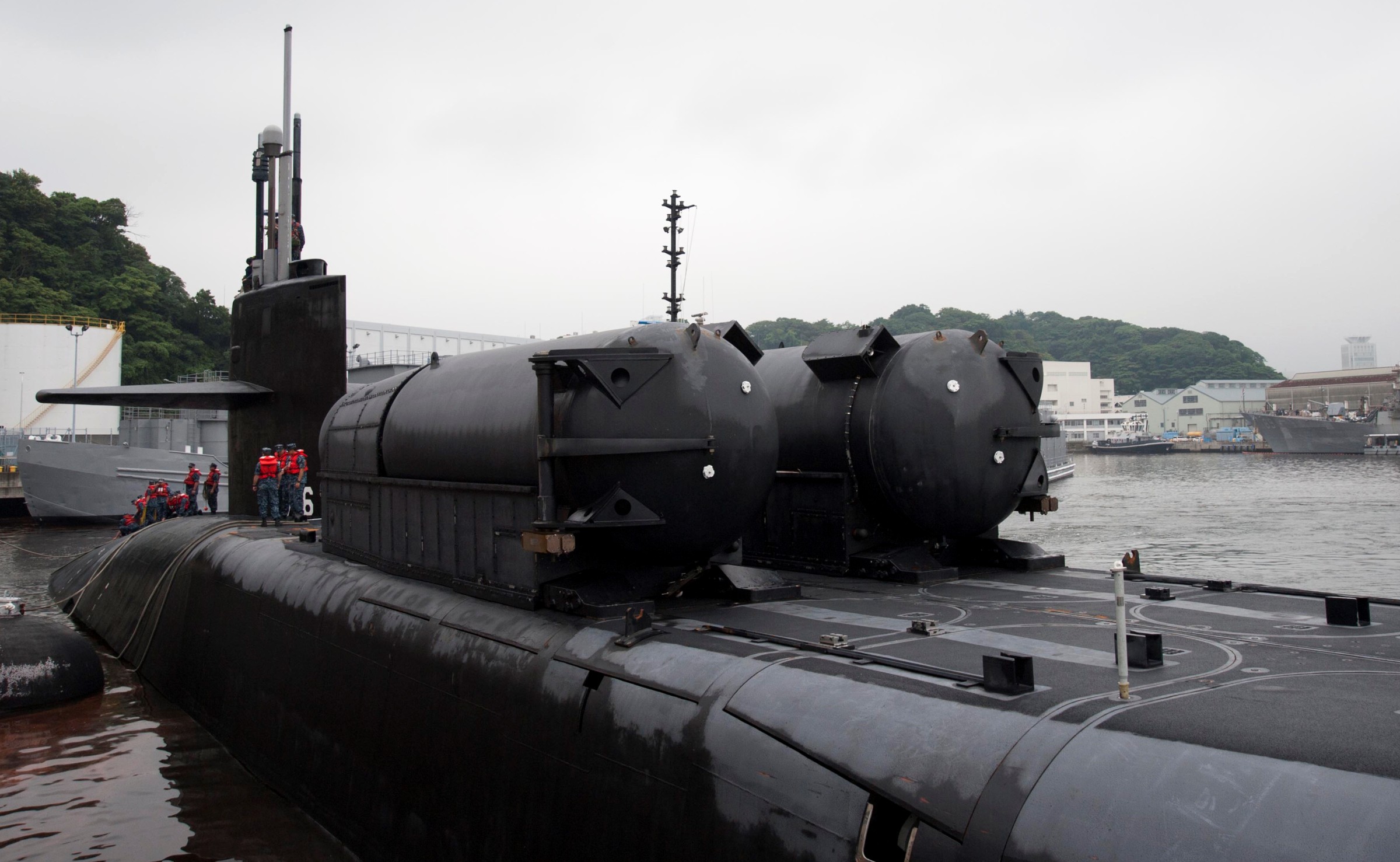  Fleet Activities Yokosuka, Japan - June 2016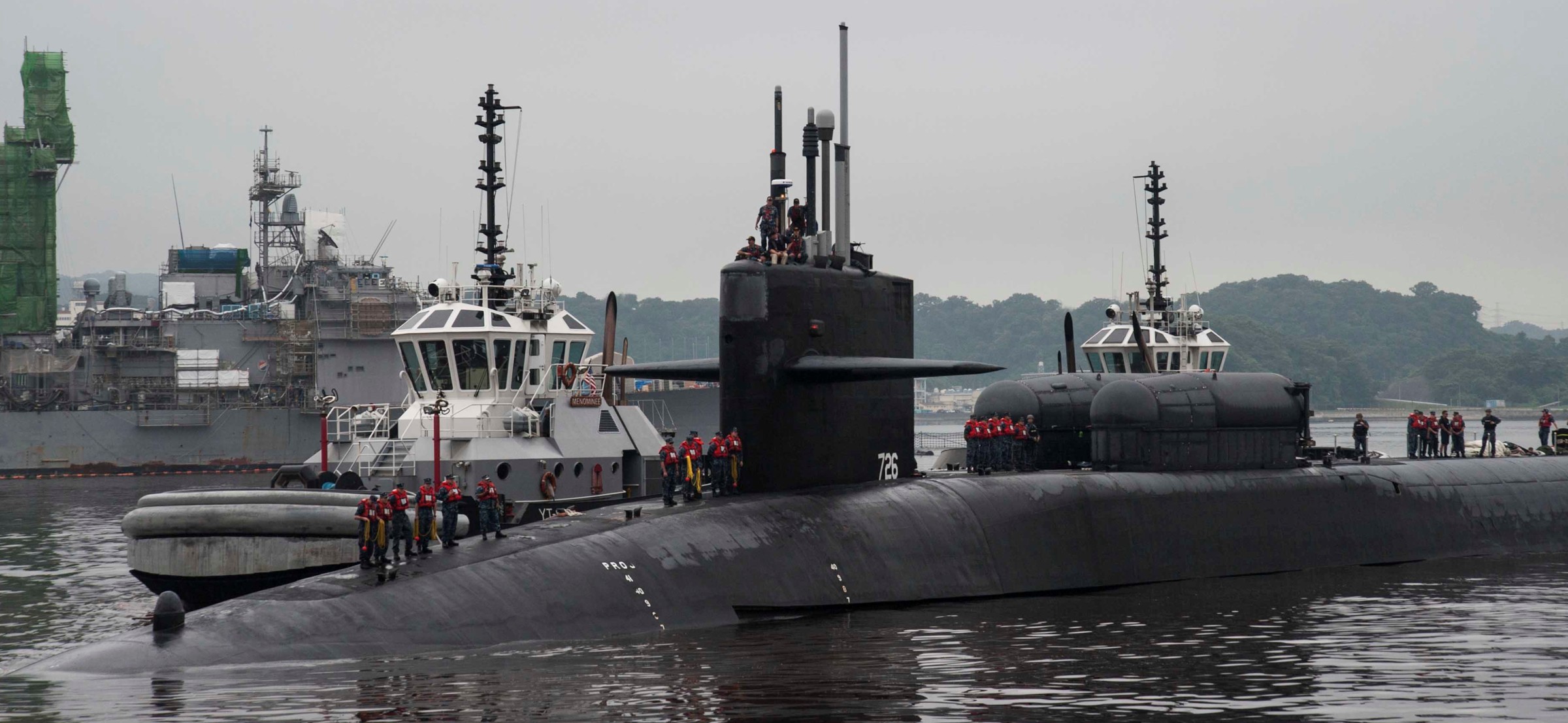  arriving at Fleet Activities Yokosuka, Japan - June 2016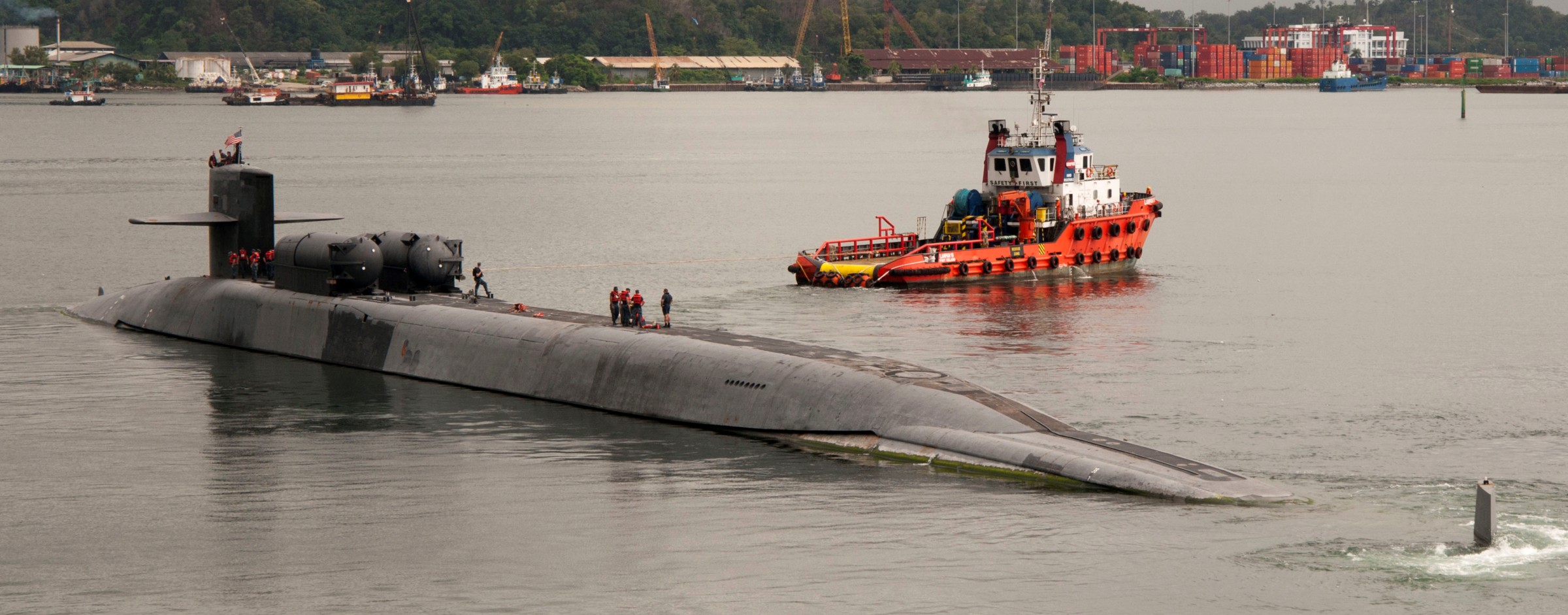  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015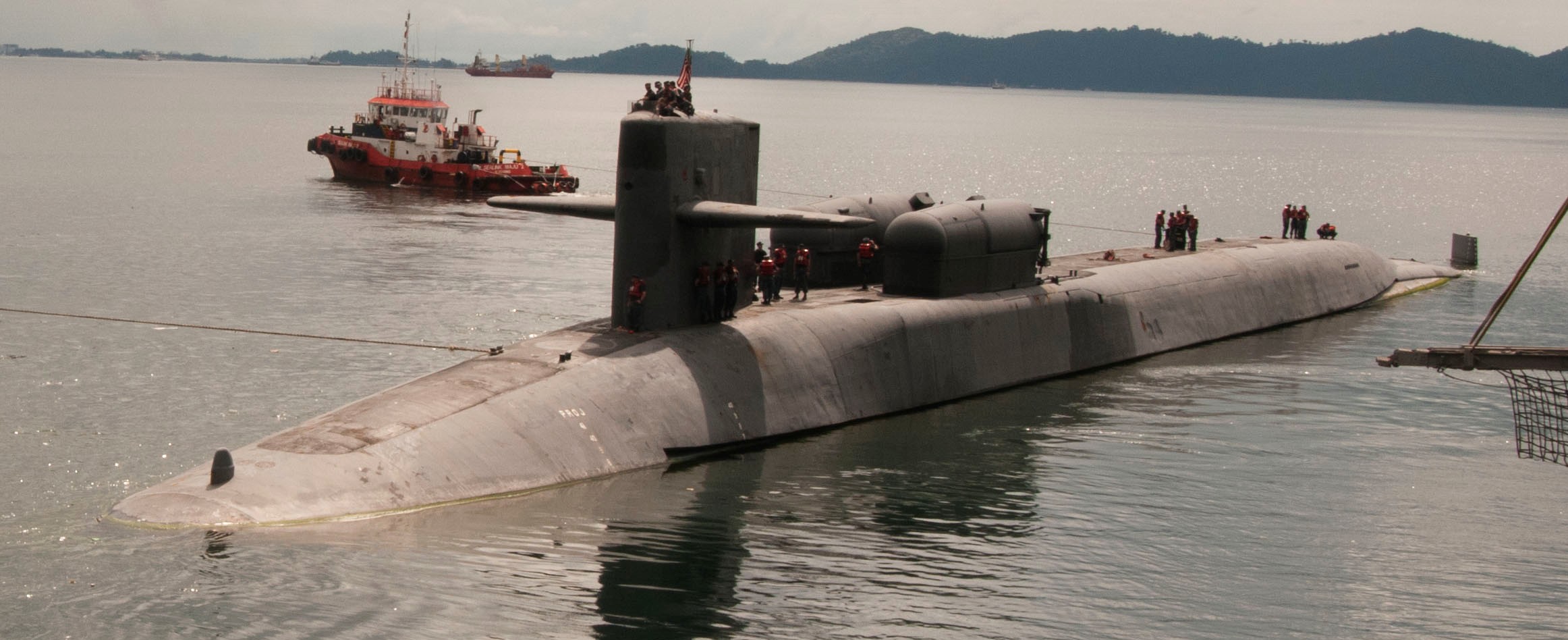  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015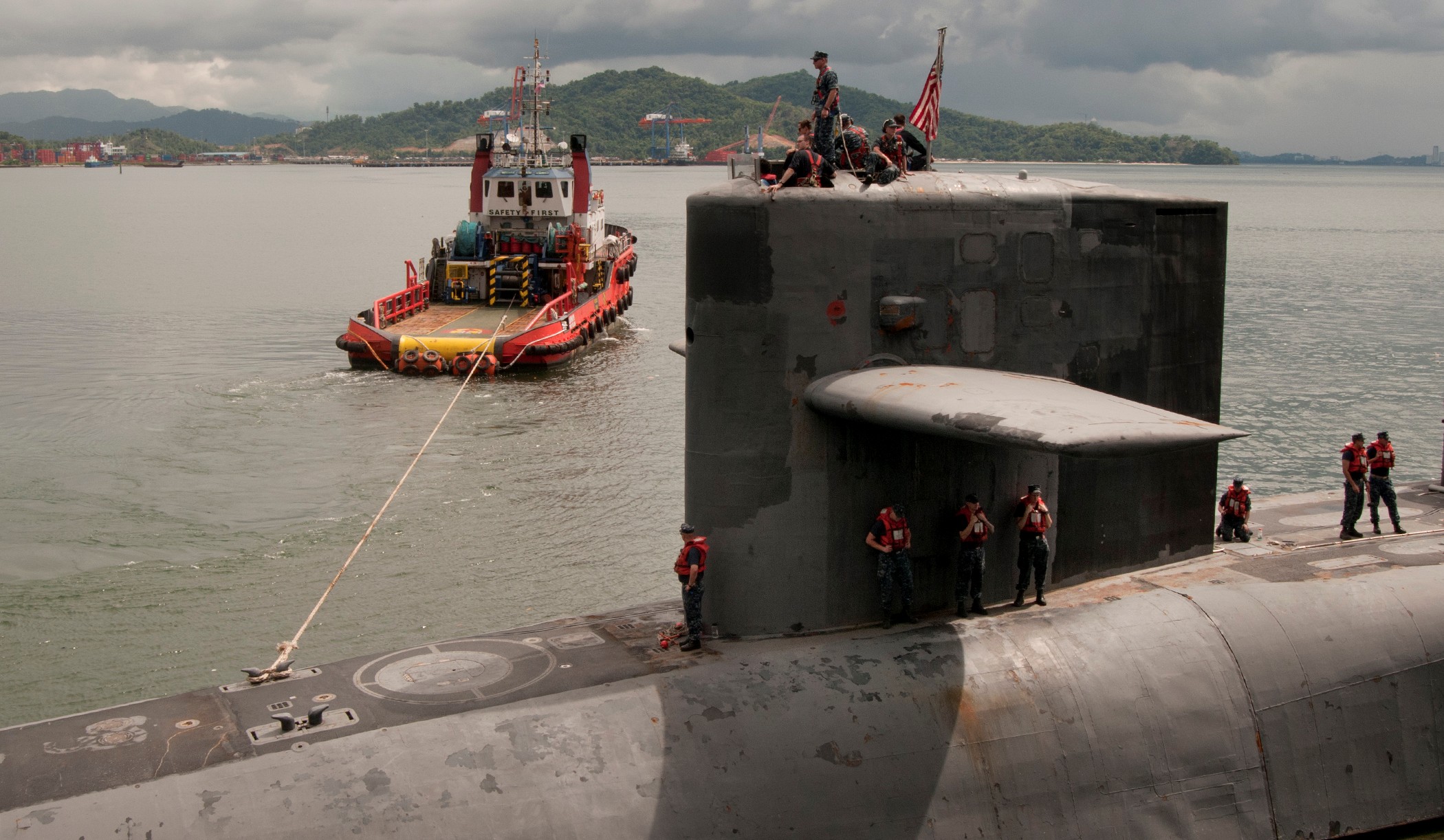  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015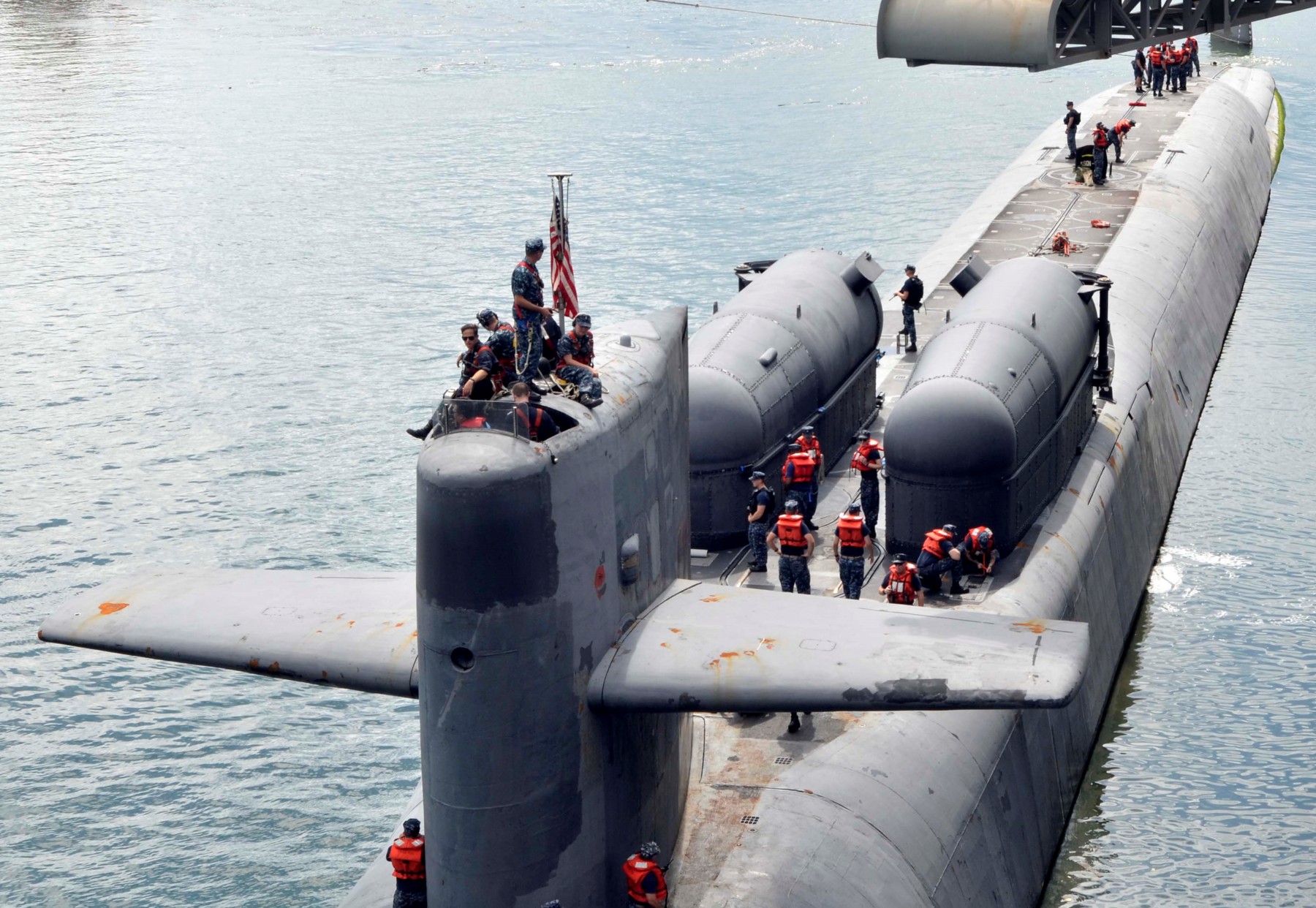  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015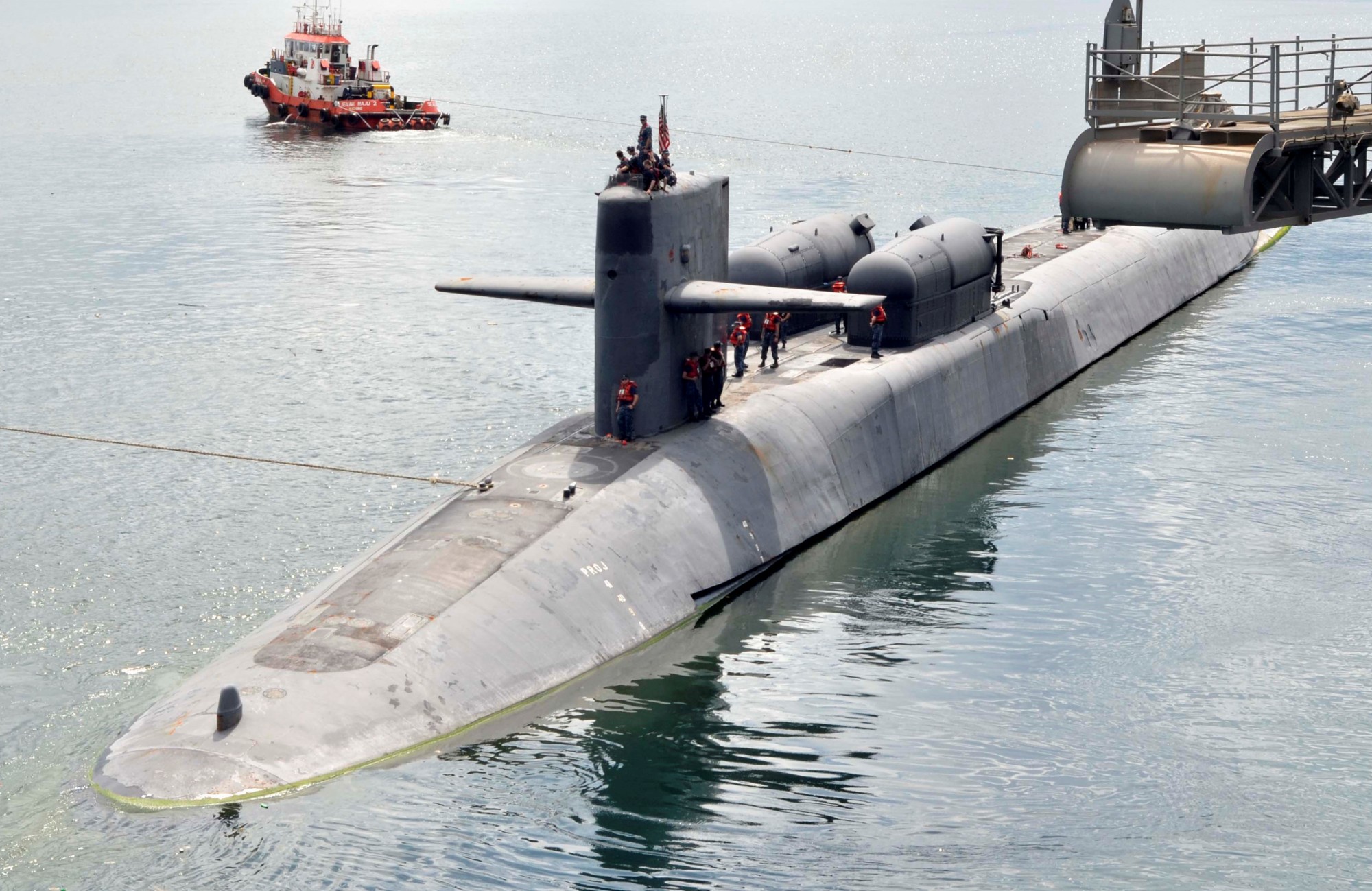  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015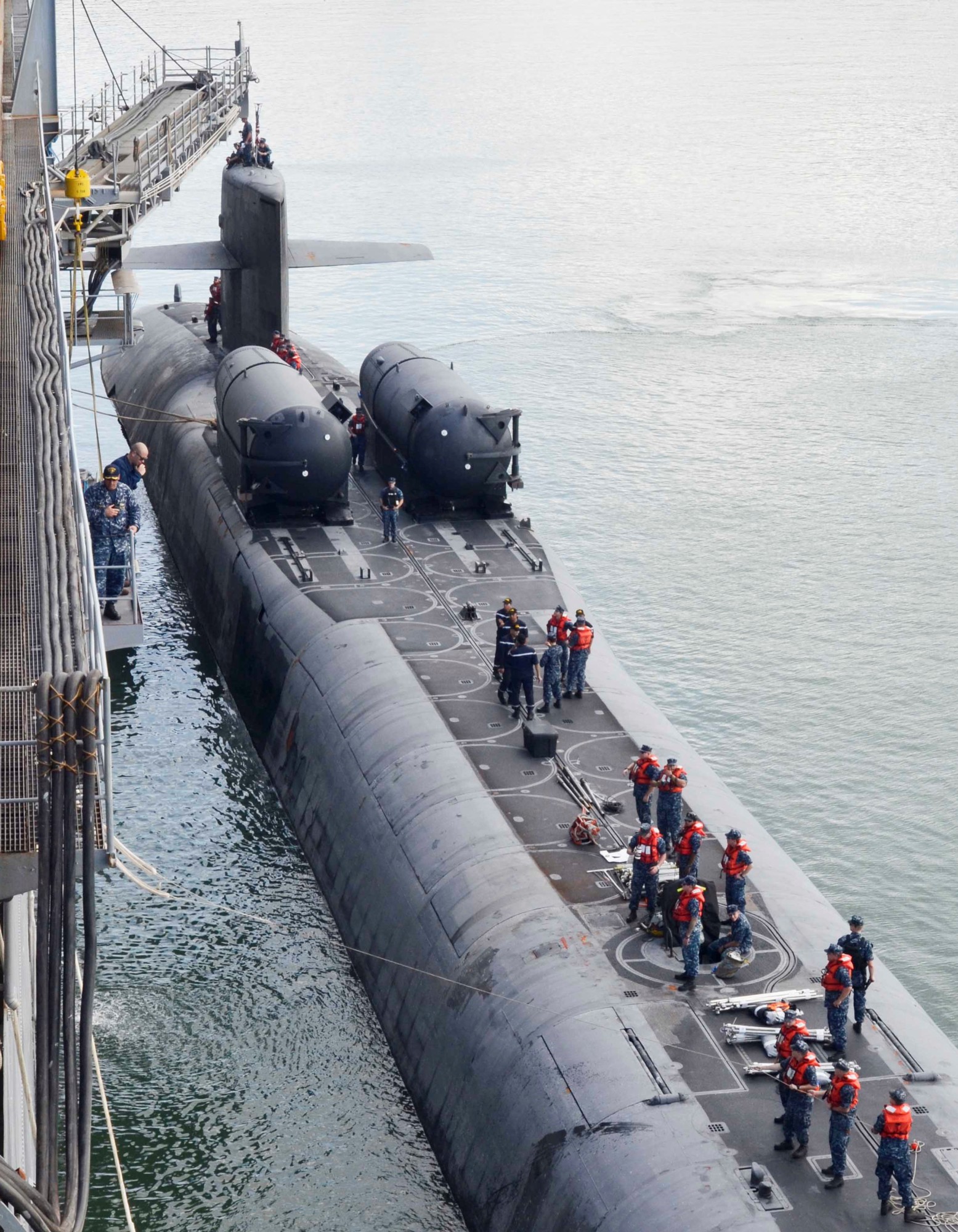  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015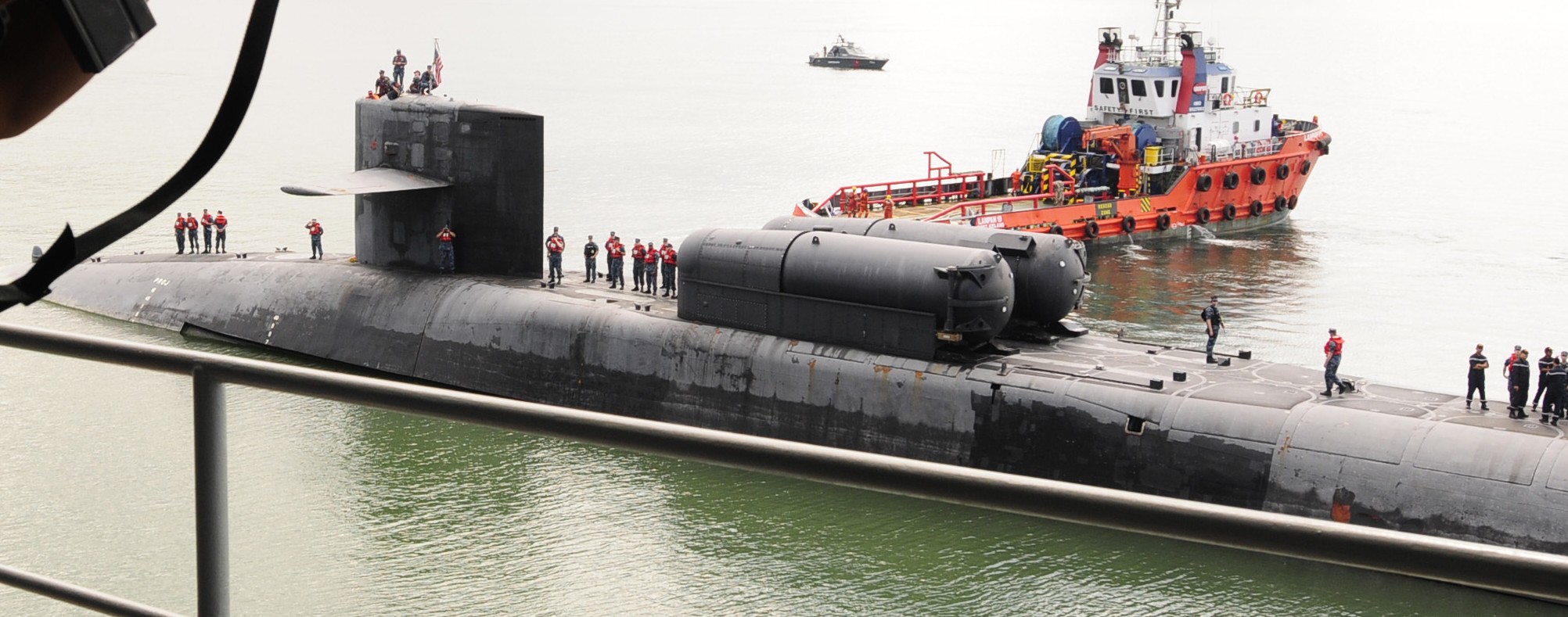  Sepanggar, Malaysia - November 2015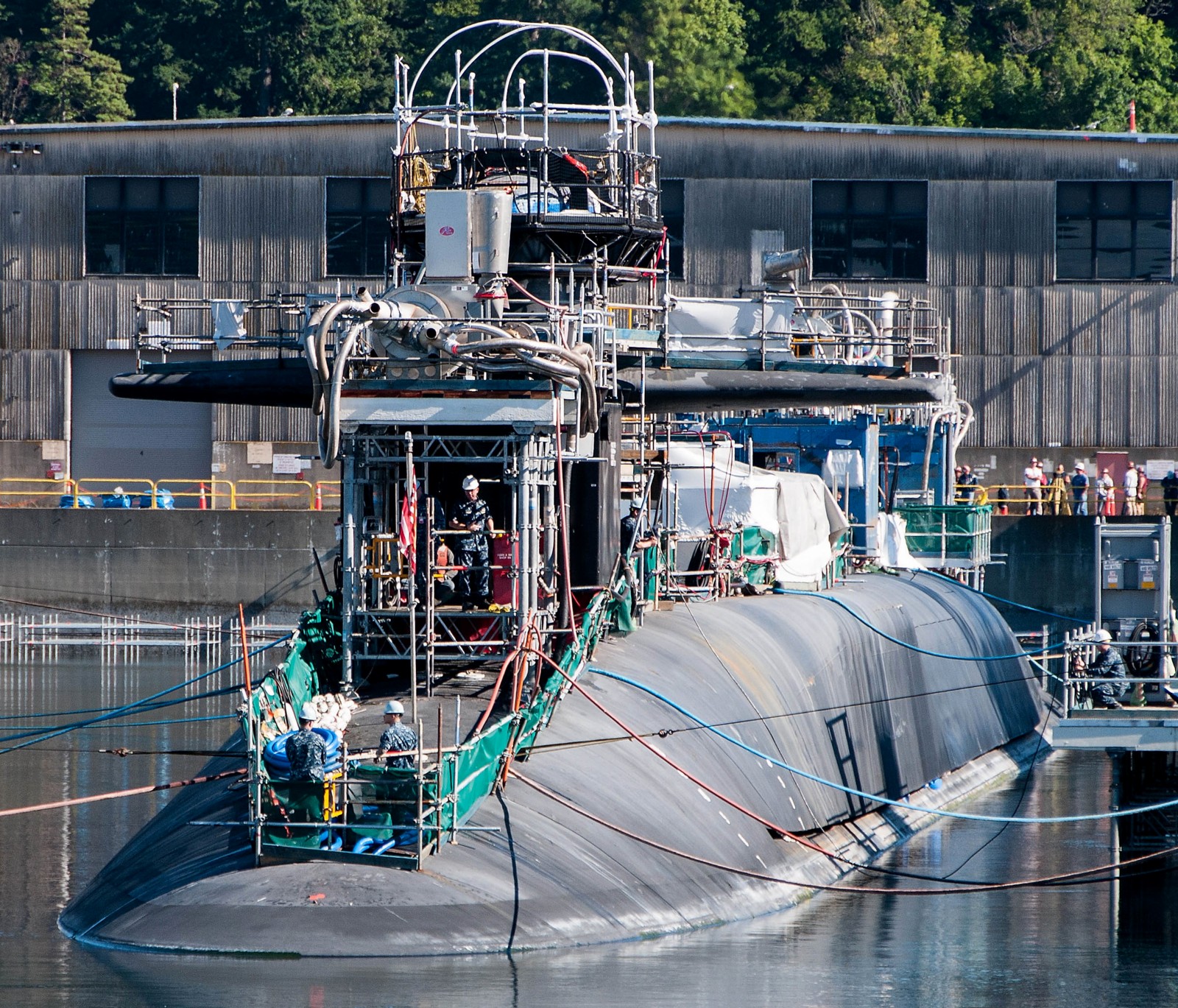  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington - June 2014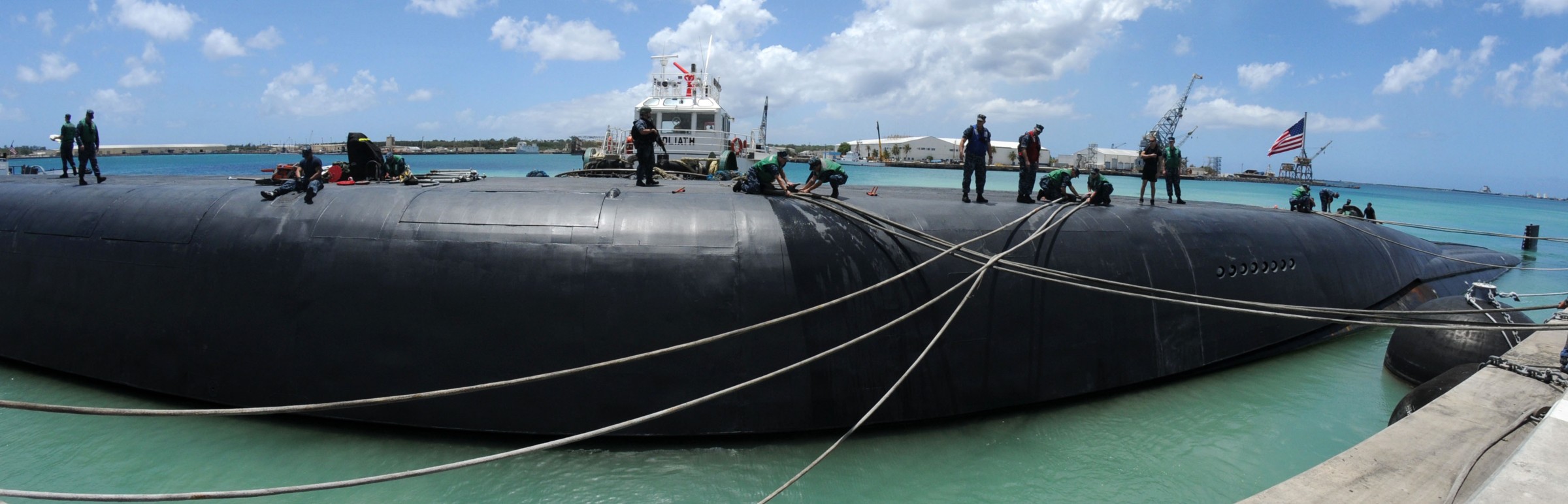  Polaris Point, Guam - April 2013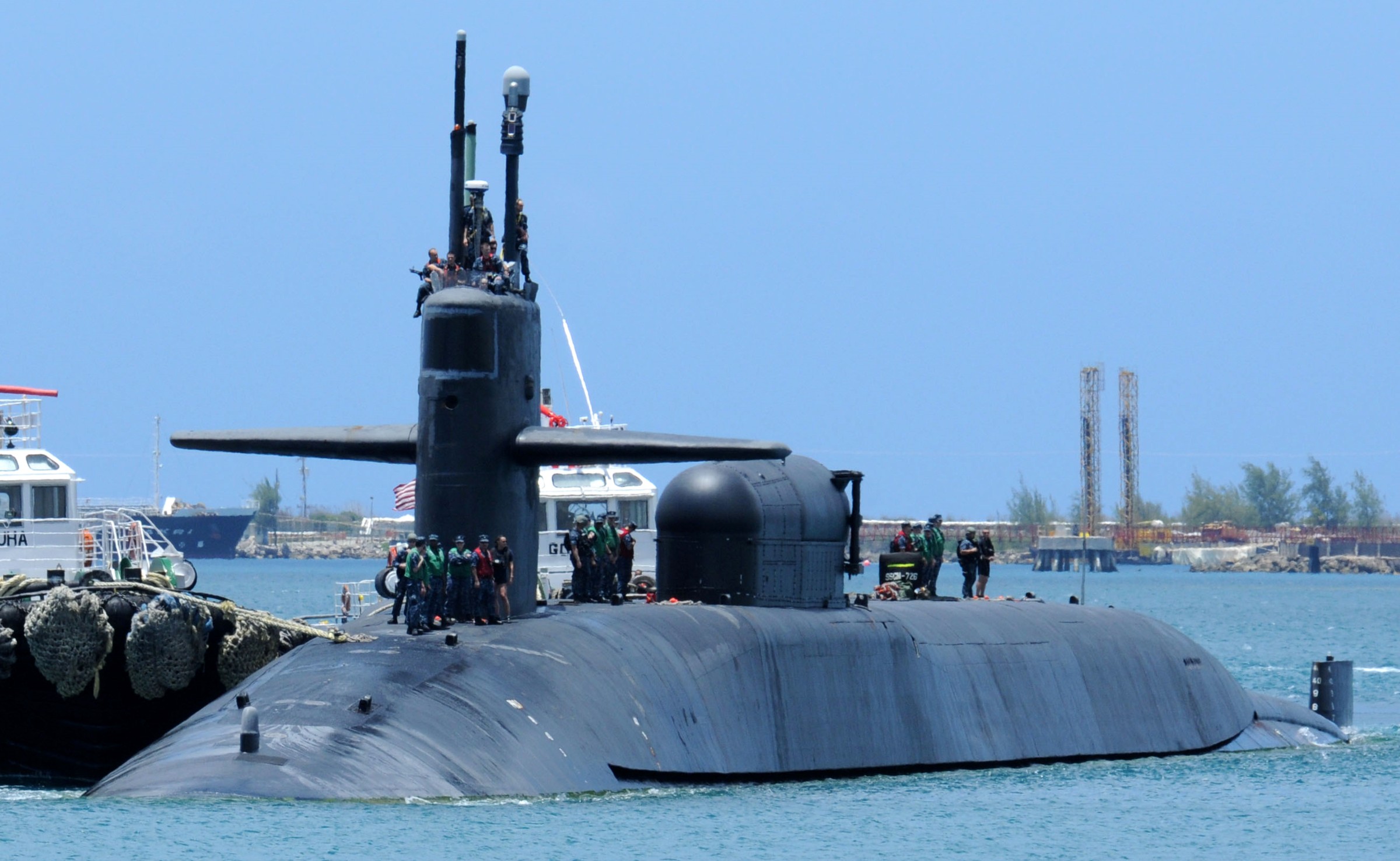  Polaris Point, Guam - April 2013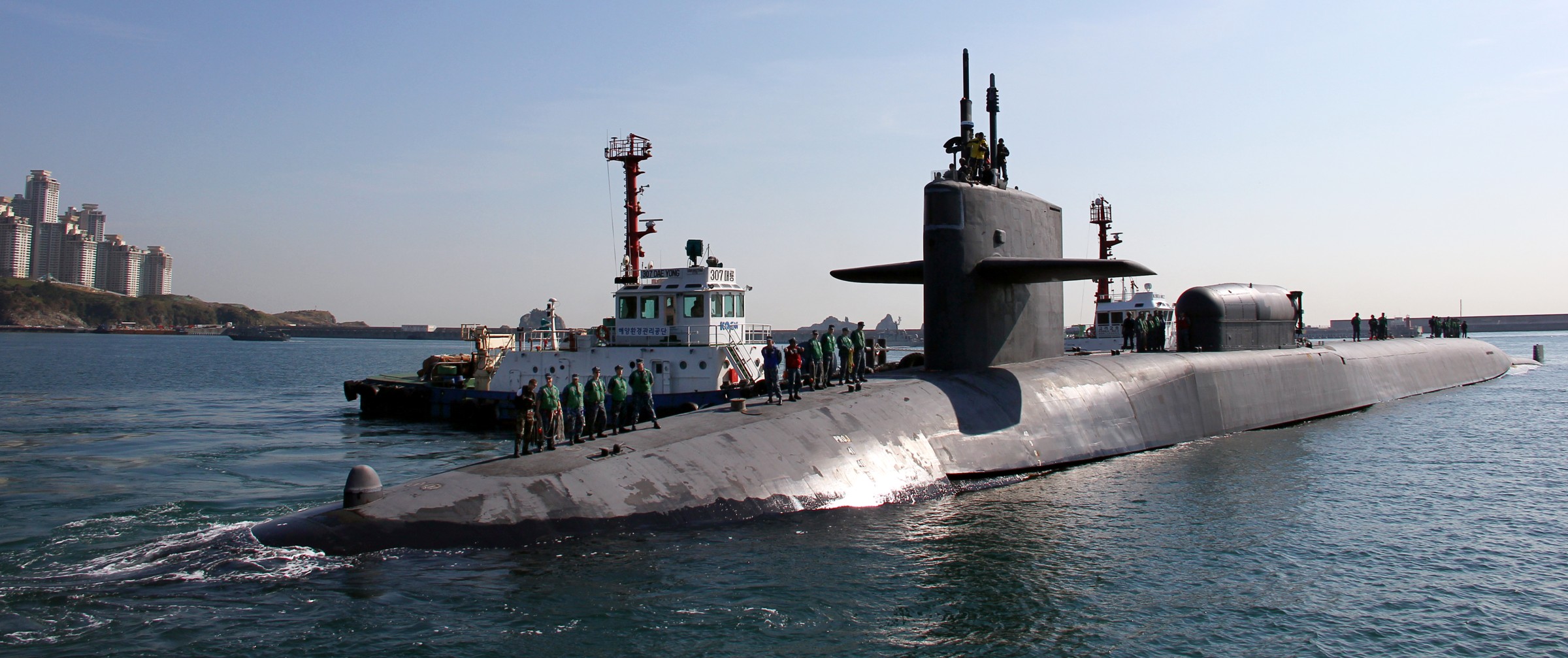  Busan, Republic of Korea - October 2012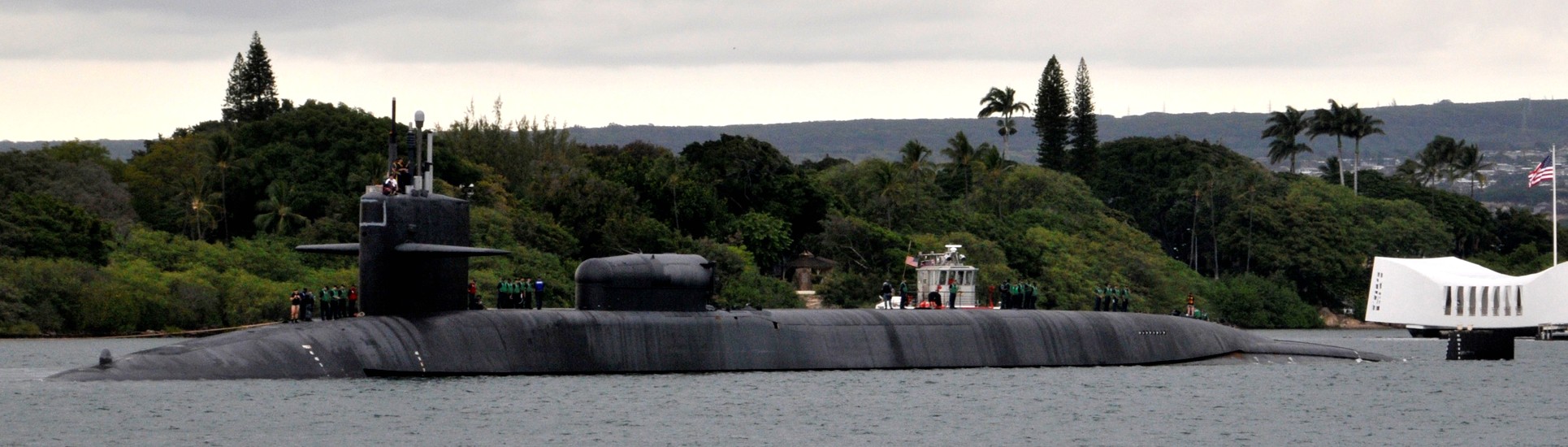  departing Joint Base Pearl Harbor Hickam, Hawaii - October 2012  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 14-month forward deployment - March 6, 2012  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 14-month forward deployment - March 6, 2012  arriving at Naval Magazine Indian Island, Washington after a 14-month forward deployment - March 6, 2012  Polaris Point, Guam - August 2011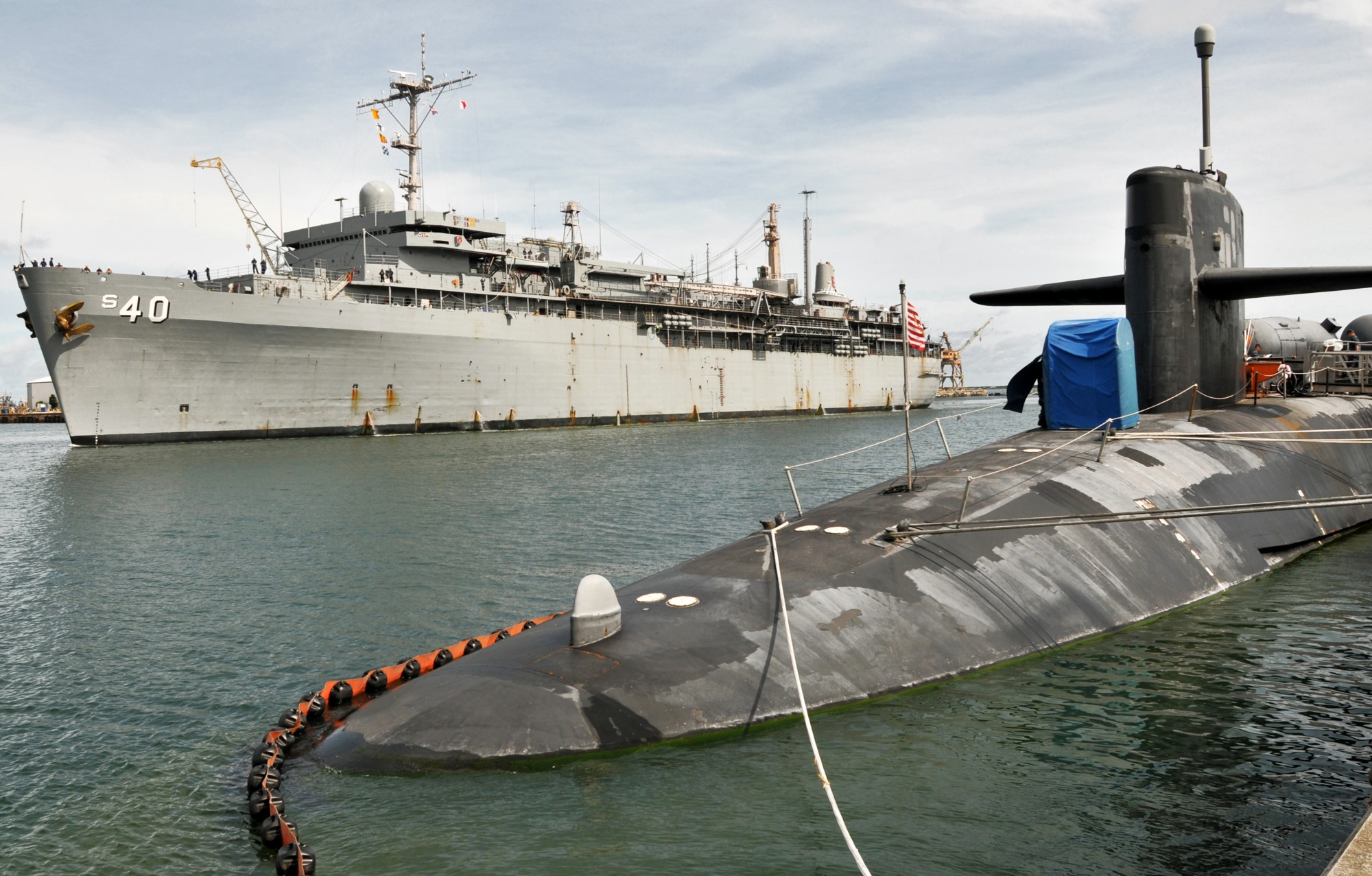  Polaris Point, Guam - August 2011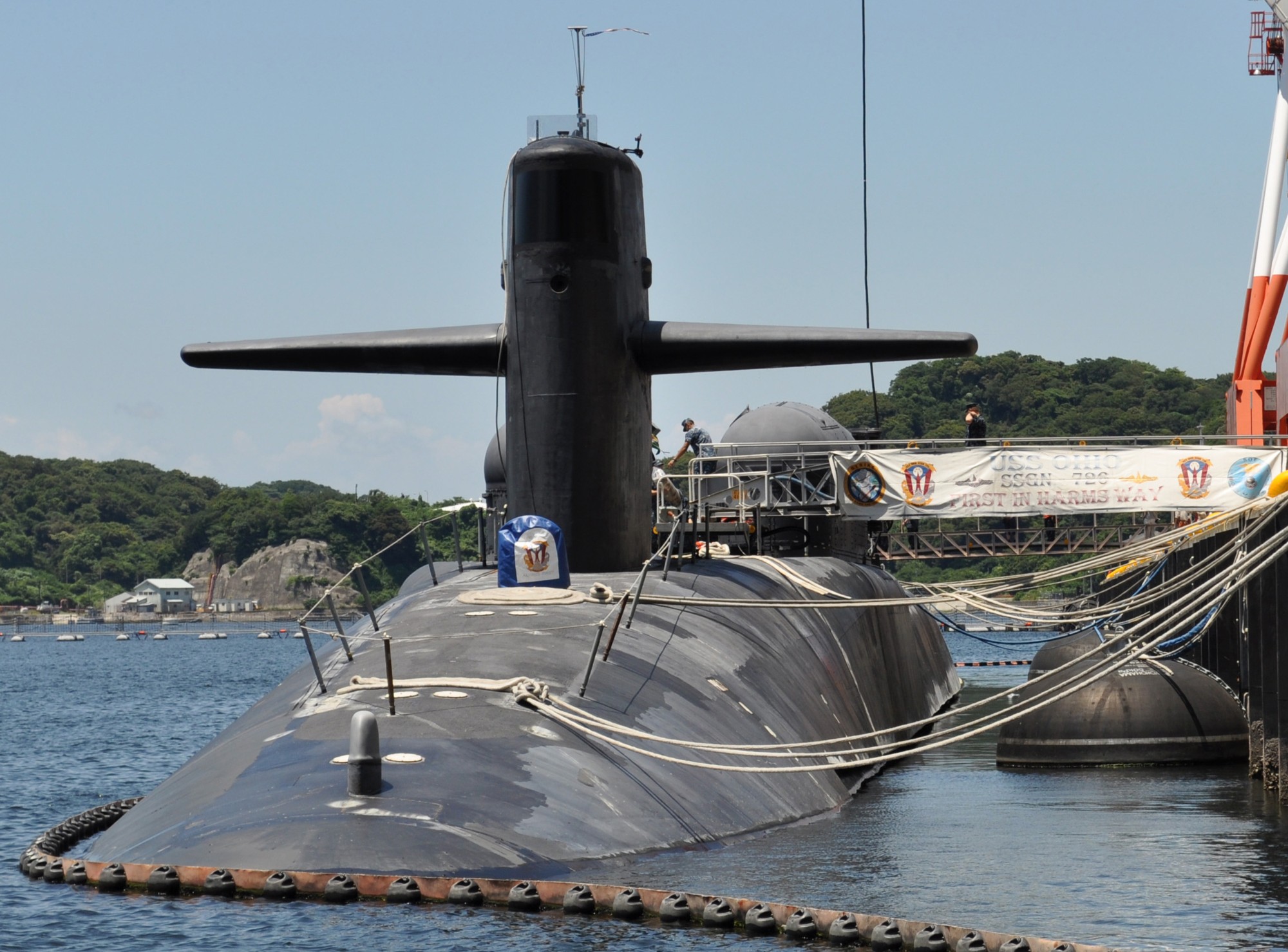  Yokosuka, Japan - July 2011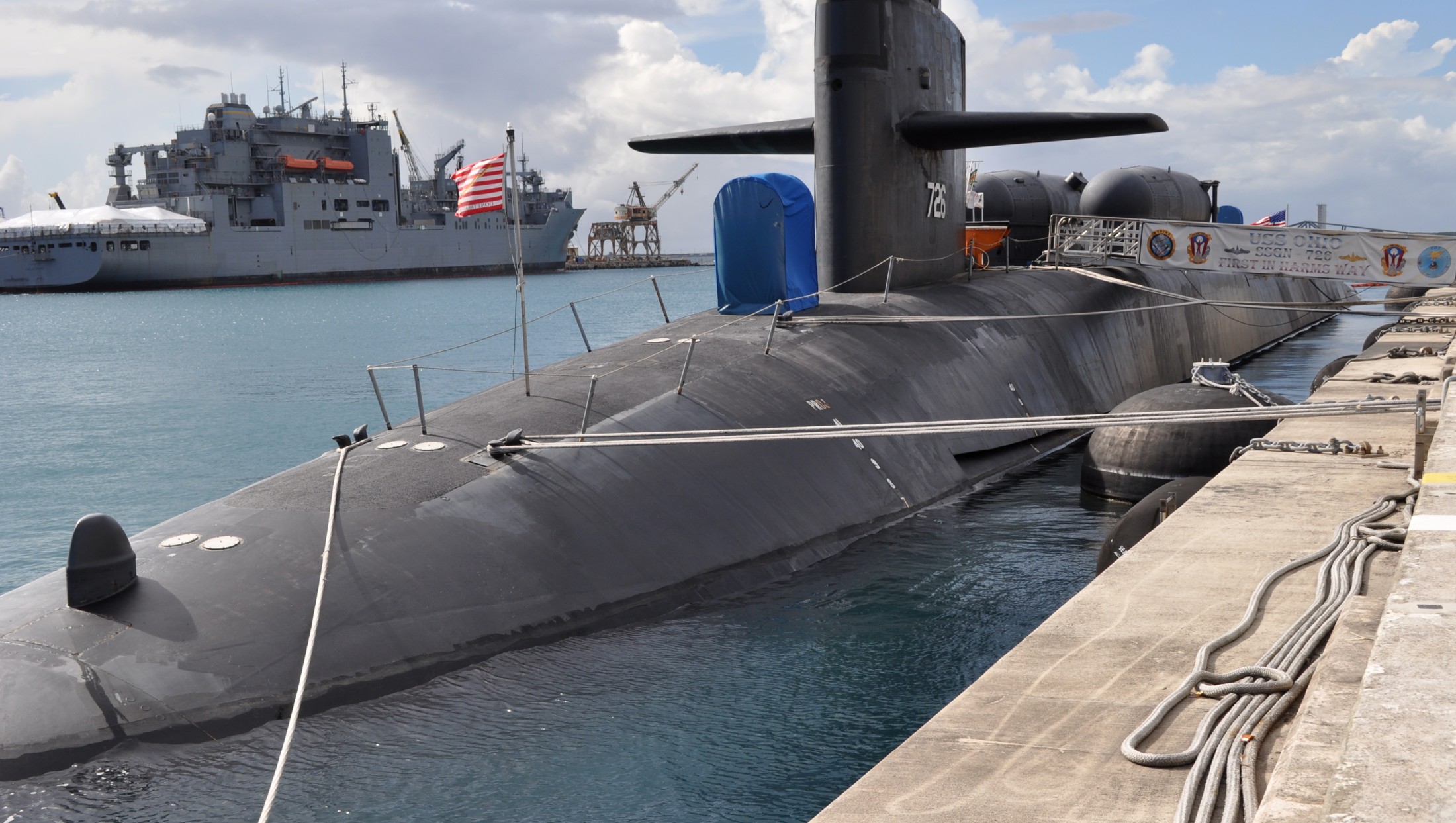  Apra Harbor, Guam - April 2011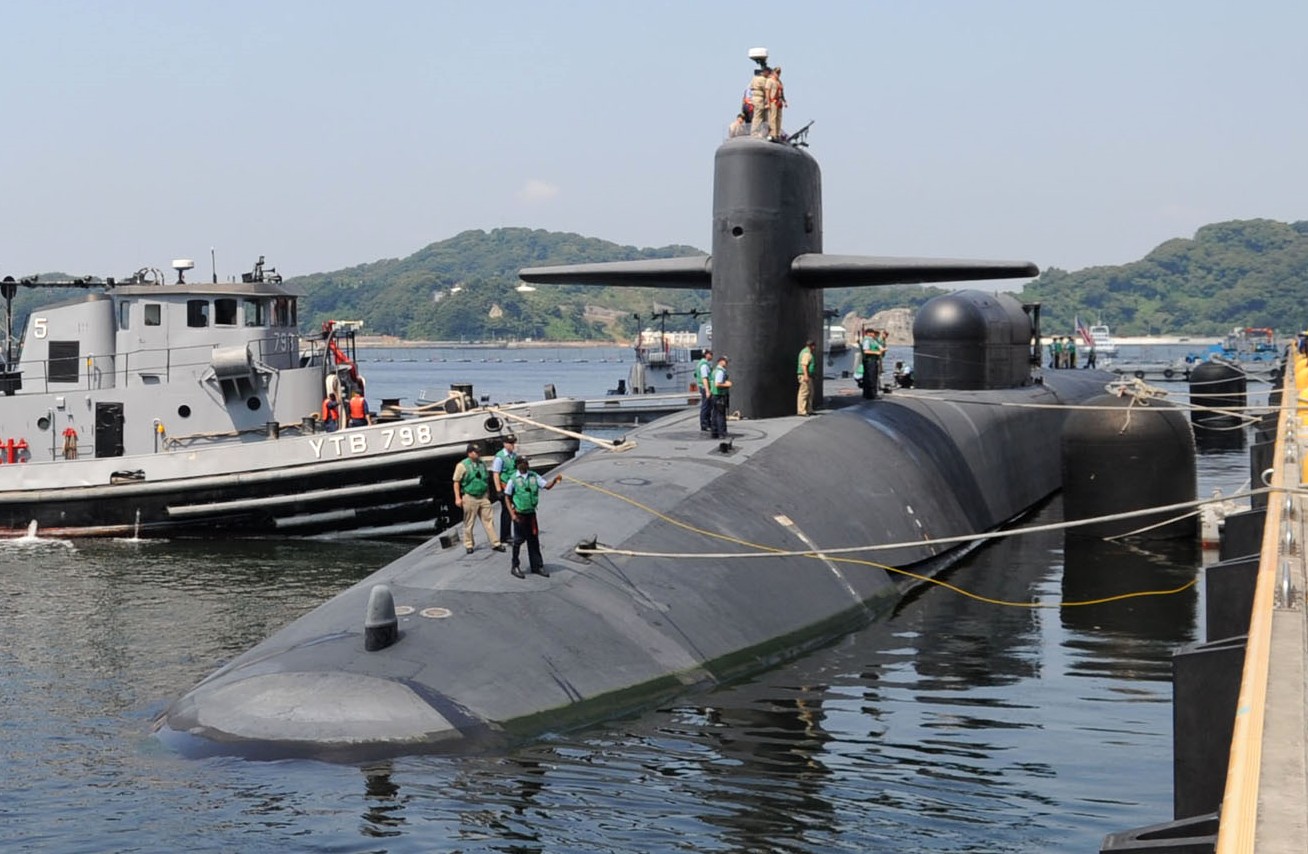  Yokosuka, Japan - August 2009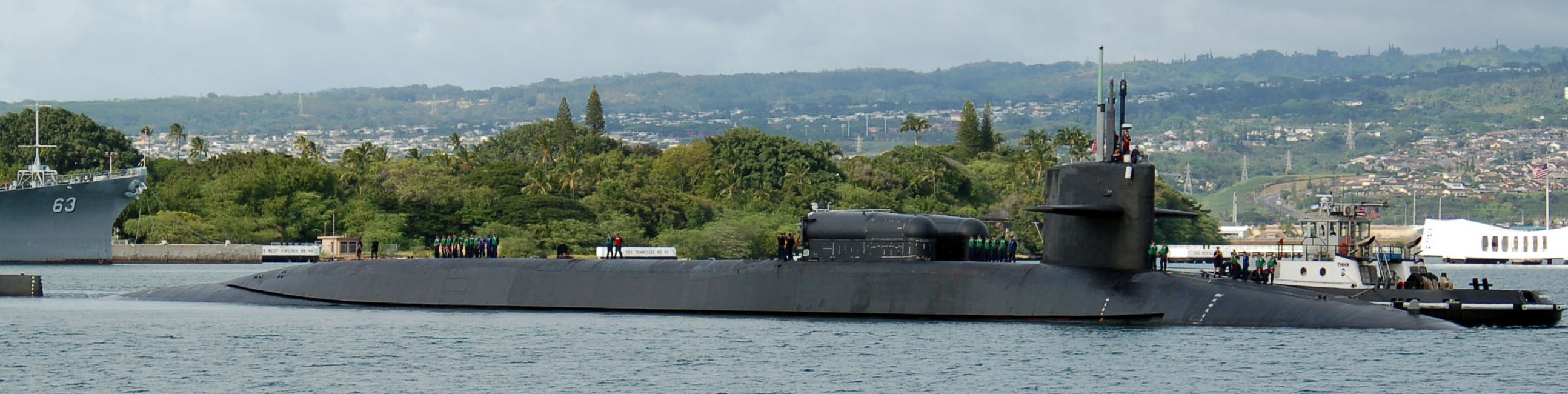  Pearl Harbor, Hawaii - December 2008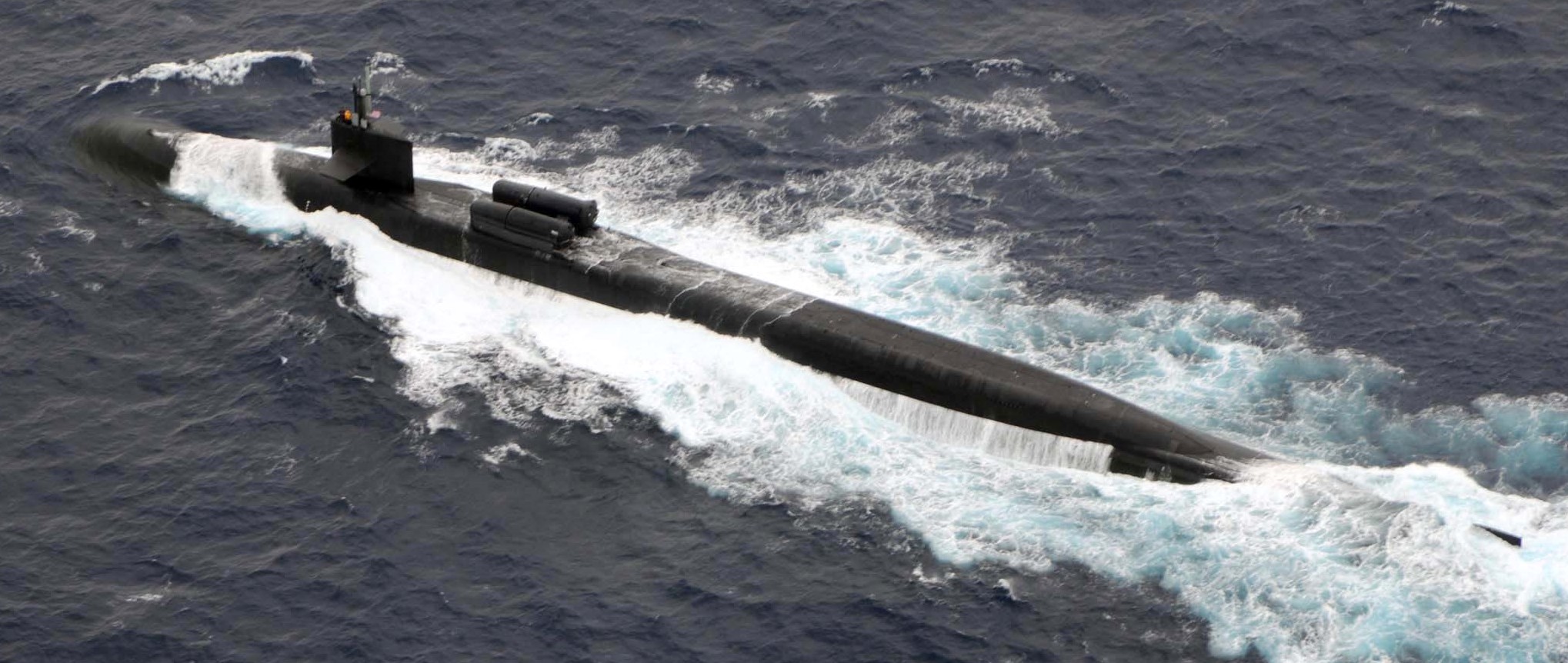  Pacific Ocean - November 2008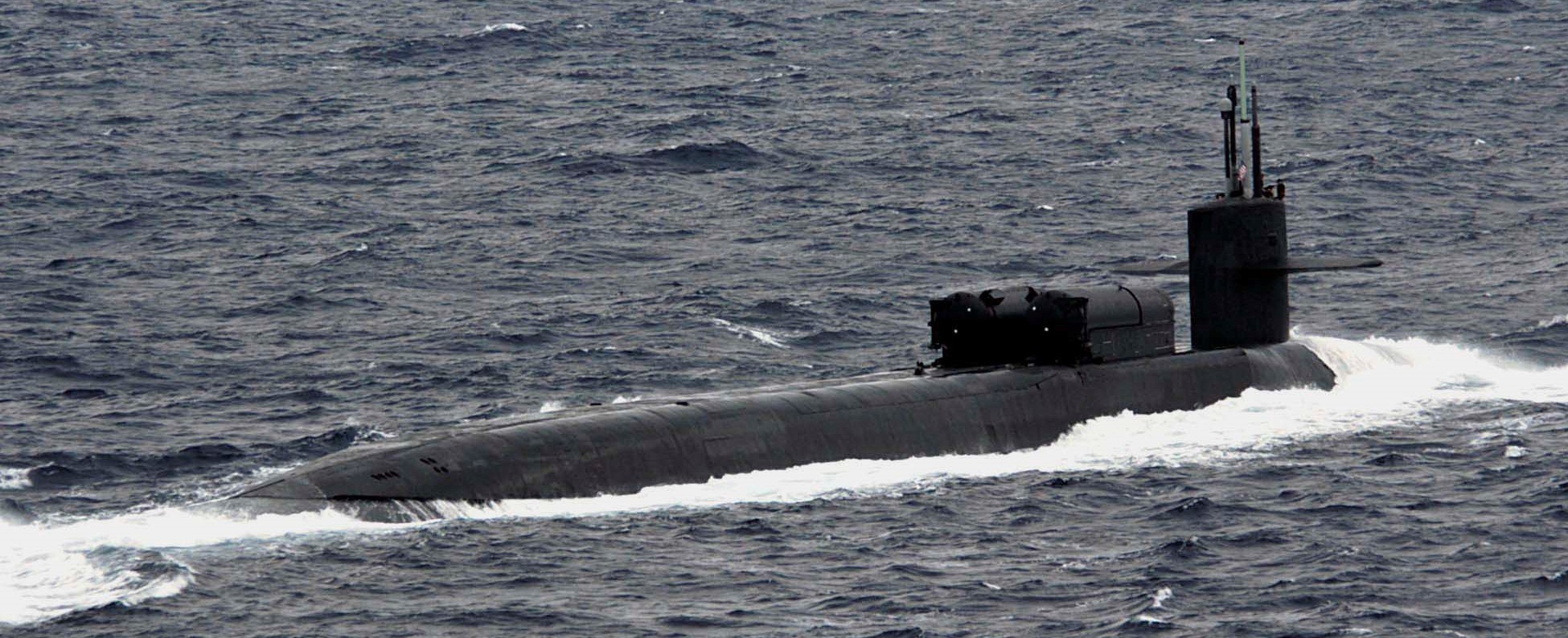  Pacific Ocean - November 2008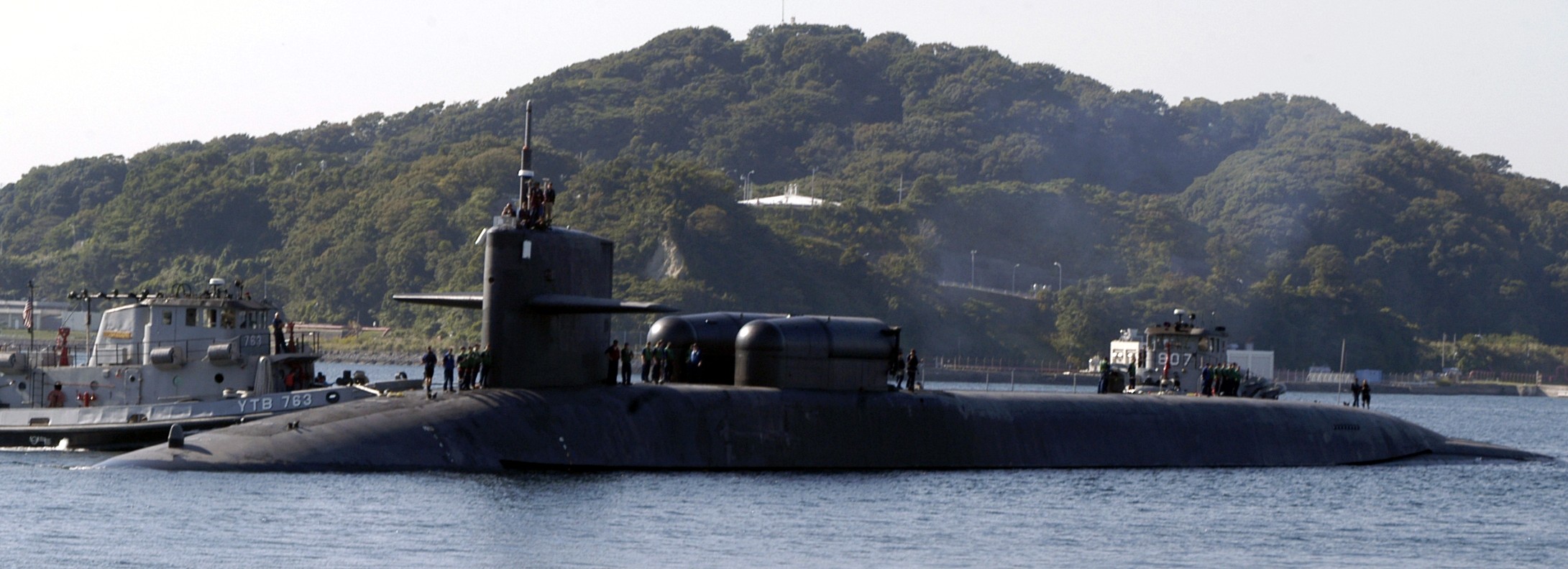  Yokosuka, Japan - October 2008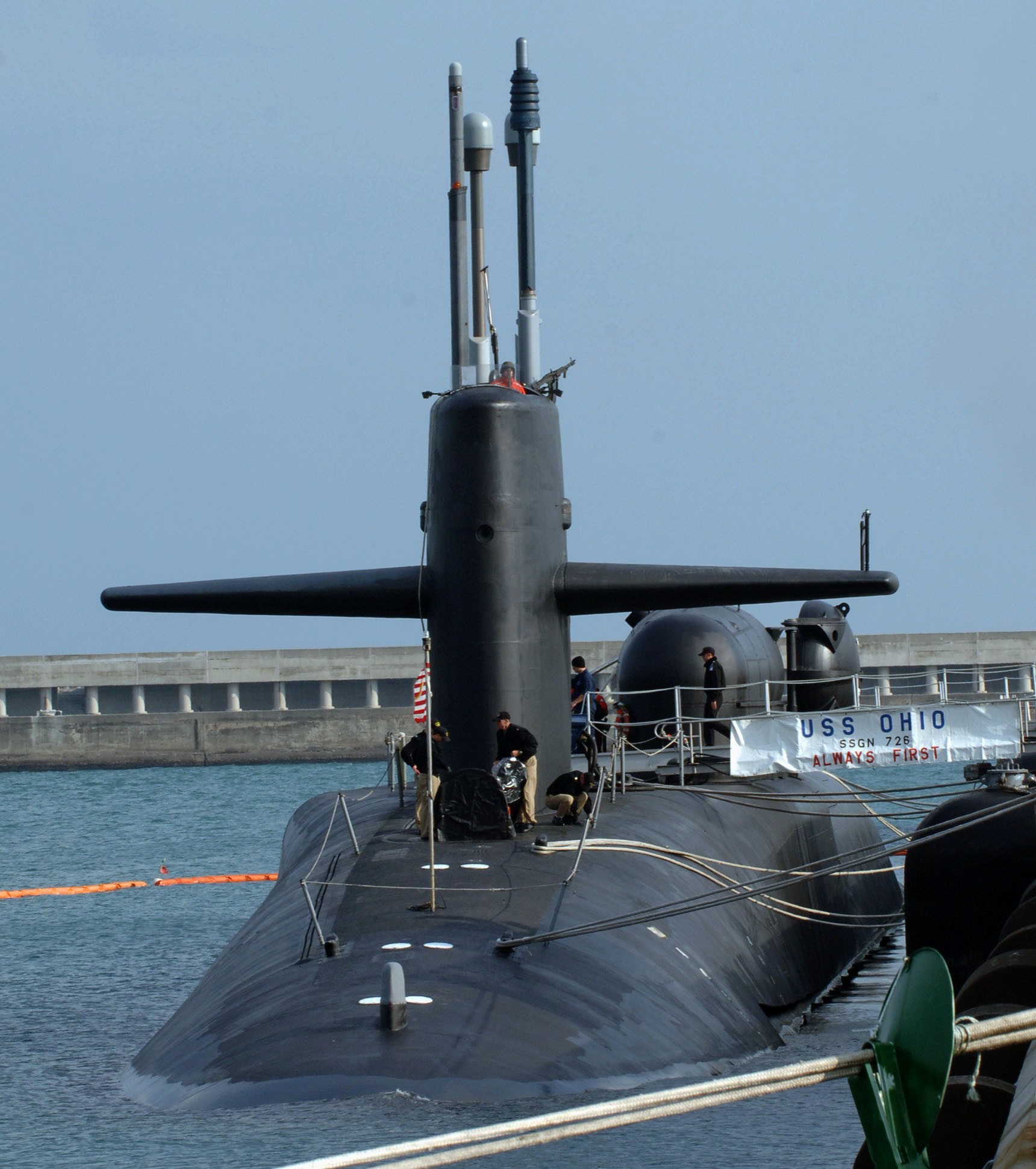  Chinhae Naval Base, Republic of Korea - February 2008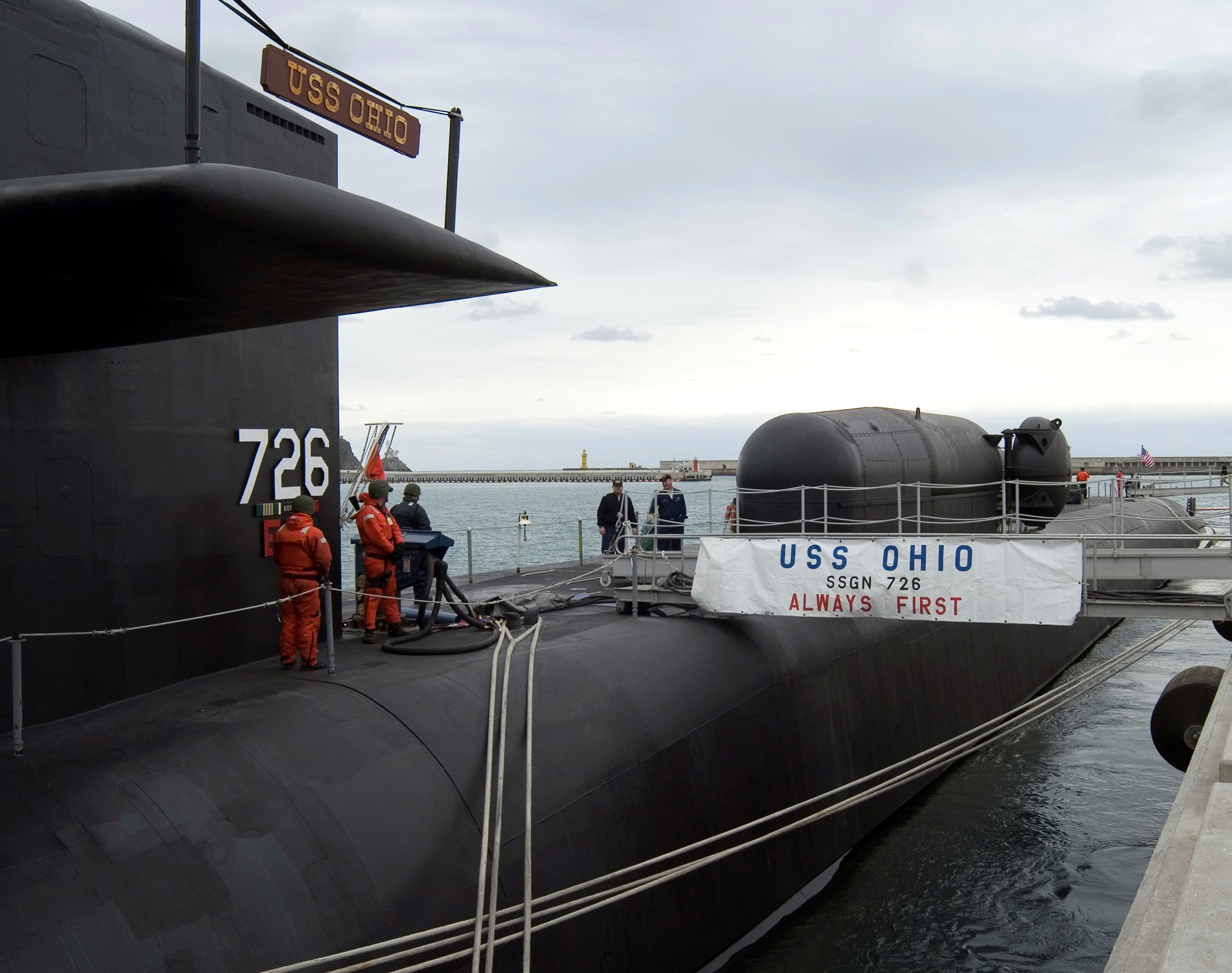  Chinhae Naval Base, Republic of Korea - February 2008  dry-deck shelter and SEAL delivery vehicle (SDV) - Chinhae Naval Base, Republic of Korea - February 2008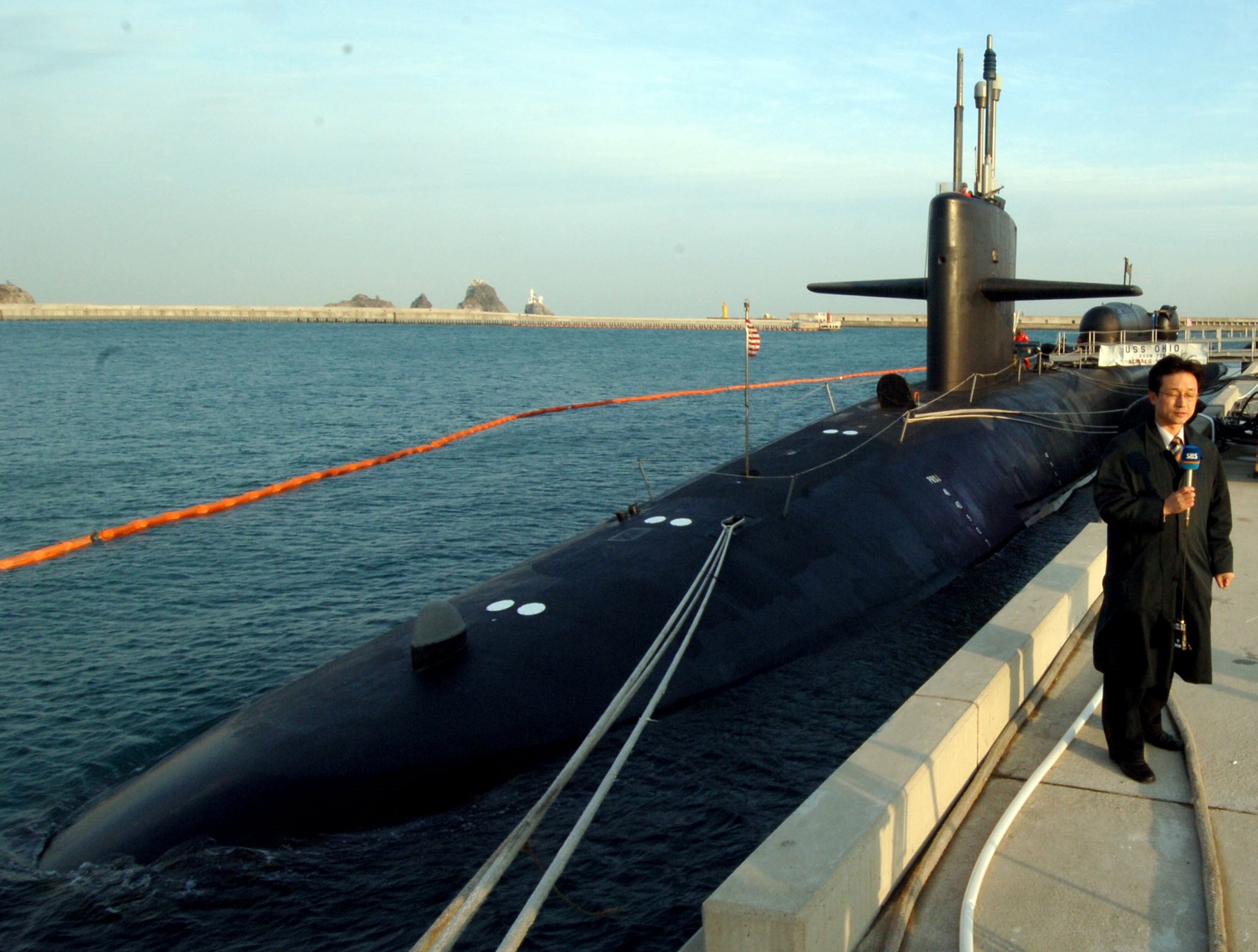  Chinhae Naval Base, Republic of Korea - February 2008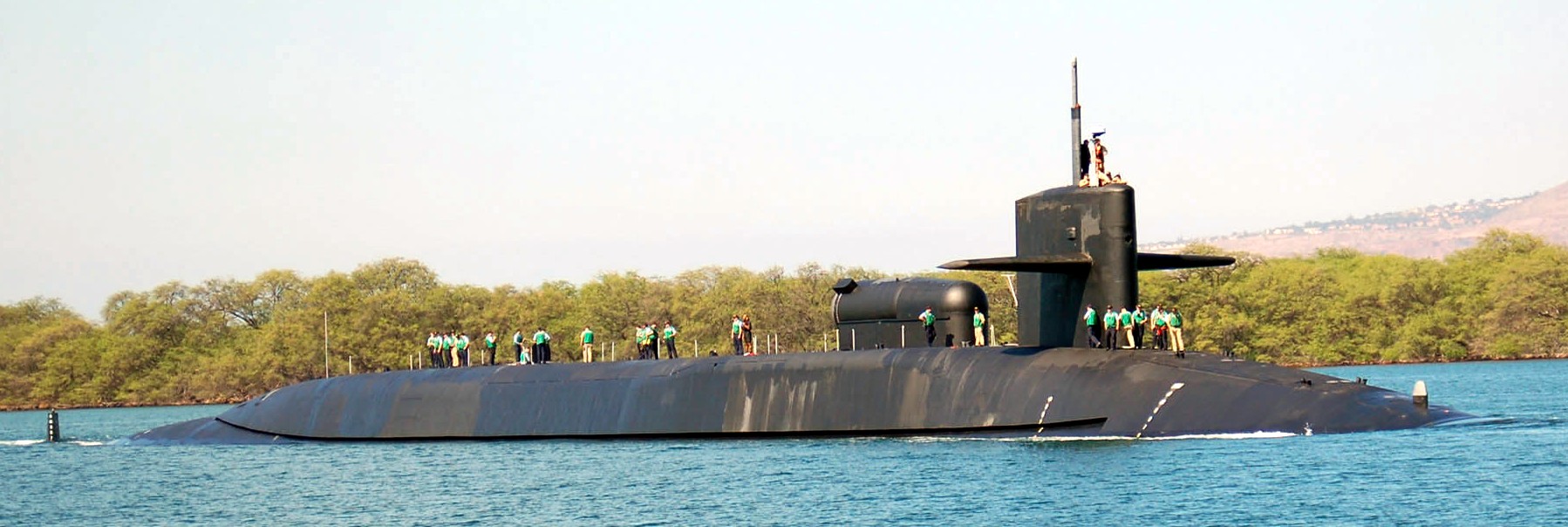  Pearl Harbor, Hawaii - October 2007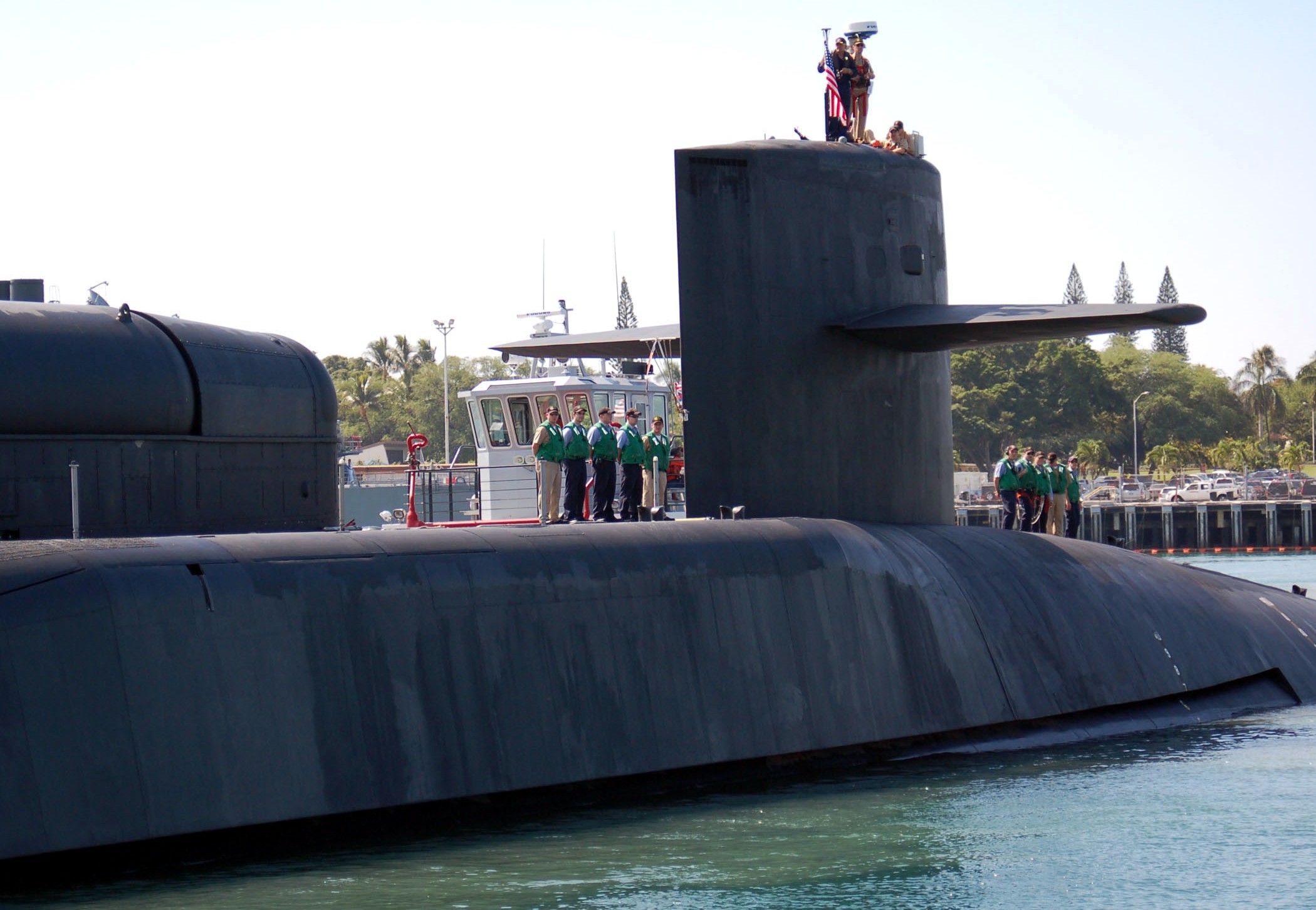  Pearl Harbor, Hawaii - October 2007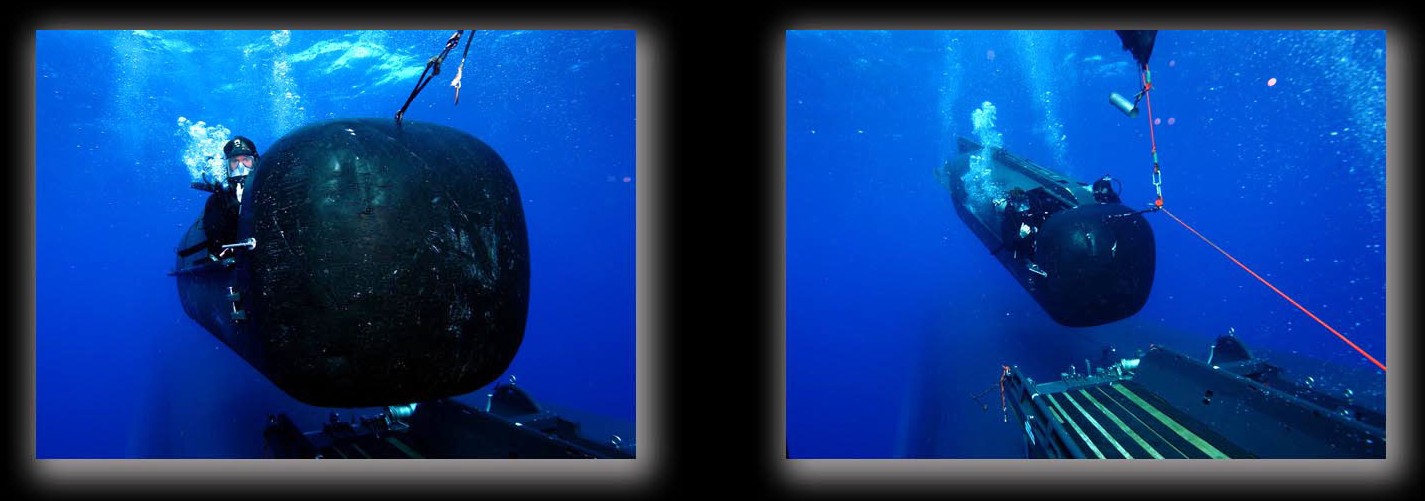  dry-deck shelter operations - undated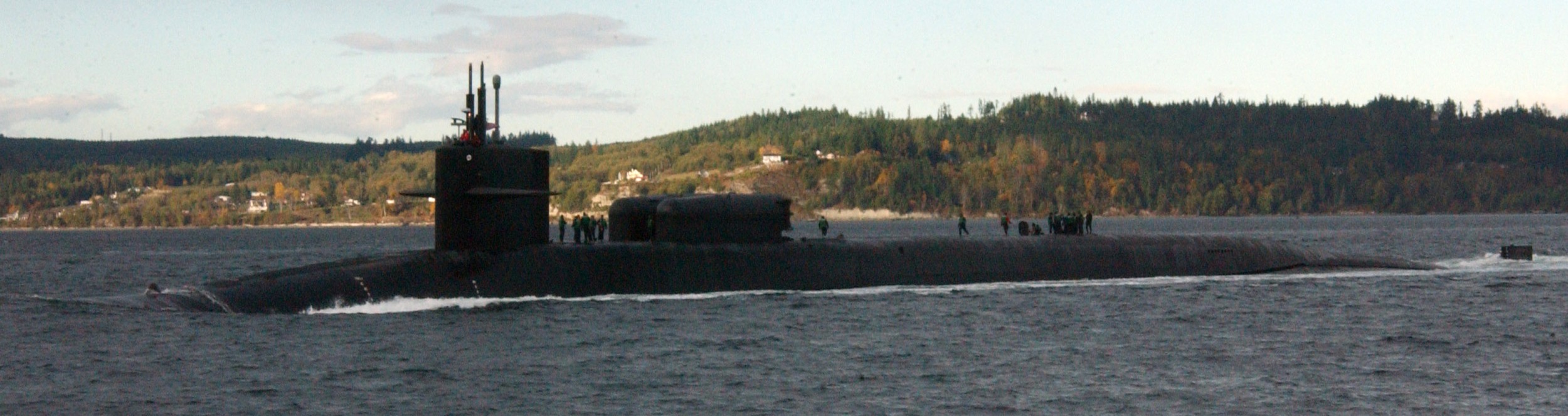  Hood Canal, Washington - October 2006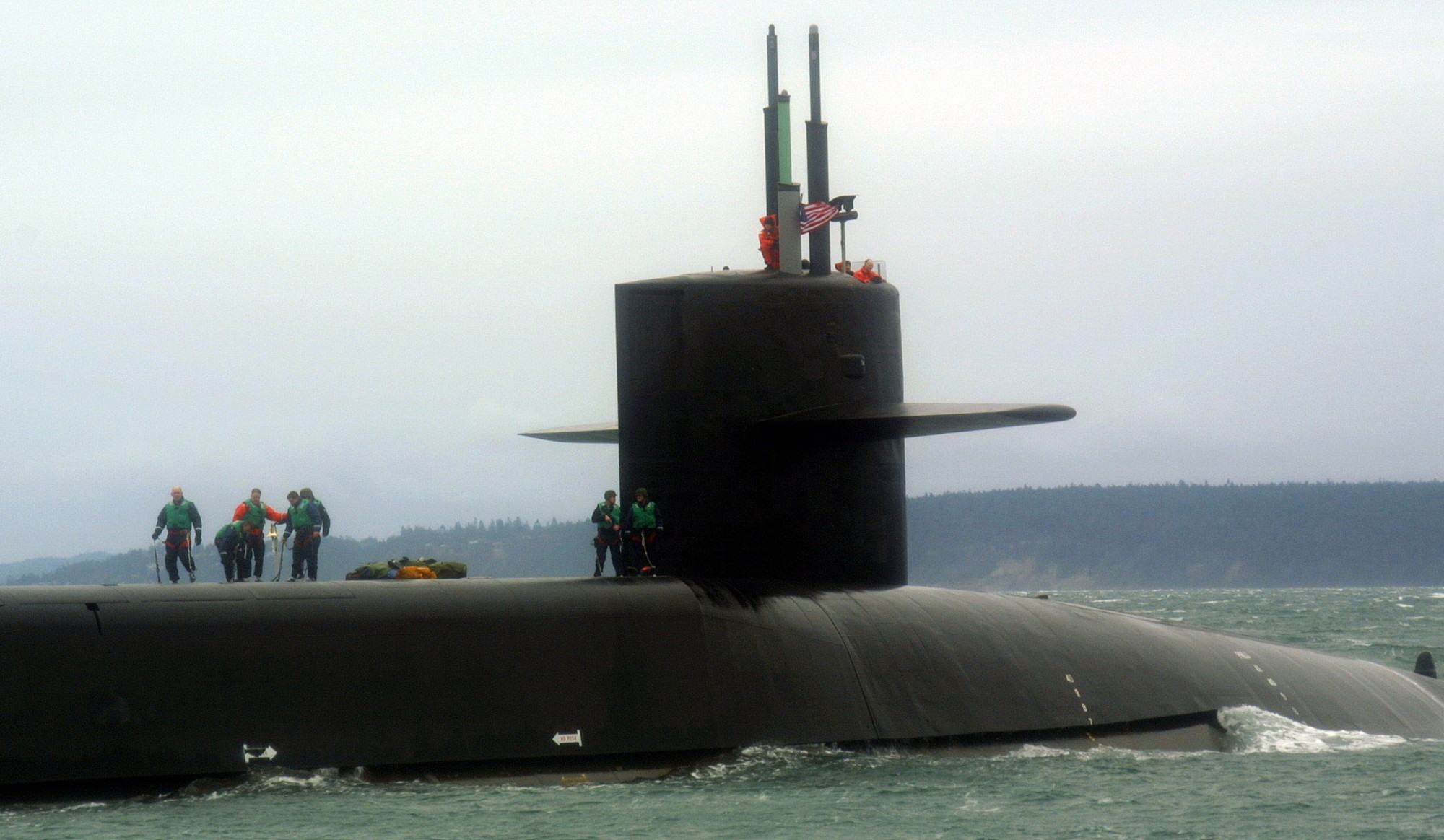  Puget Sound, Washington - January 2006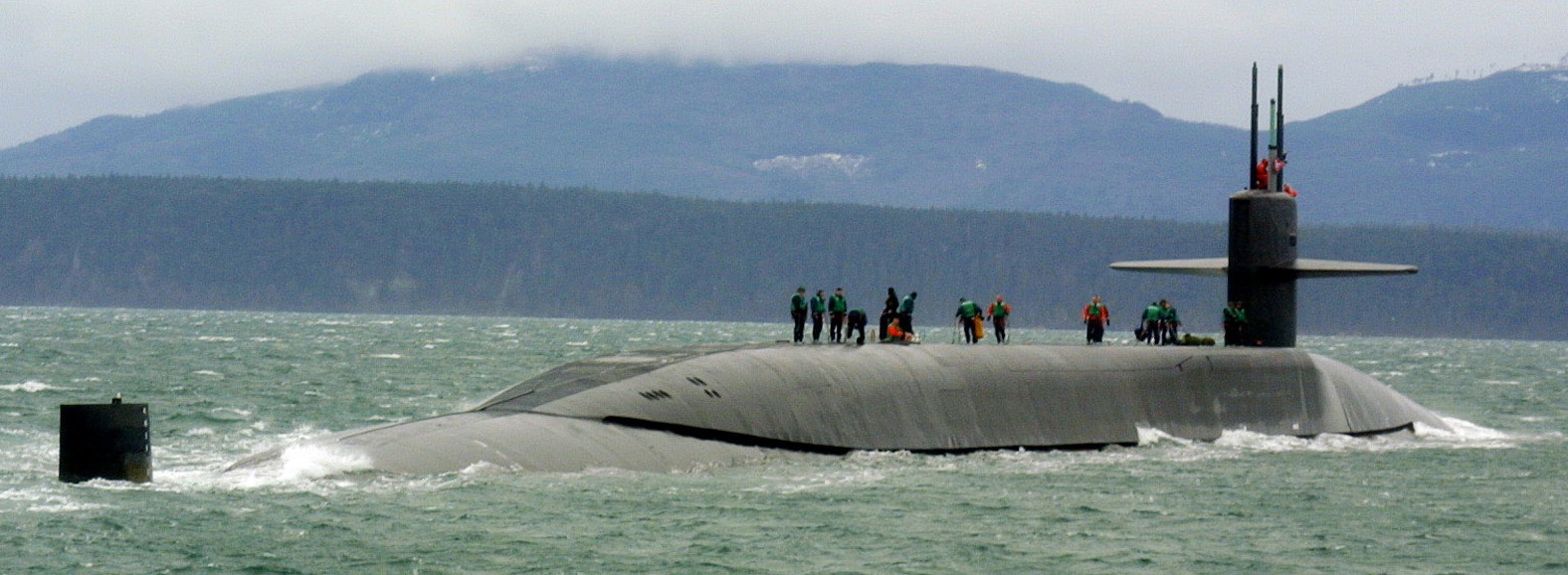  Puget Sound, Washington - January 2006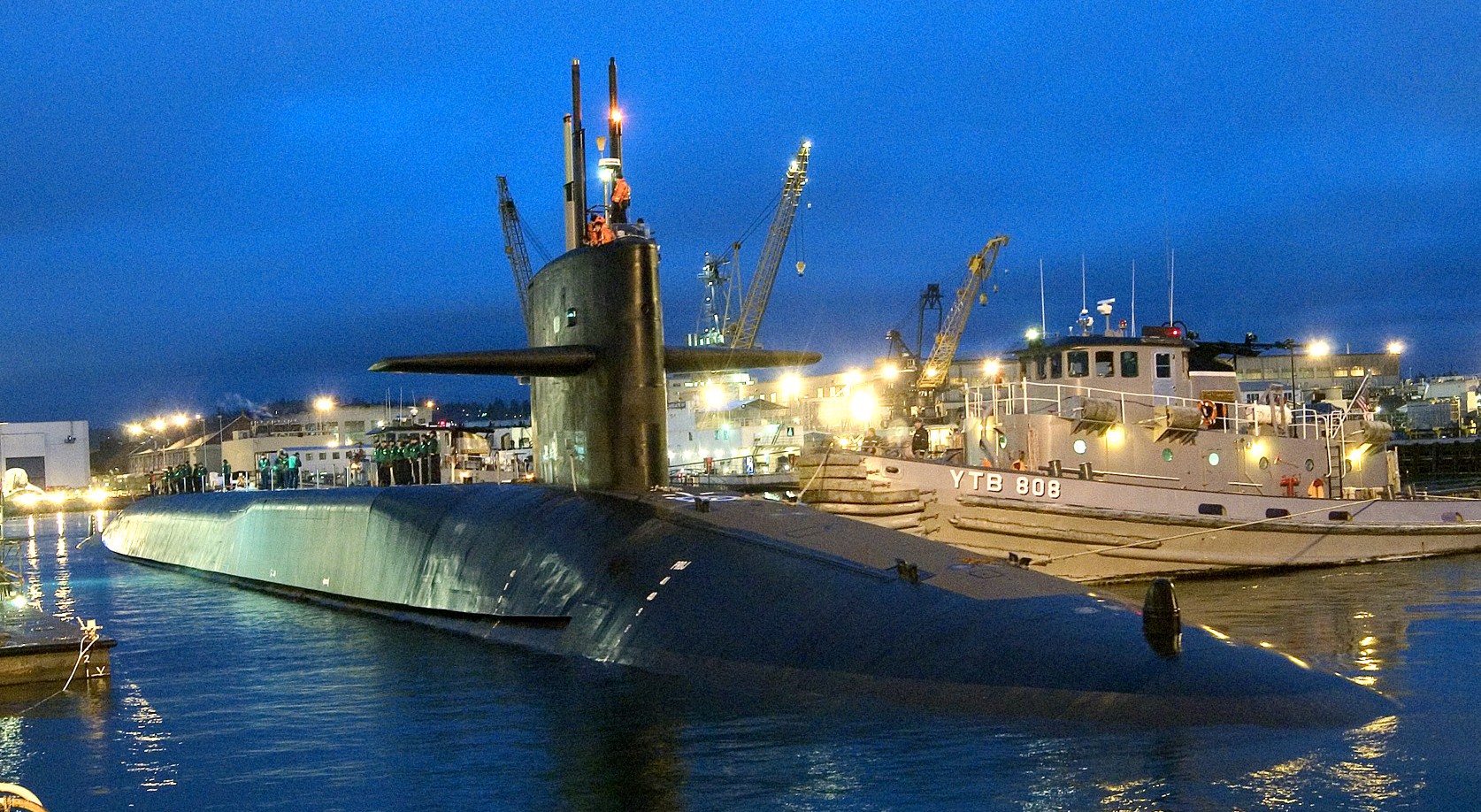  after sea trials following the conversion to a SSGN - Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington - December 2005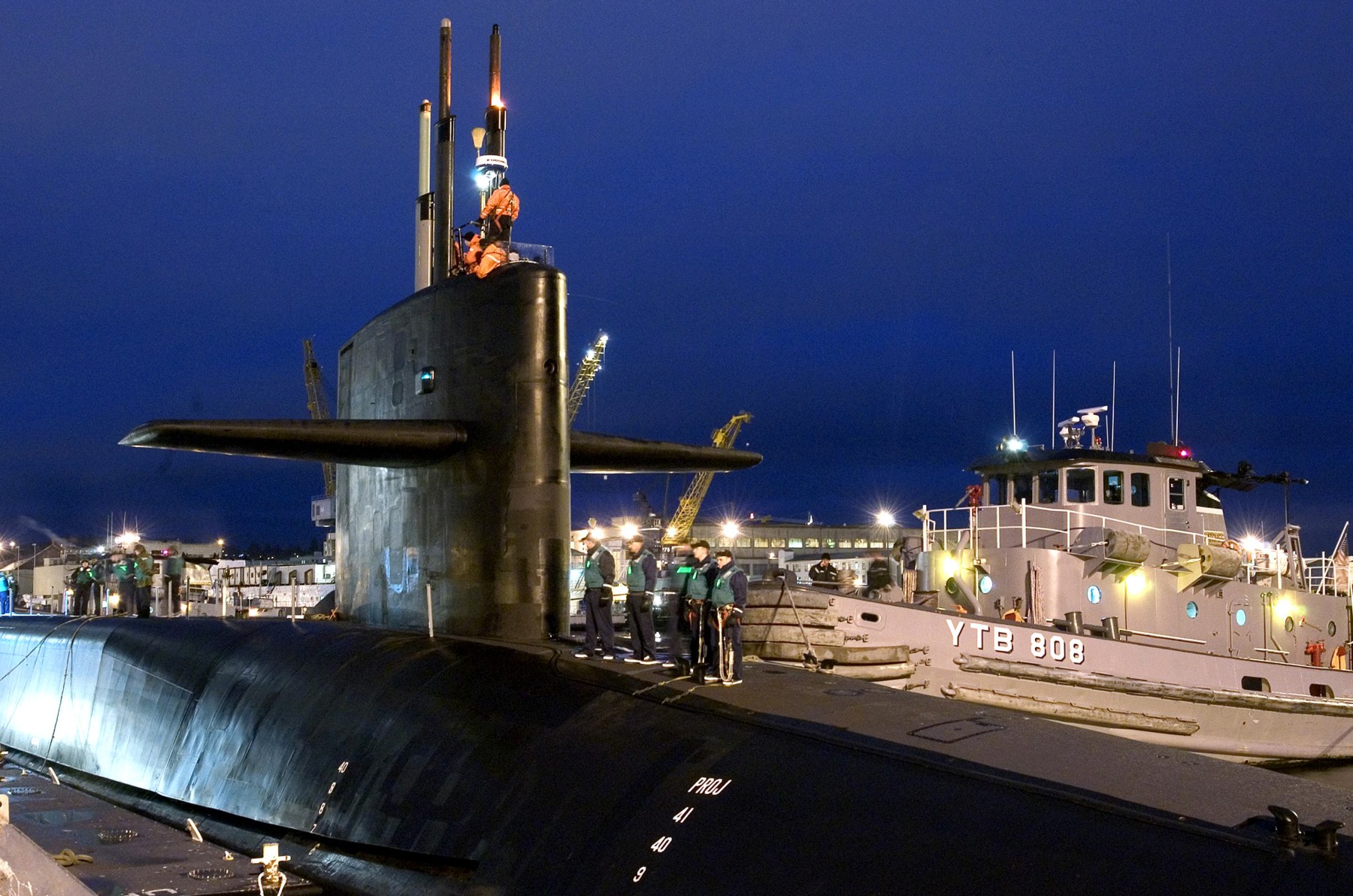  returning to Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), Bremerton, Washington after sea trials following the conversion to an SSGN - December 22, 2005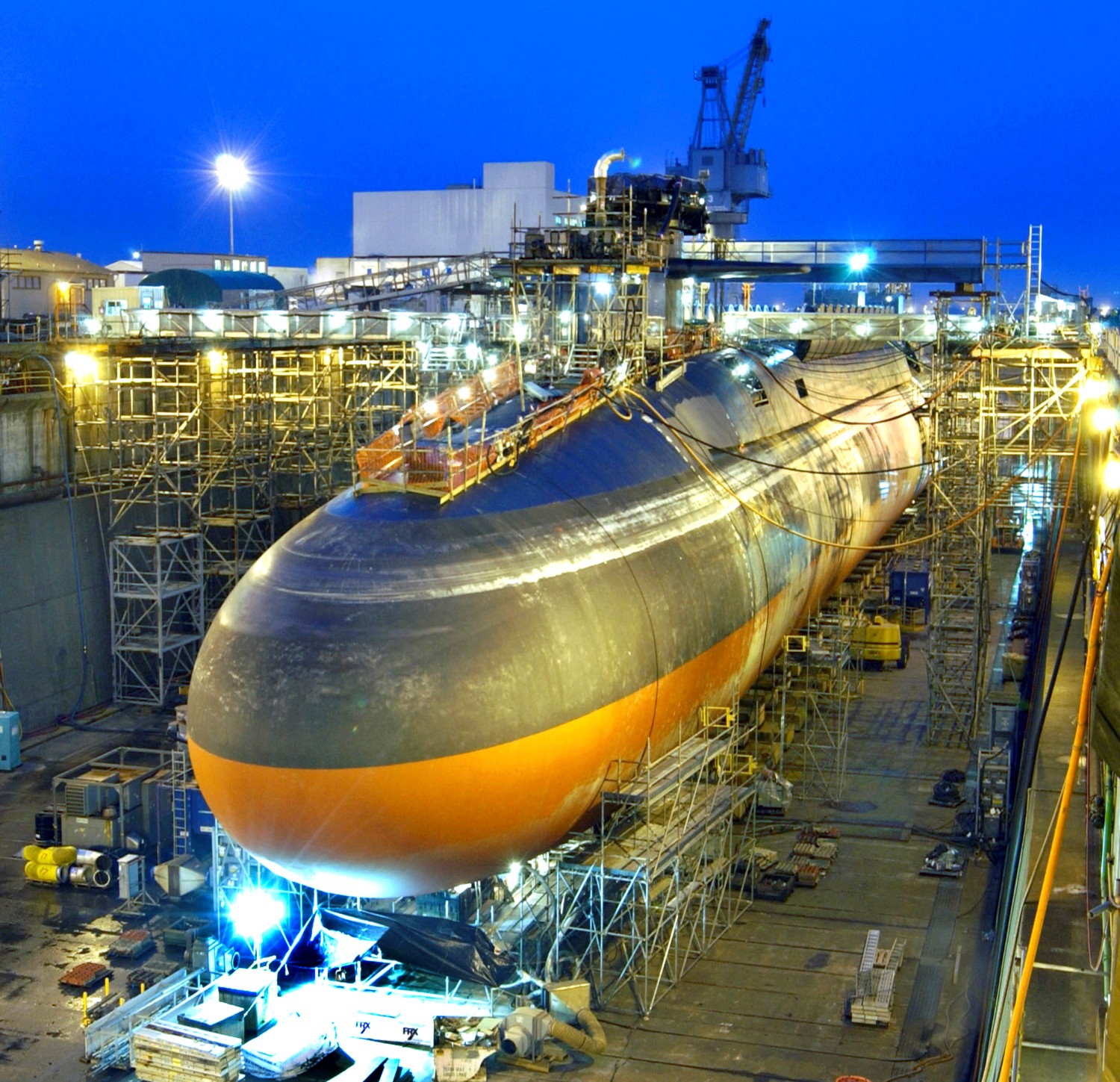  conversion to SSGN in progress at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington - March 2004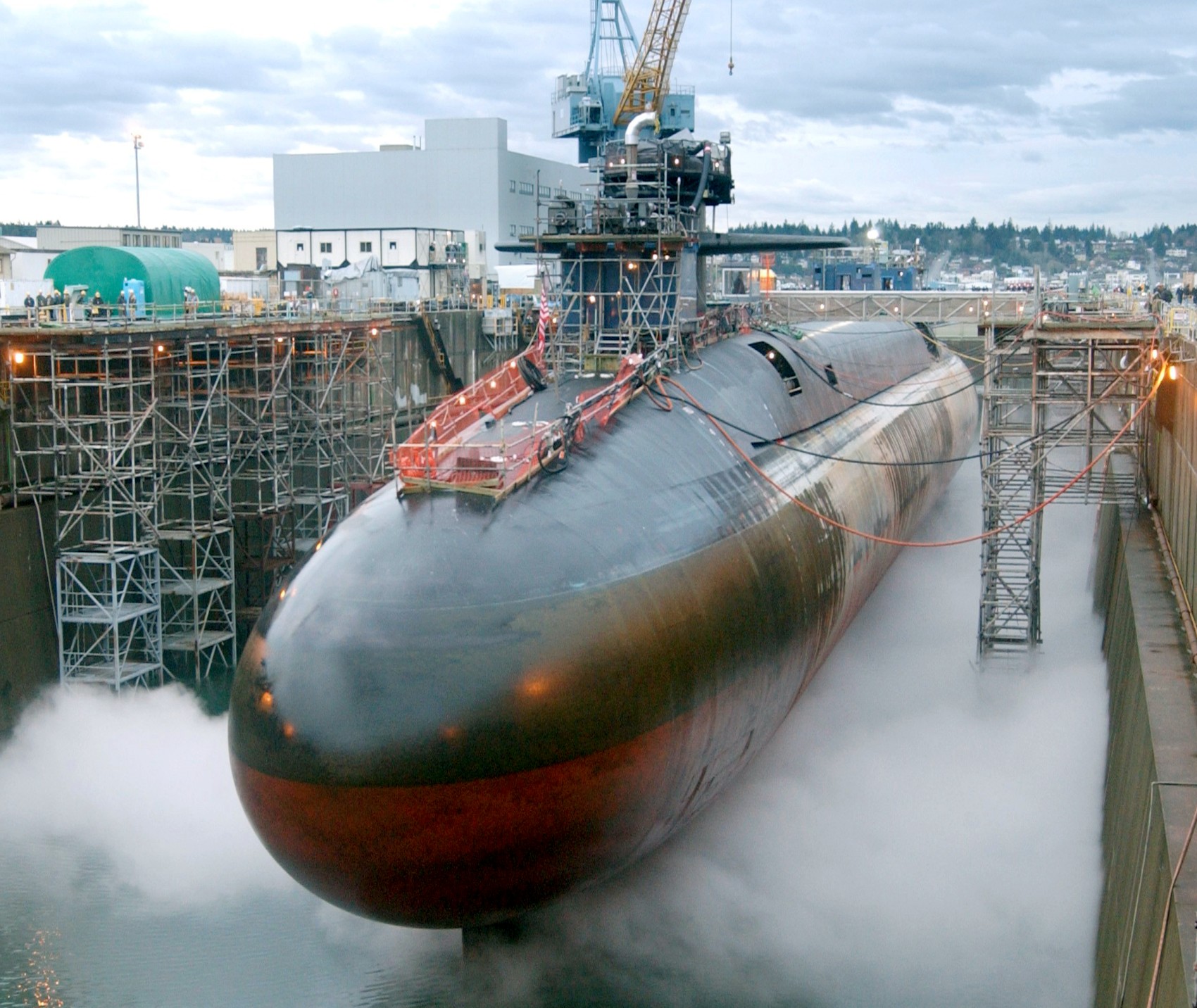  conversion to SSGN in progress at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington - August 2003 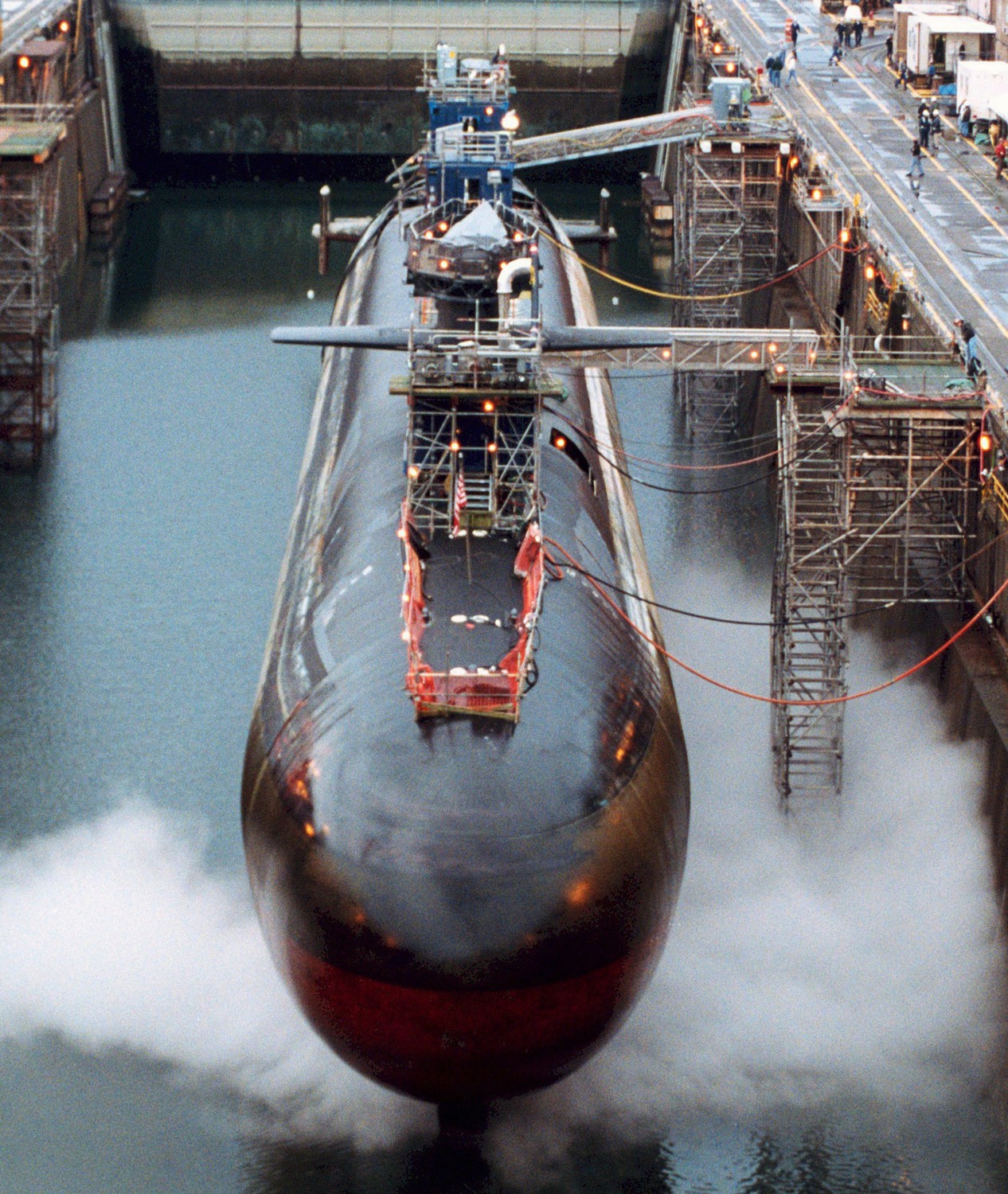 conversion to SSGN in progress at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington - August 2003  SSBN 726 - USS Ohio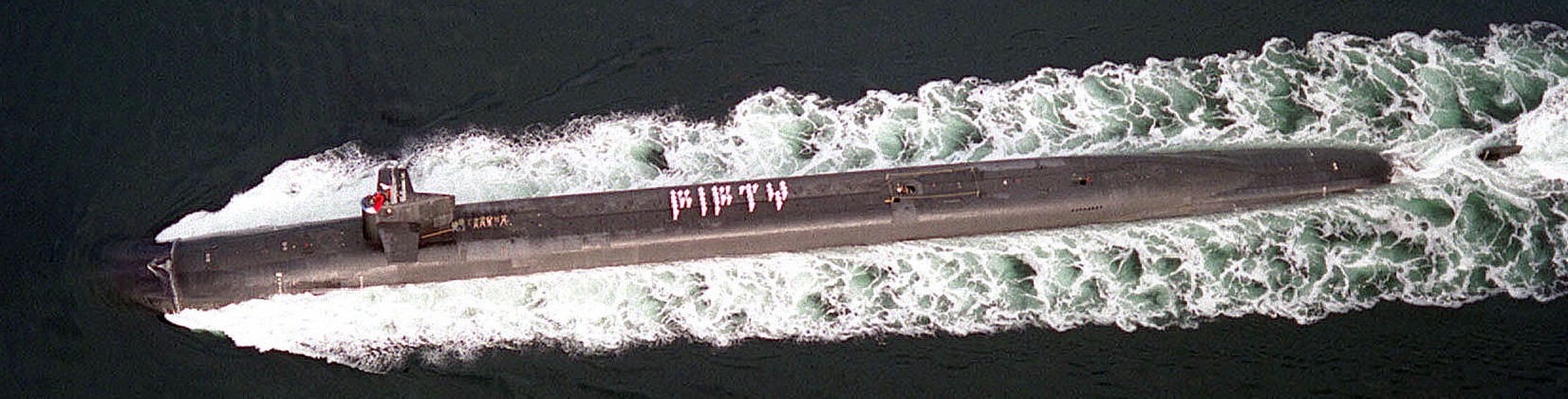  commemorate the completion of a historic 50th strategic patrol - March 12, 1998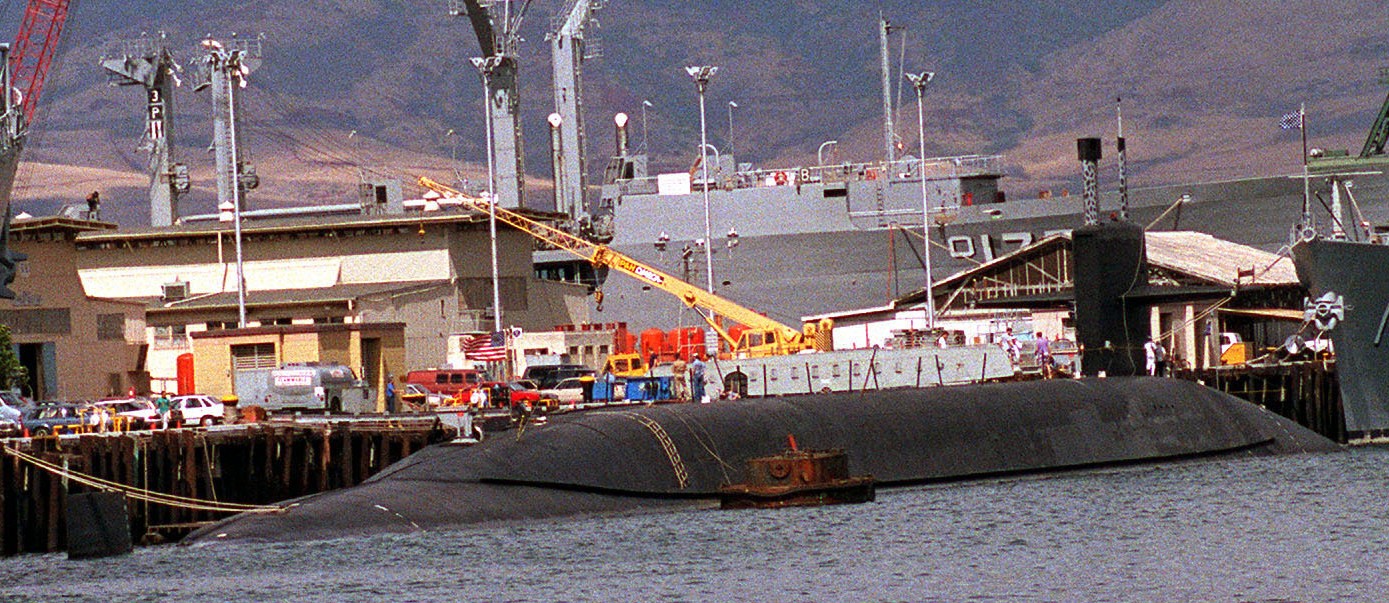  Pearl Harbor, Hawaii - 1989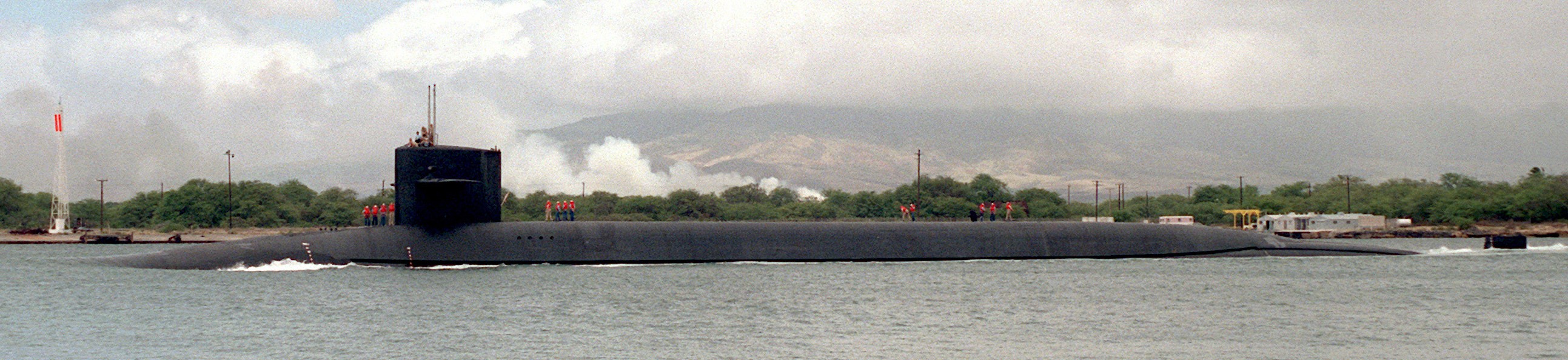  during exercise RIMPAC 86 - June 1986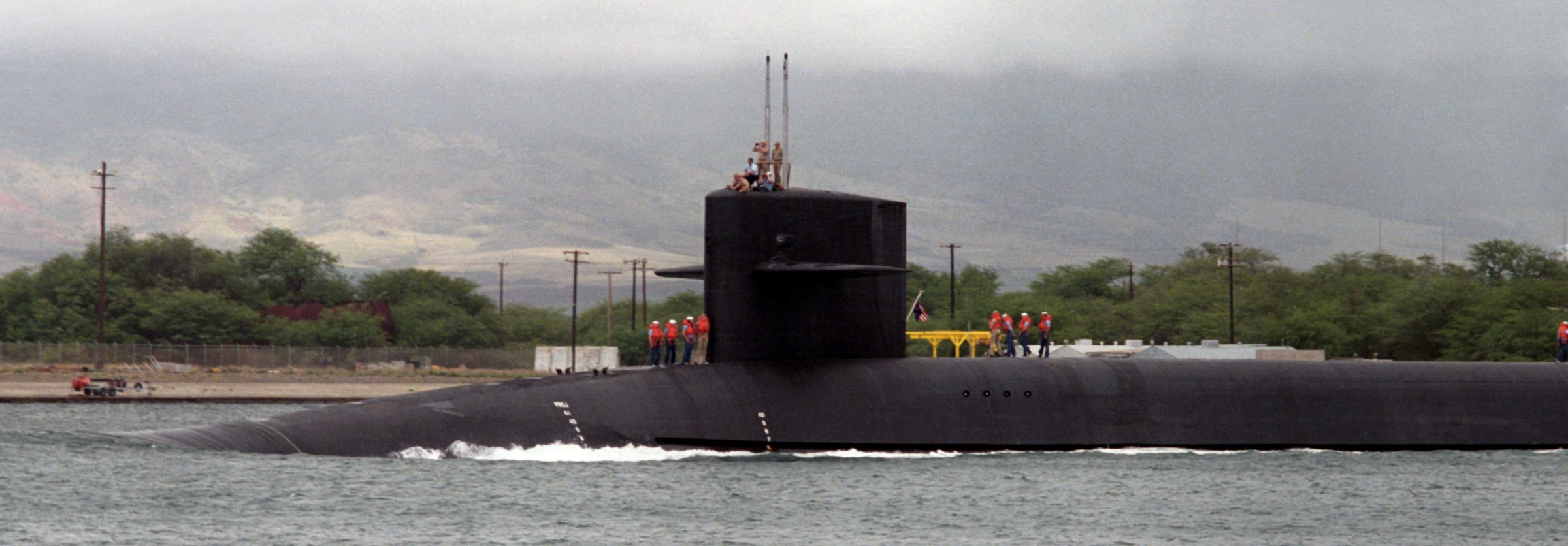  during exercise RIMPAC 86 - June 1986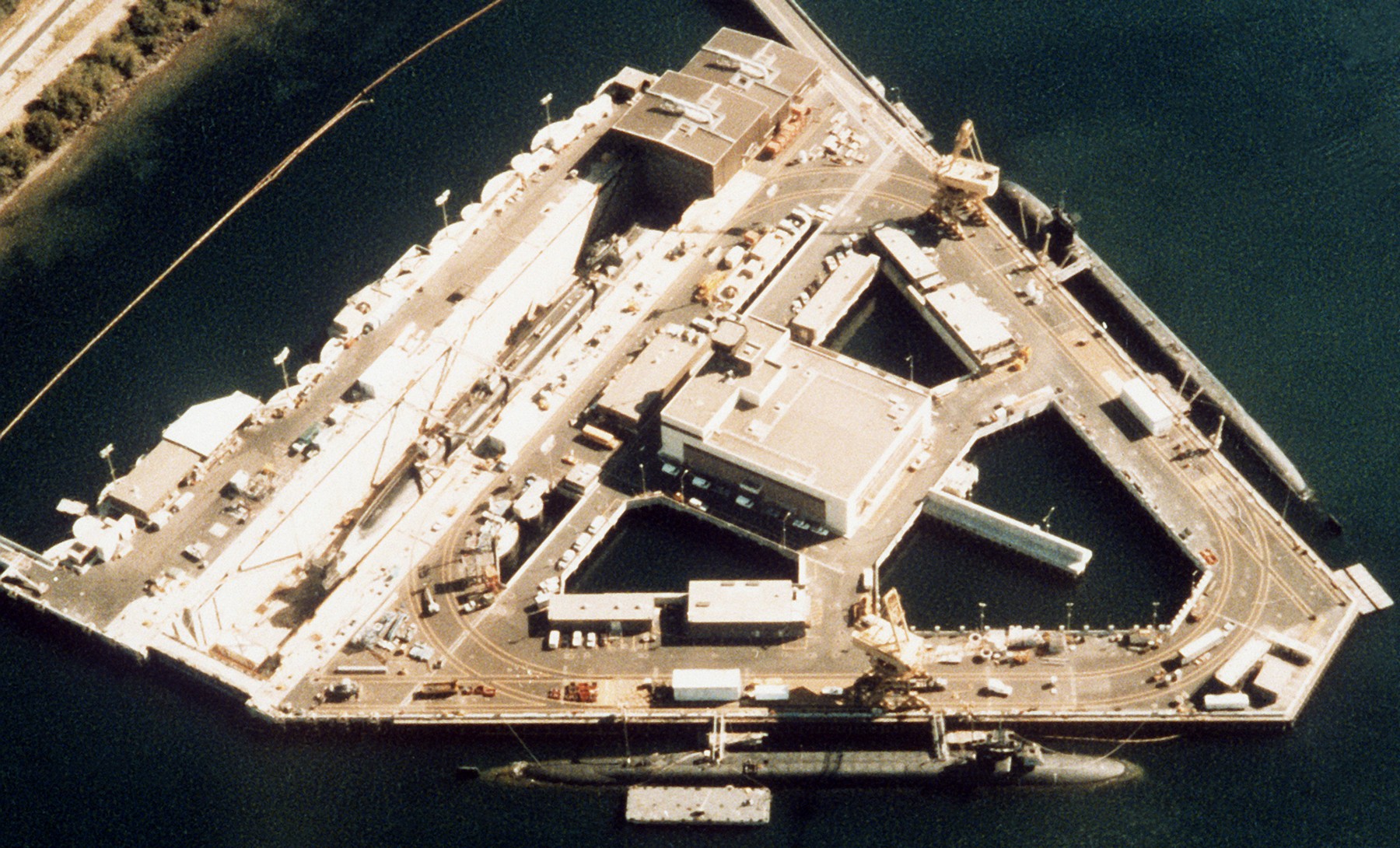  Delta Pier at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1985 bottom: USS Henry M. Jackson (SSBN 730) / right: USS Ohio (SSBN 726) / in dry-dock: USS Florida (SSBN 728)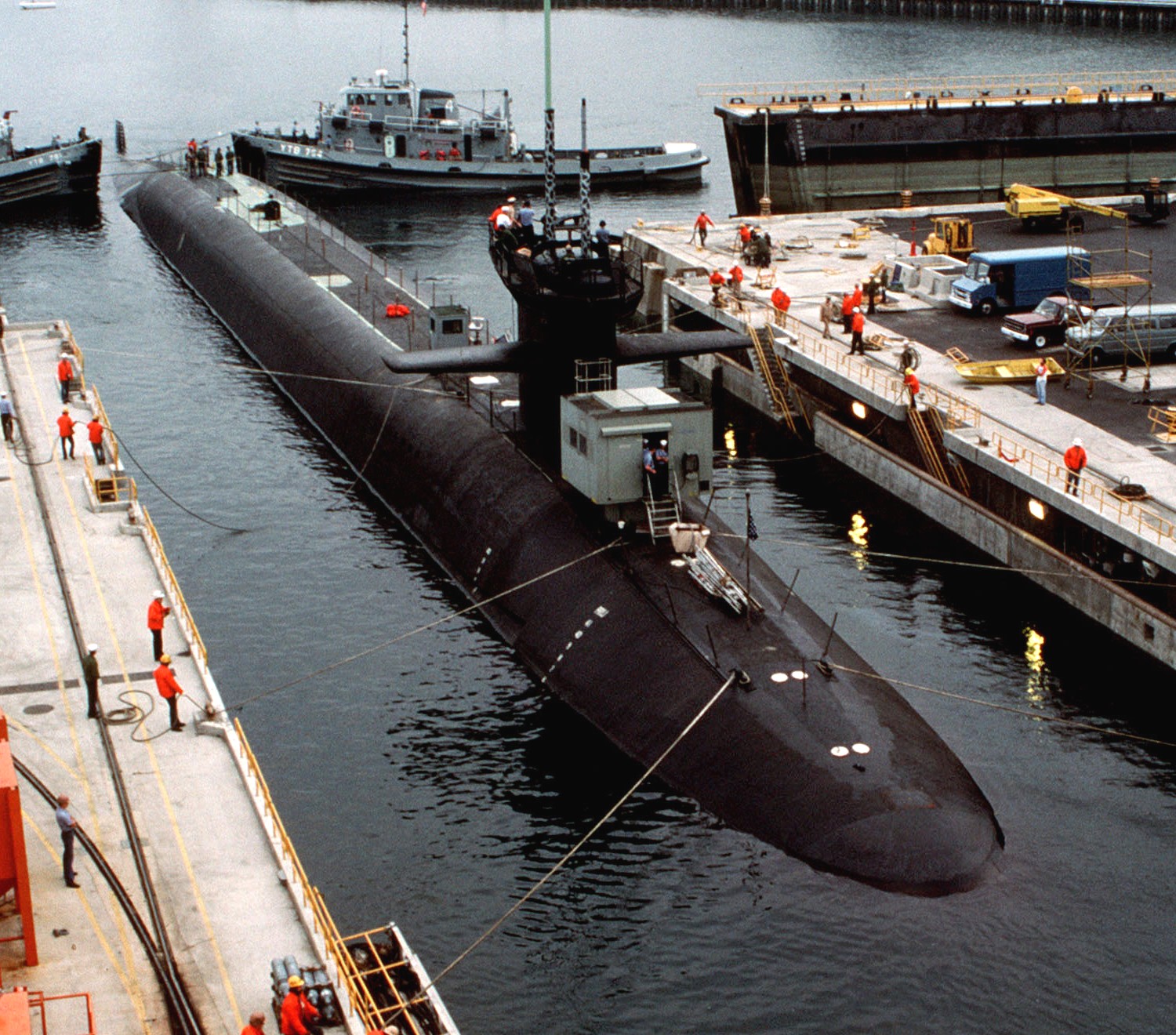  Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1983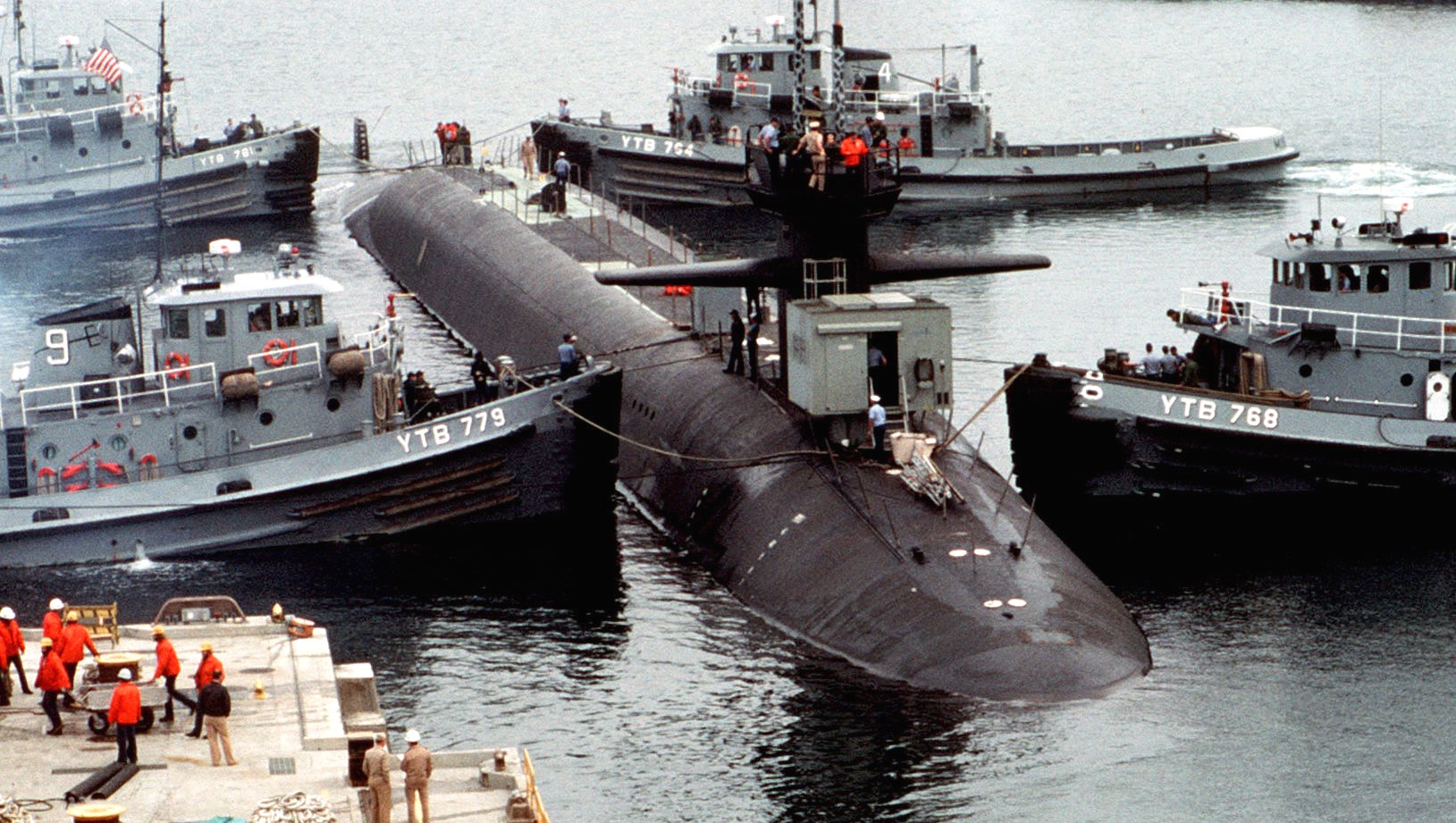  Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1983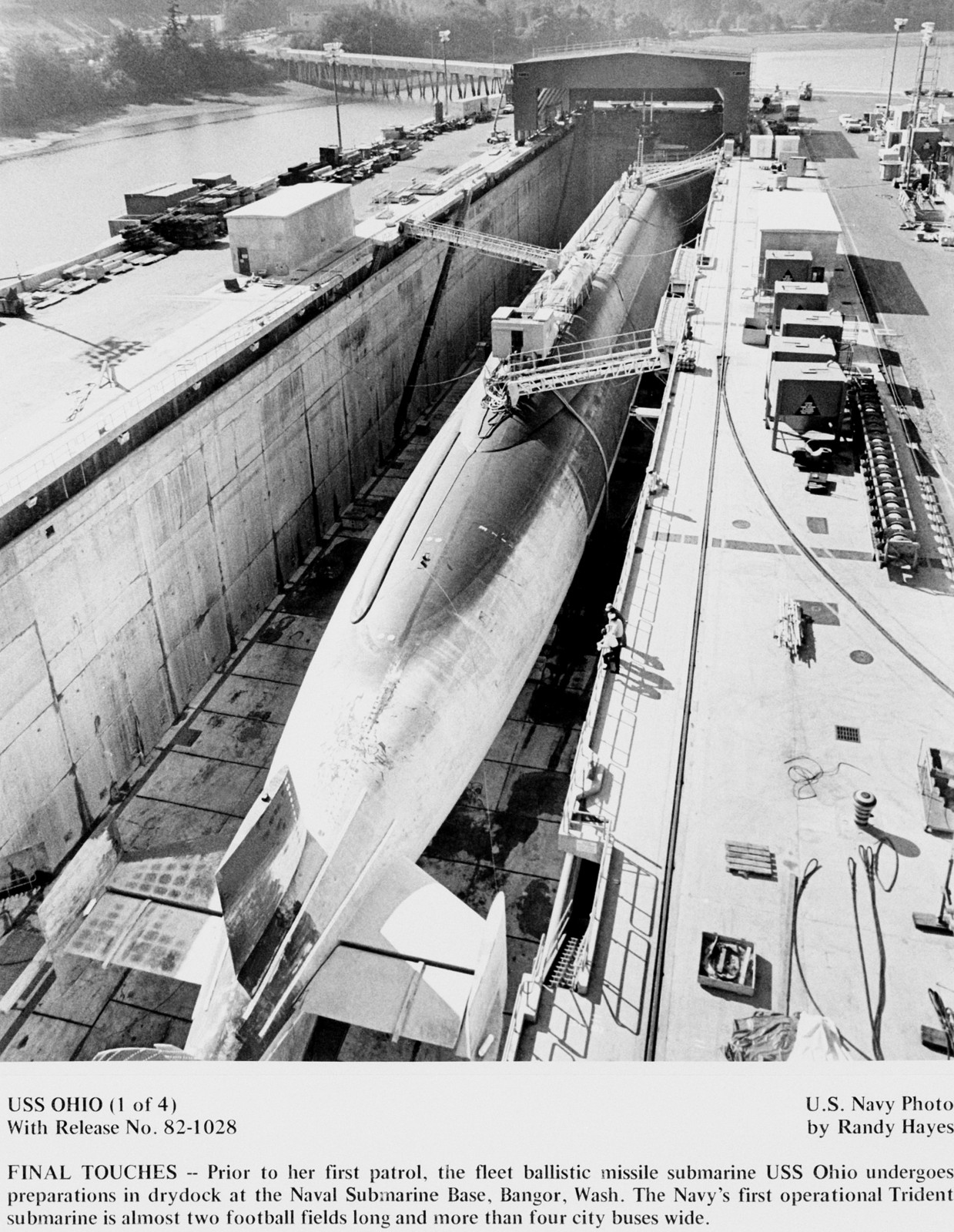  March 1983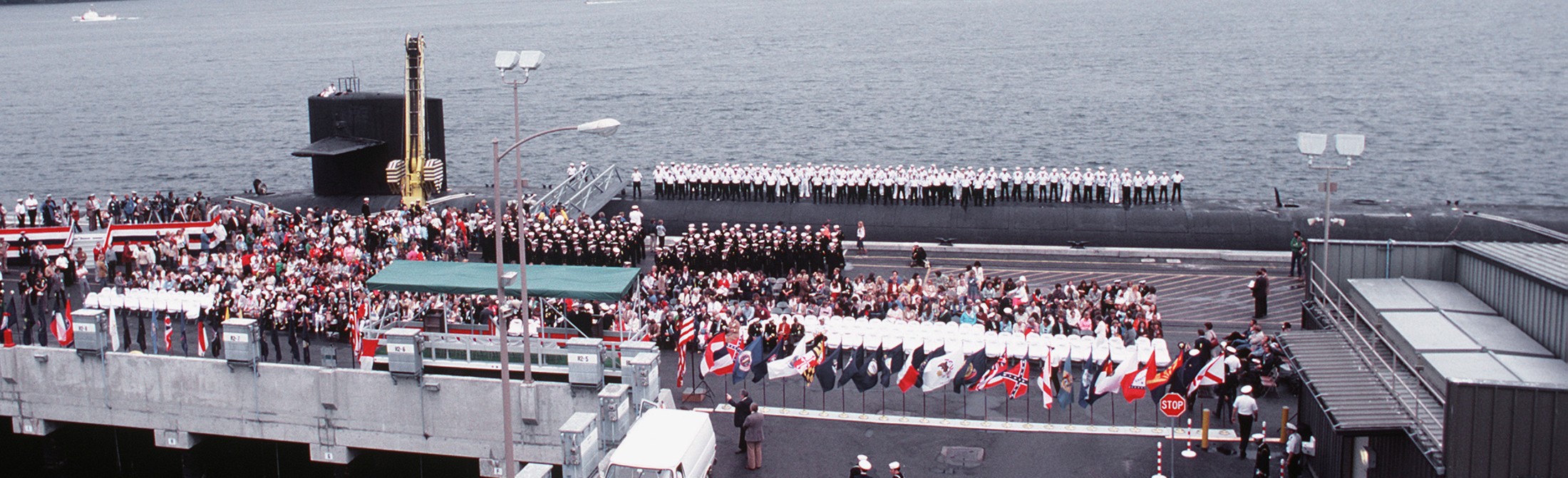  welcoming ceremony at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982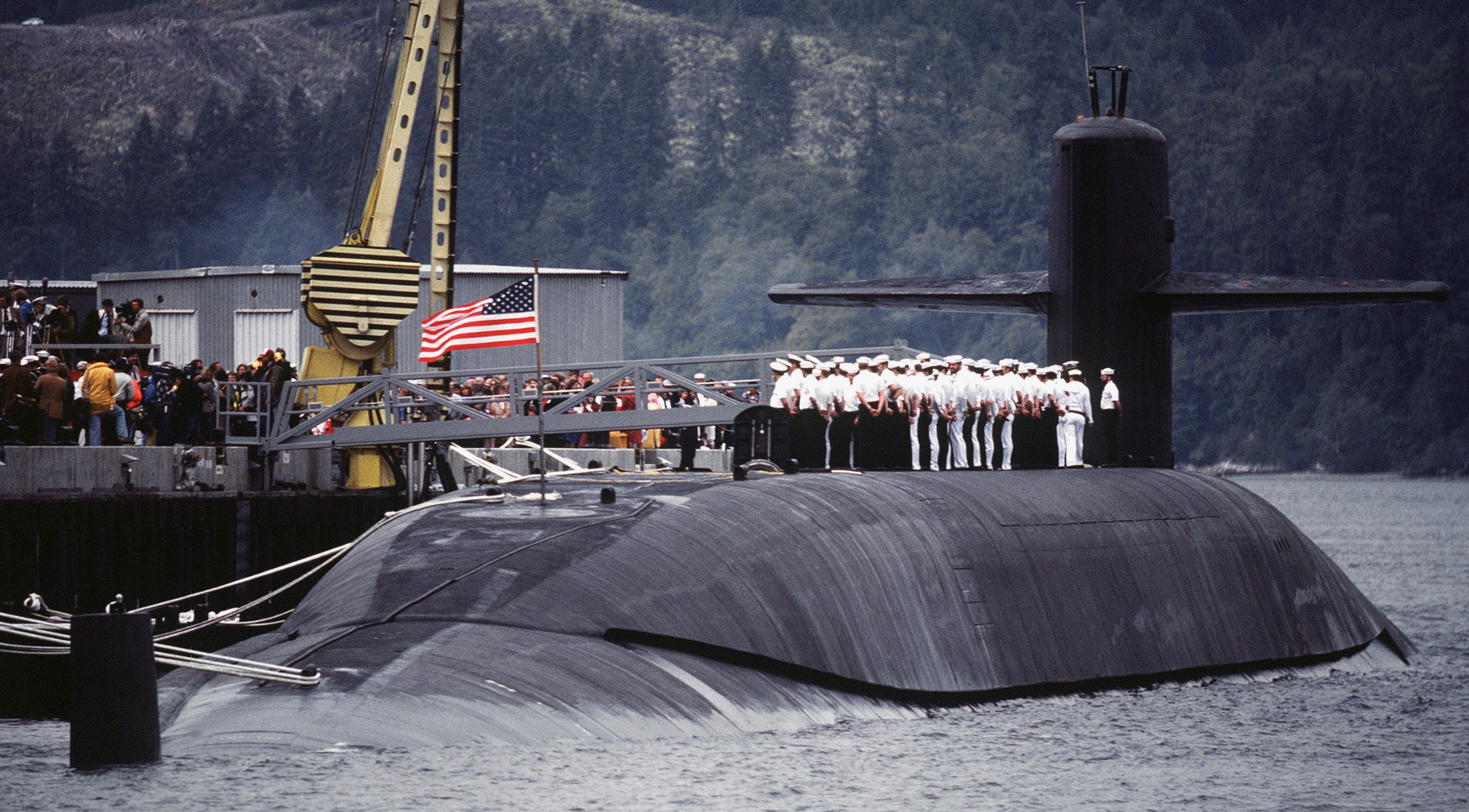  welcoming ceremony at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982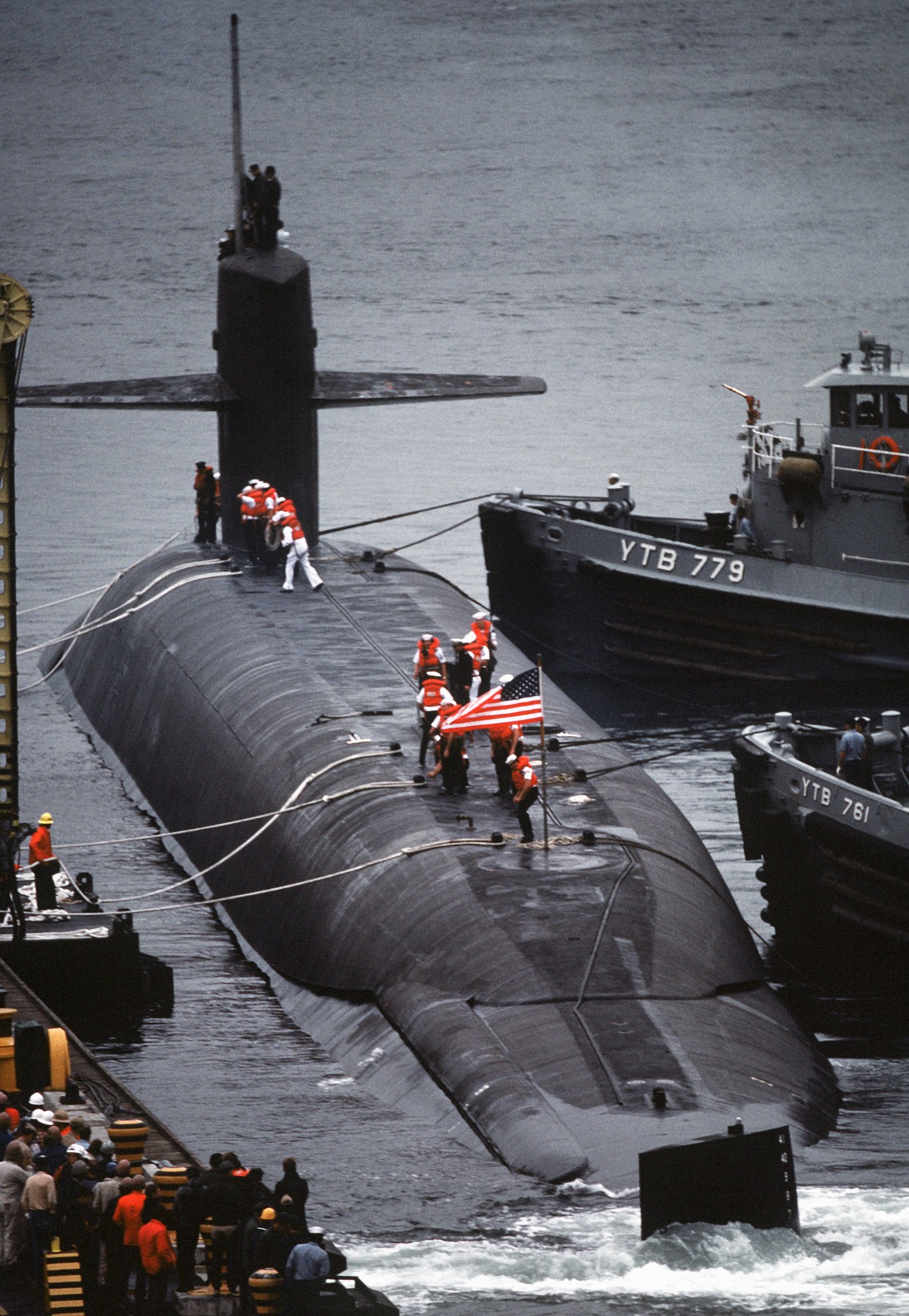  arriving at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982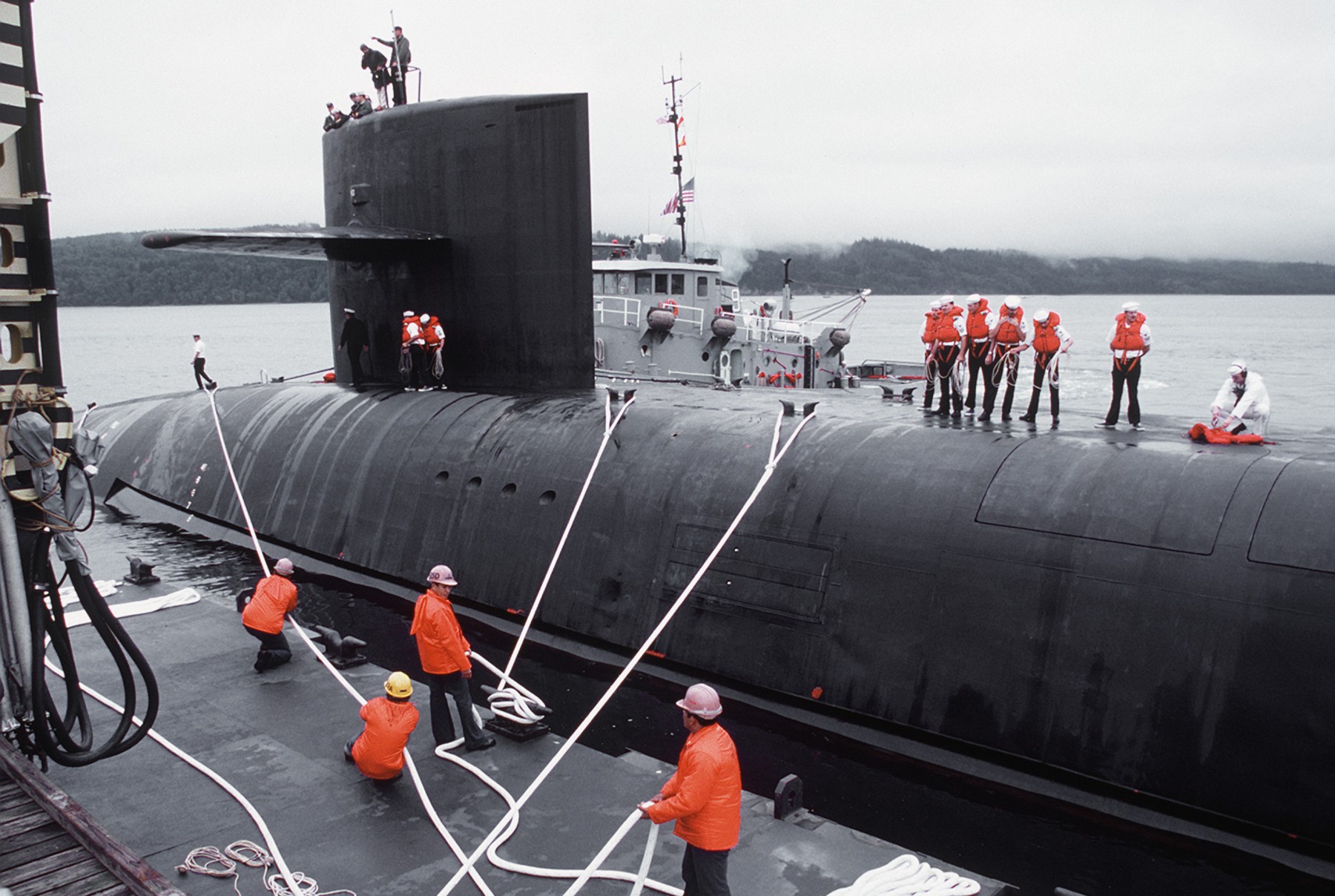  arriving at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982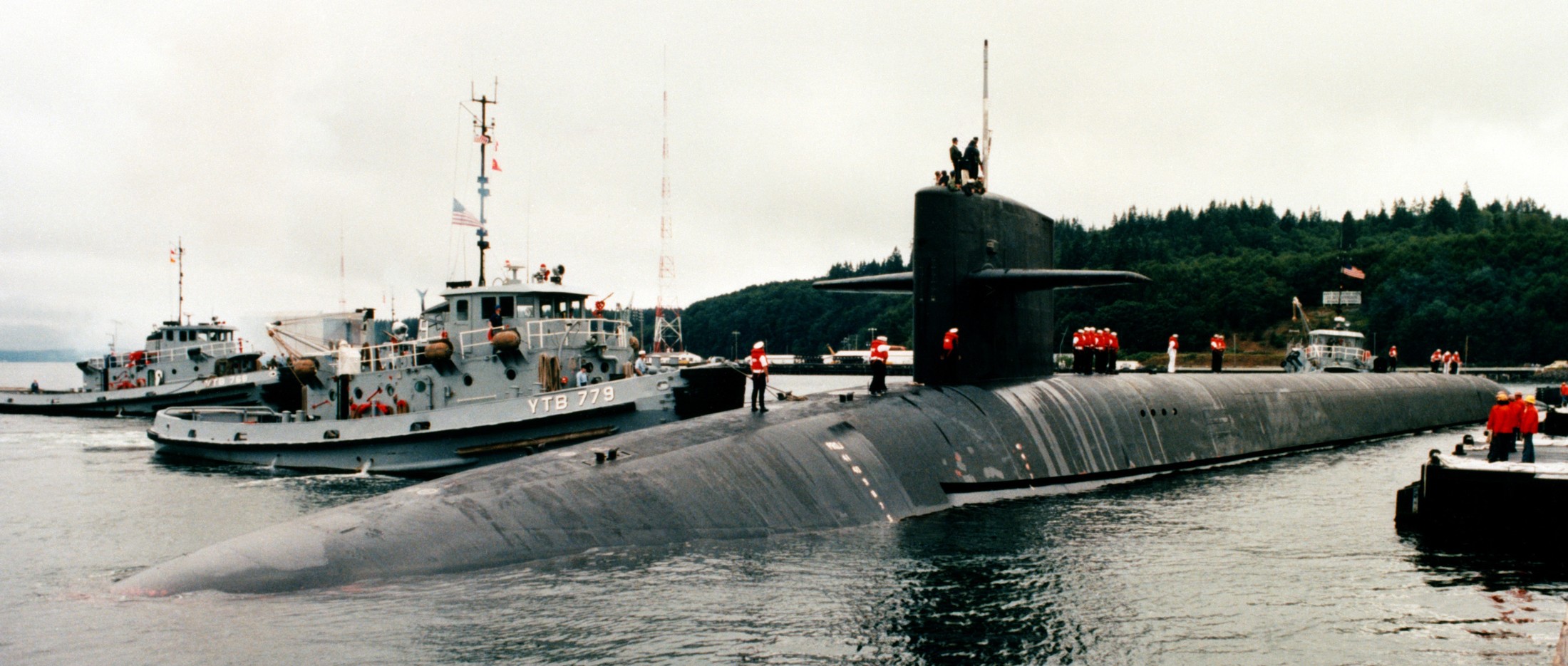  arriving at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982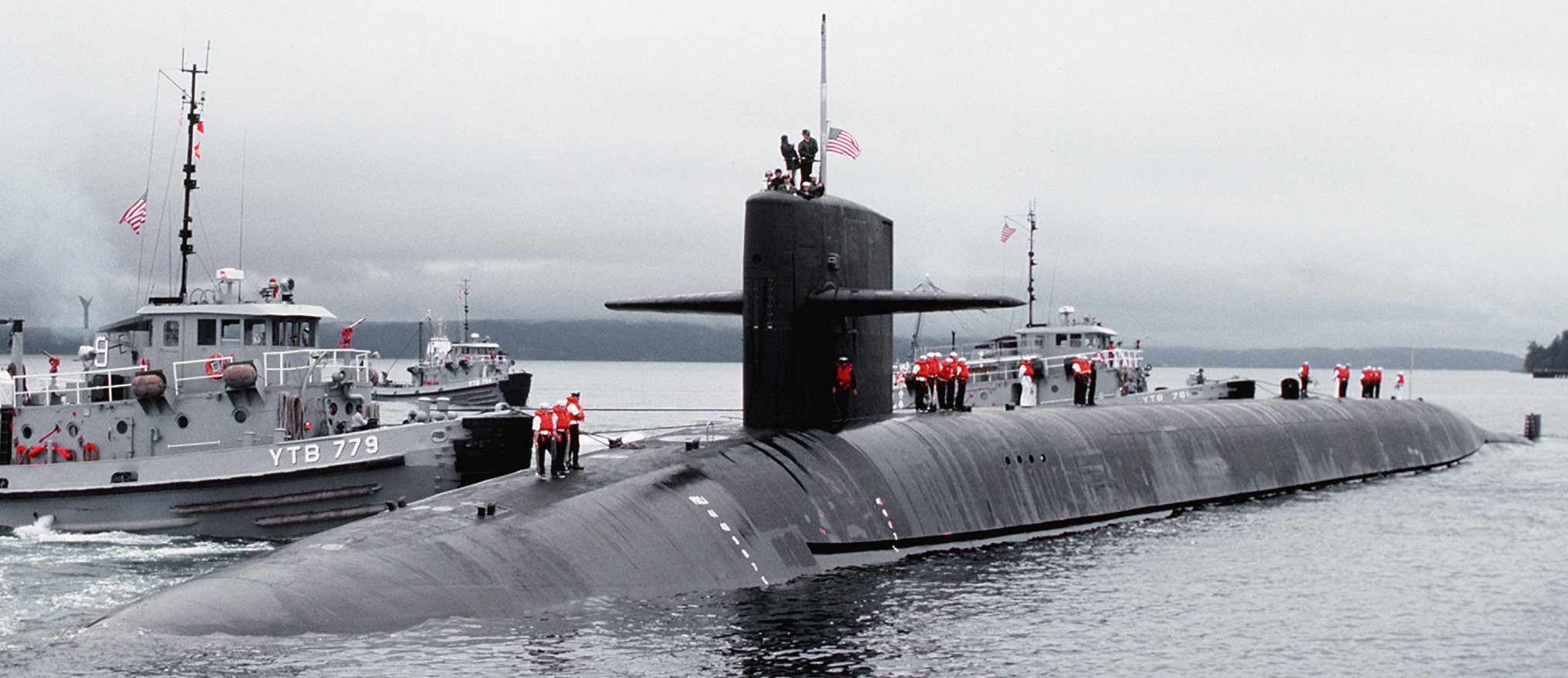  arriving at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982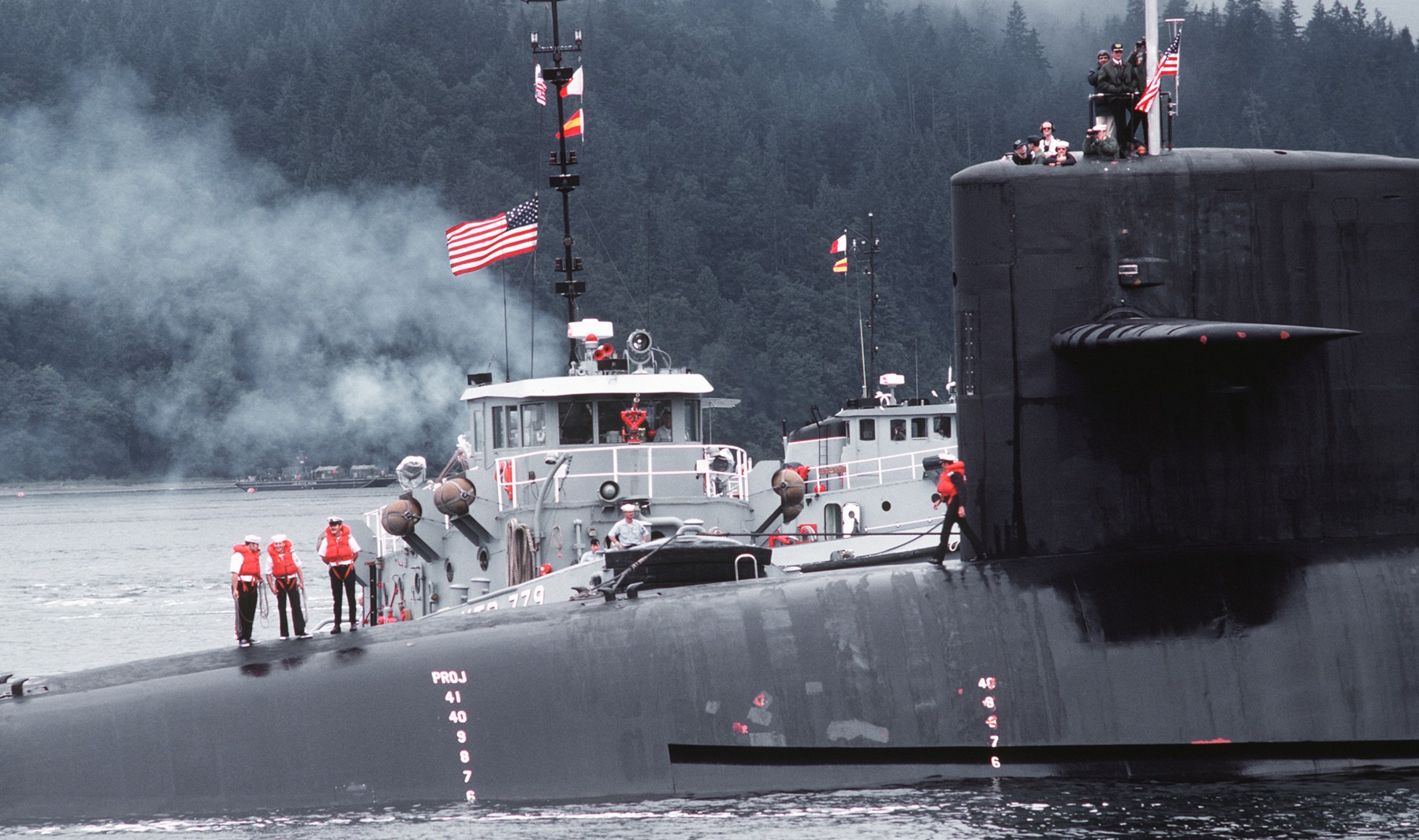  arriving at Naval Submarine Base Bangor, Washington - August 1982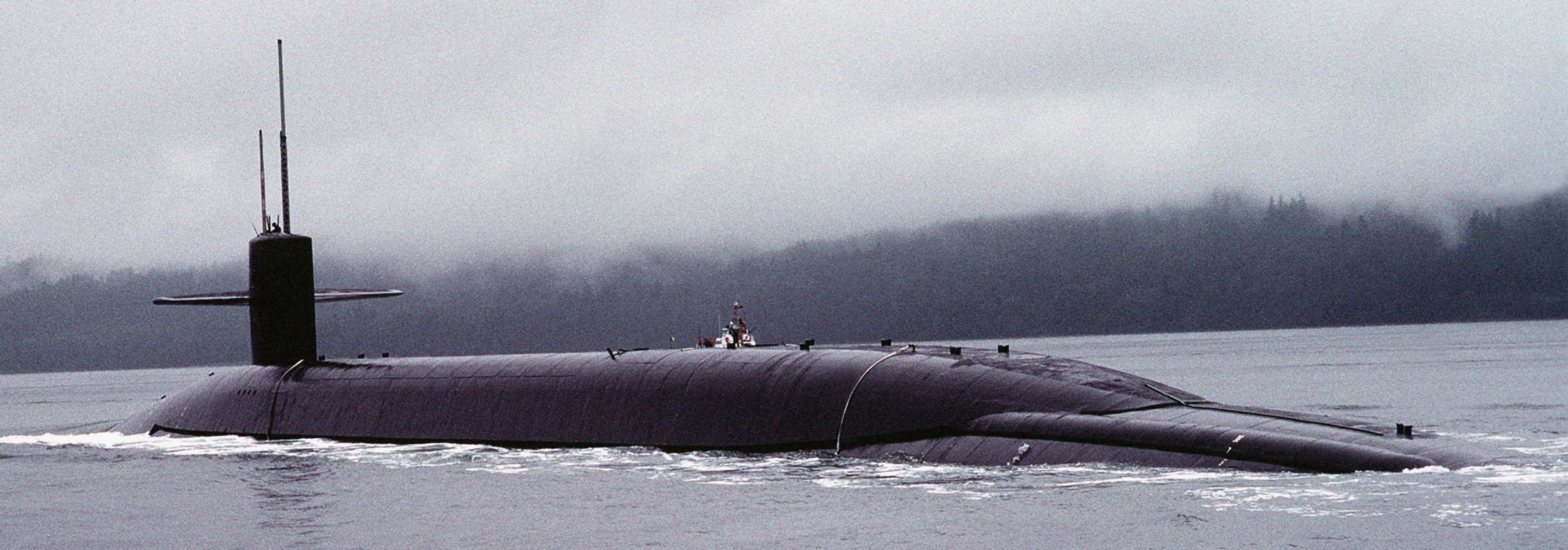  Hood Canal, Washington - August 1982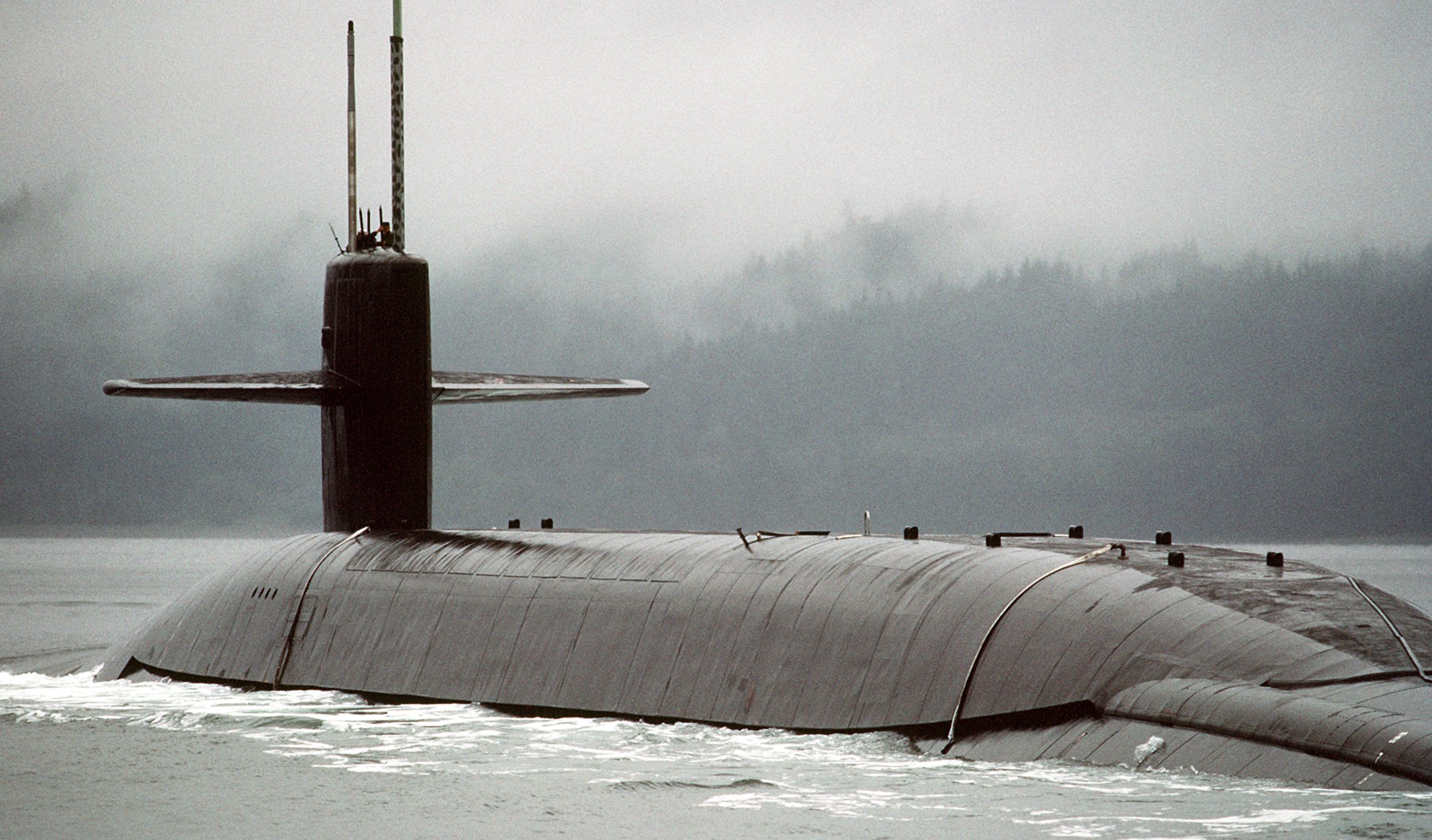  Hood Canal, Washington - August 1982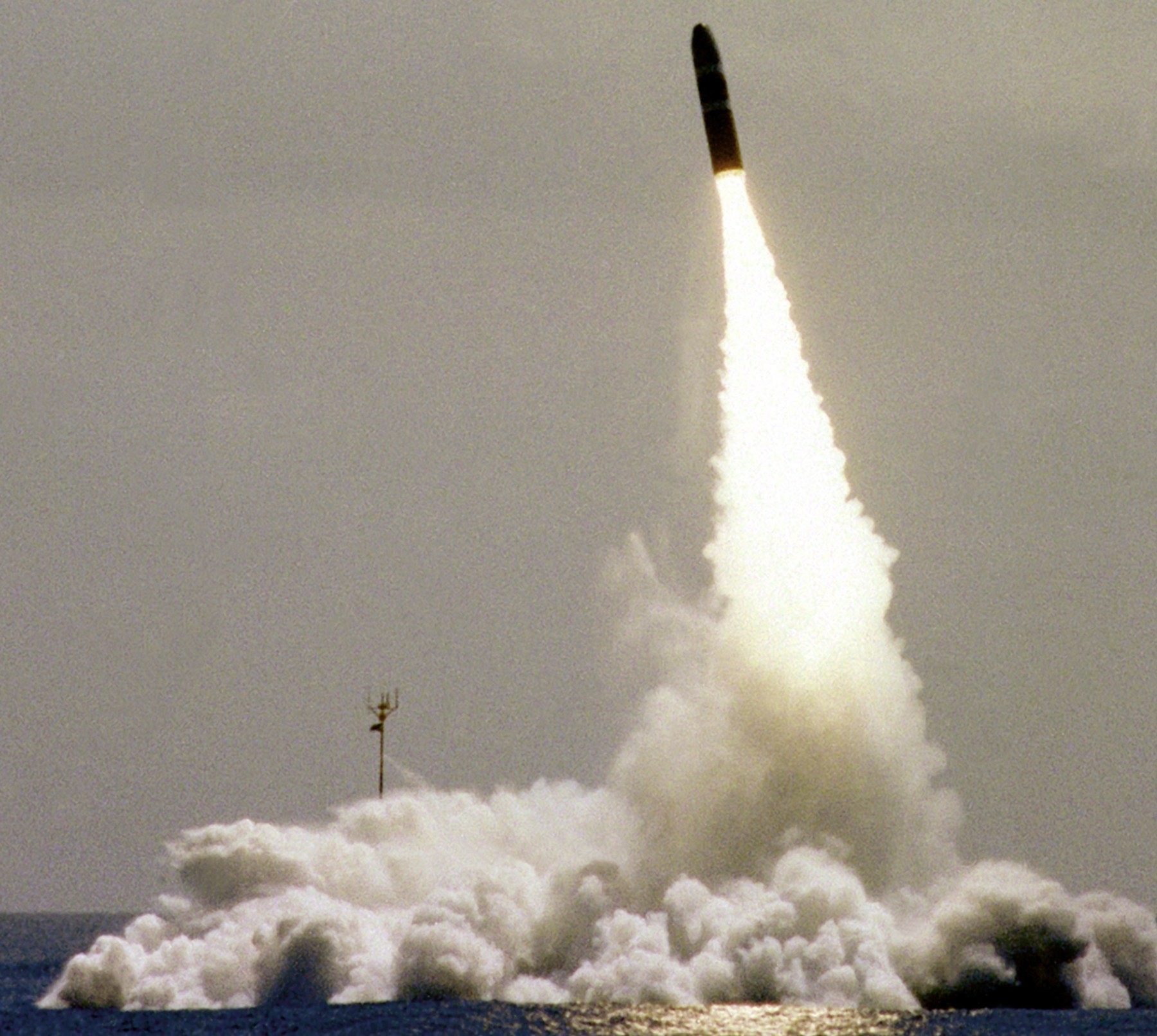  an UGM-96 Trident I C4 ballistic missile (SLBM) was launched from USS Ohio - 1982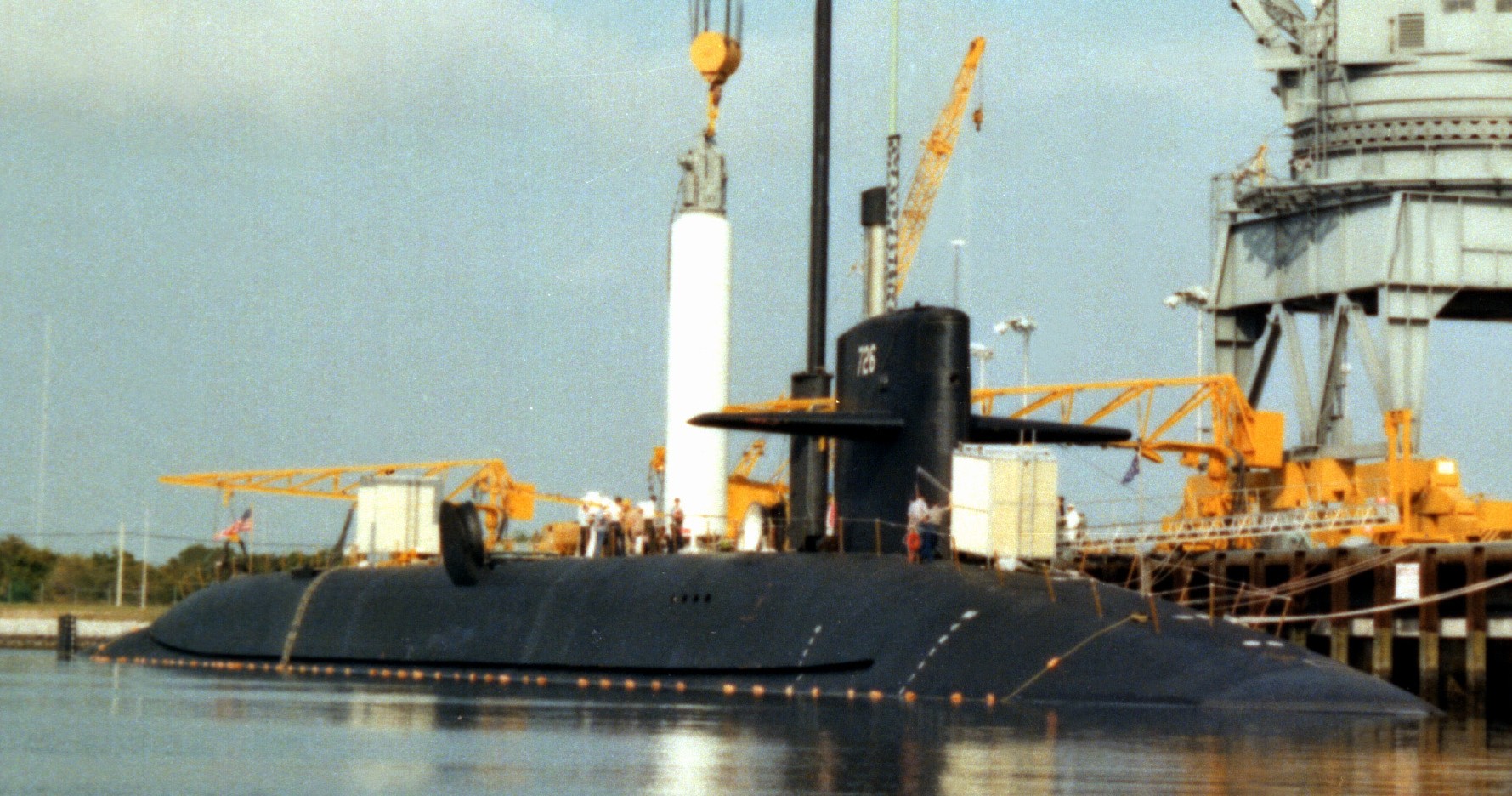  an UGM-96 Trident I C4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) was loaded into USS Ohio - 1982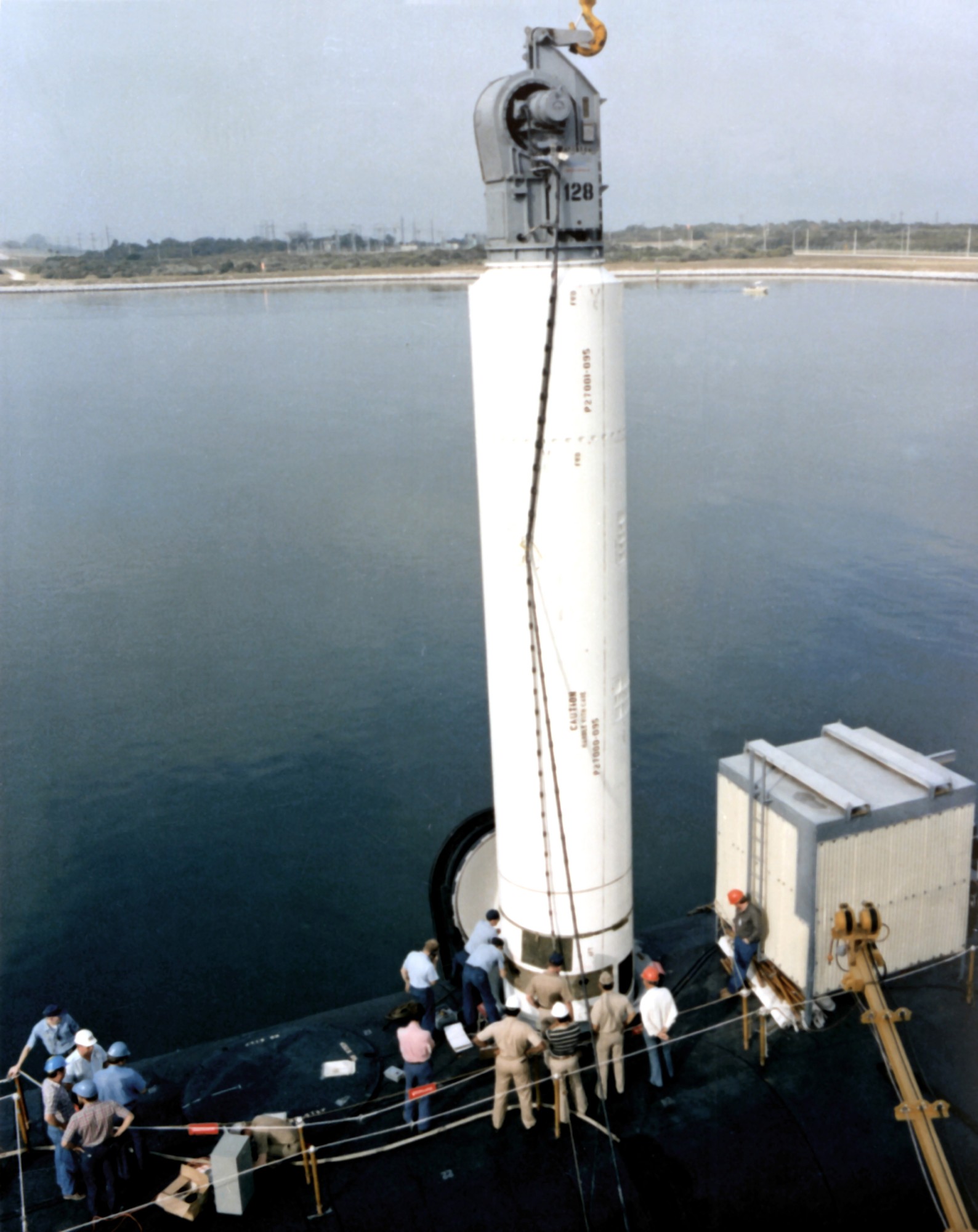  an UGM-96 Trident I C4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) was loaded into USS Ohio - 1982  an UGM-96 Trident I C4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) was loaded into USS Ohio - 1982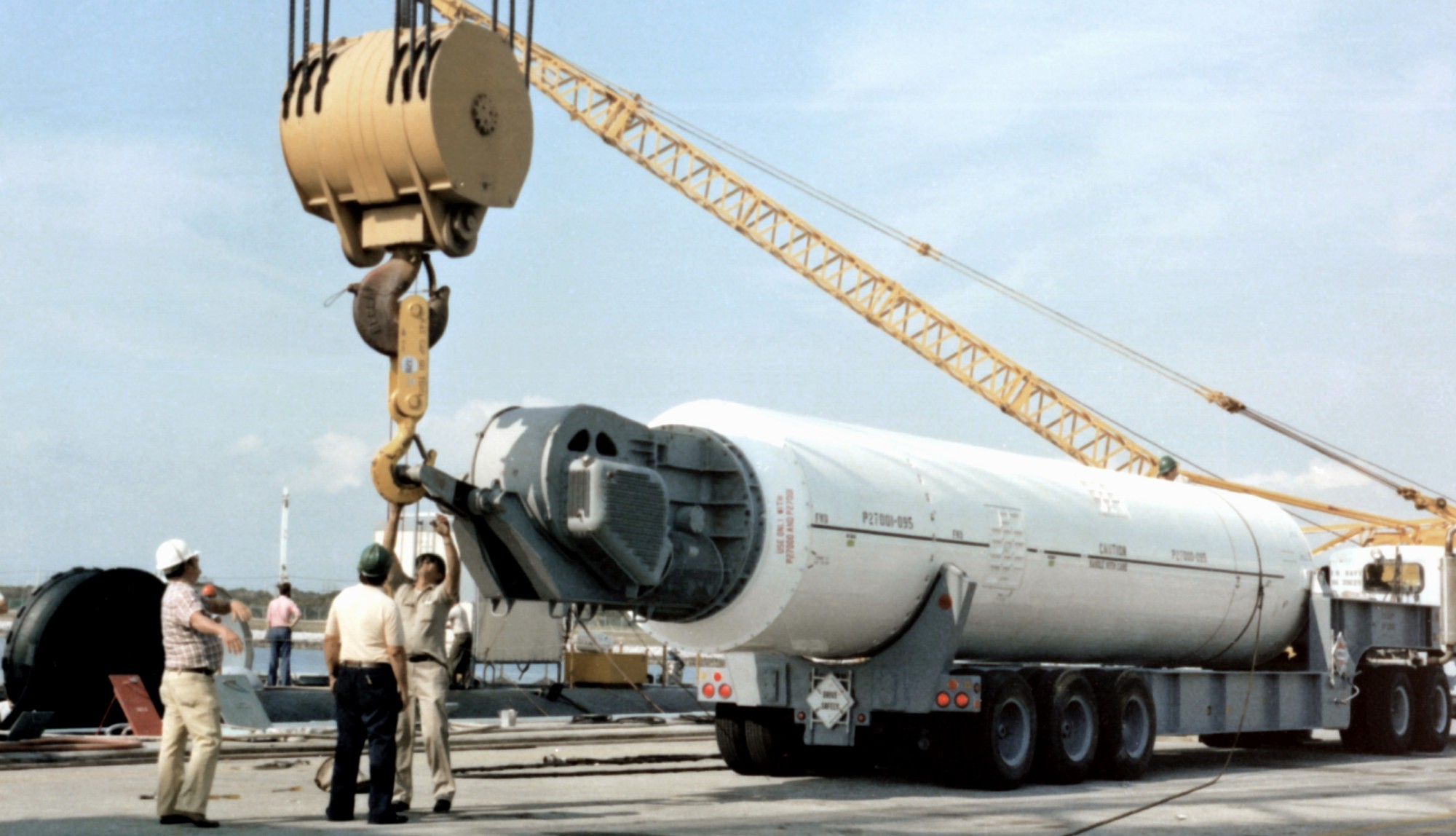  an UGM-96 Trident I C4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) was loaded into USS Ohio - 1982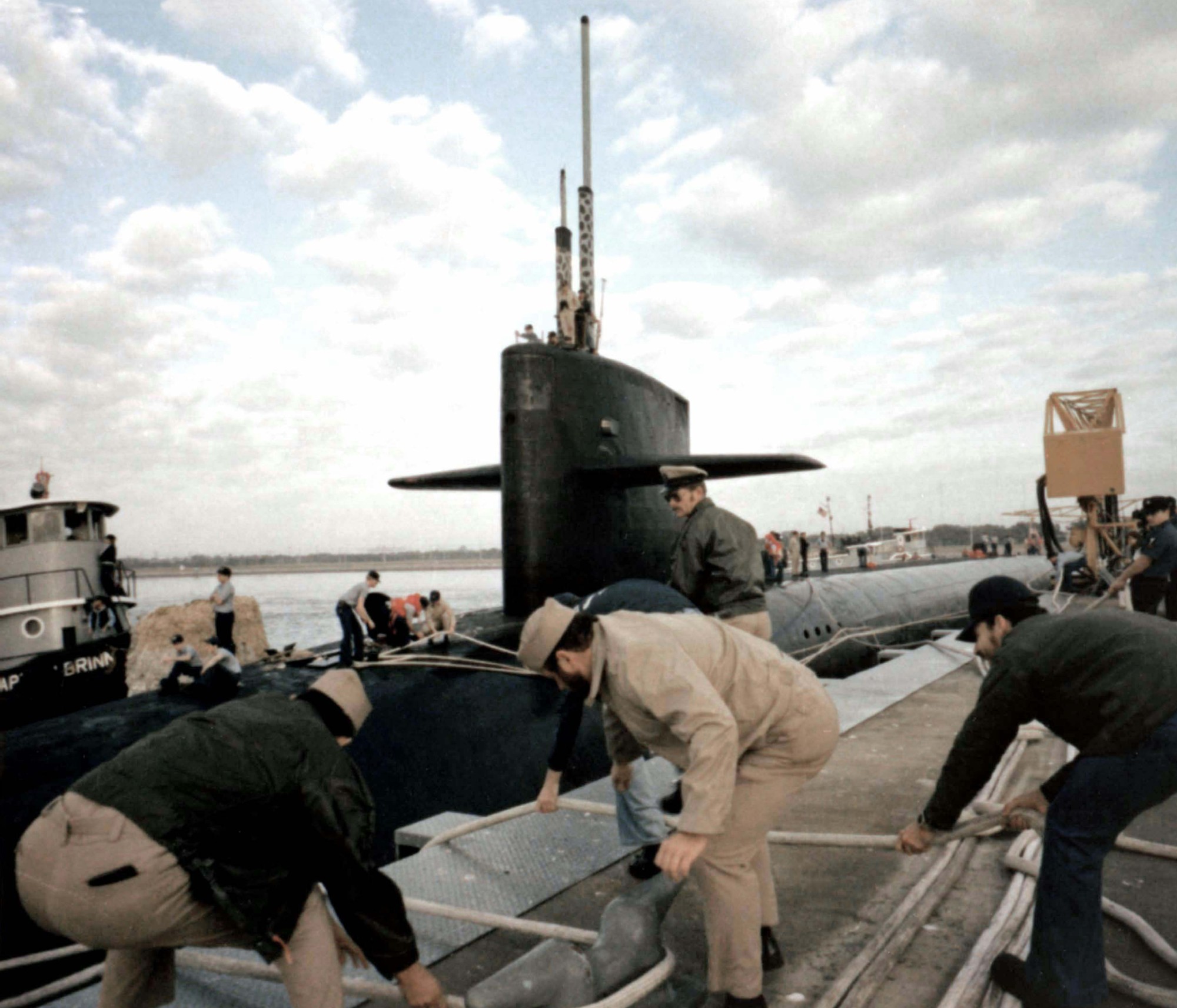  Cape Canaveral, Florida - 1982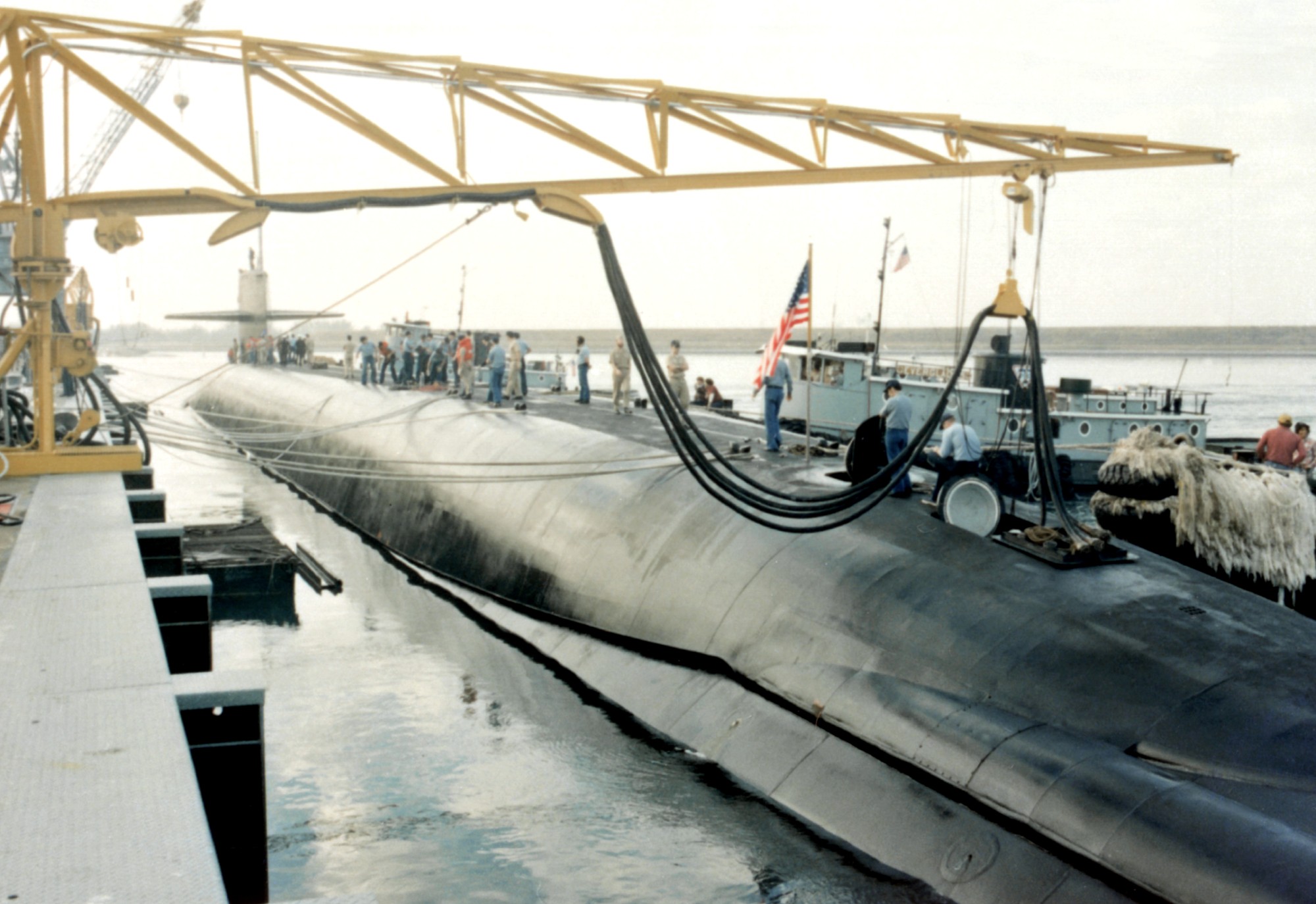  Cape Canaveral, Florida - 1982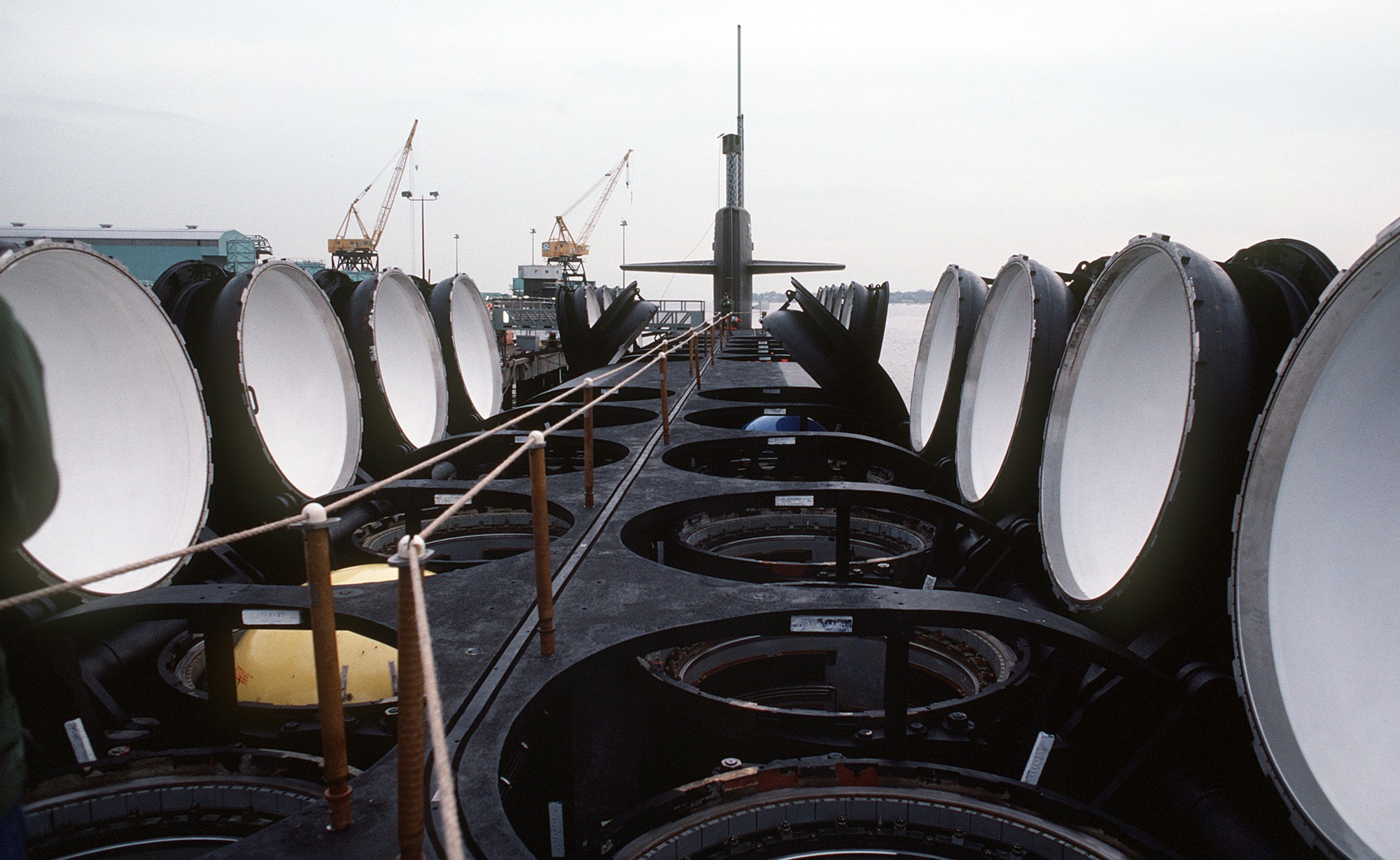  missile launching tubes opened - 1981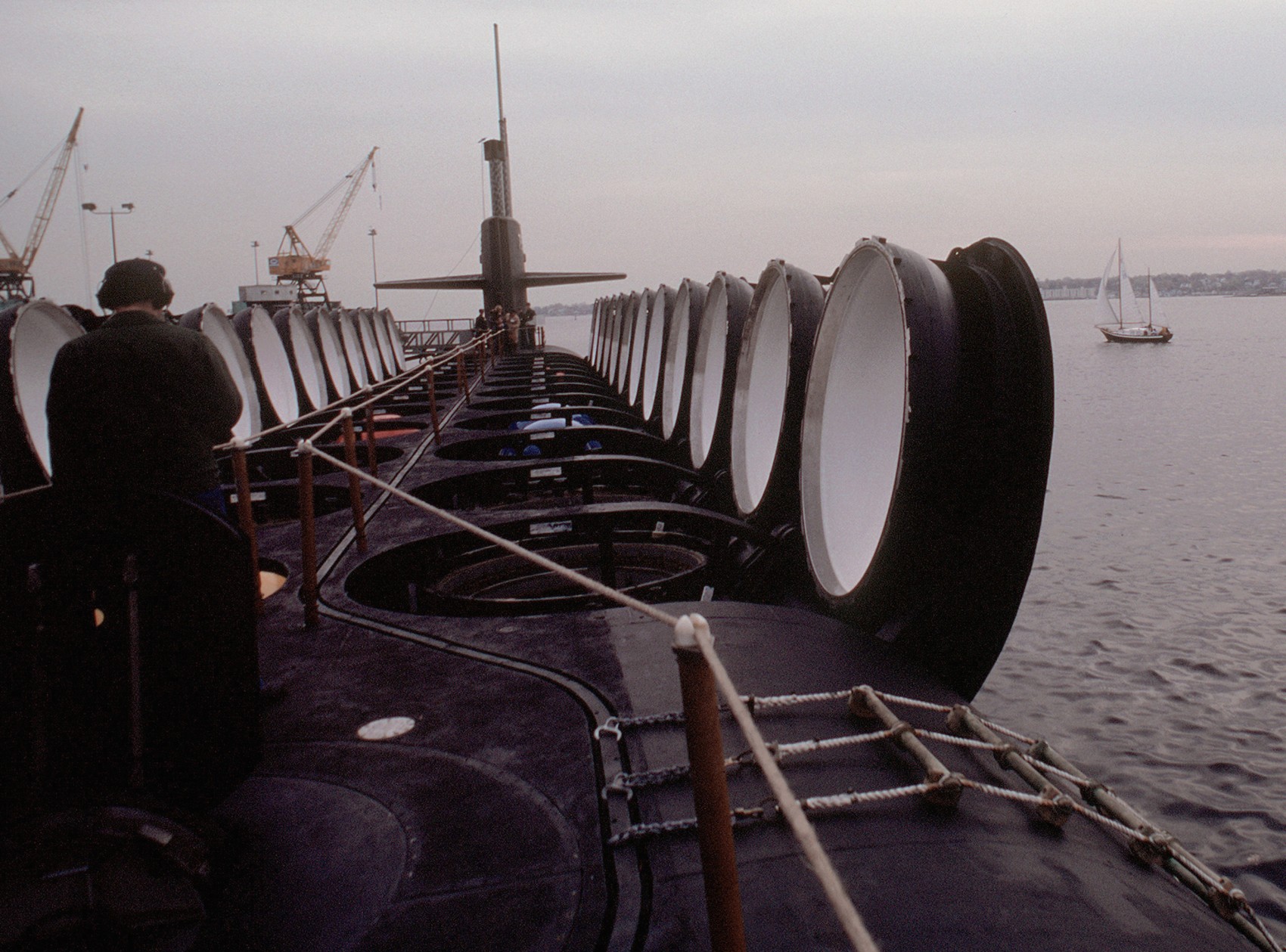  missile launching tubes opened - 1981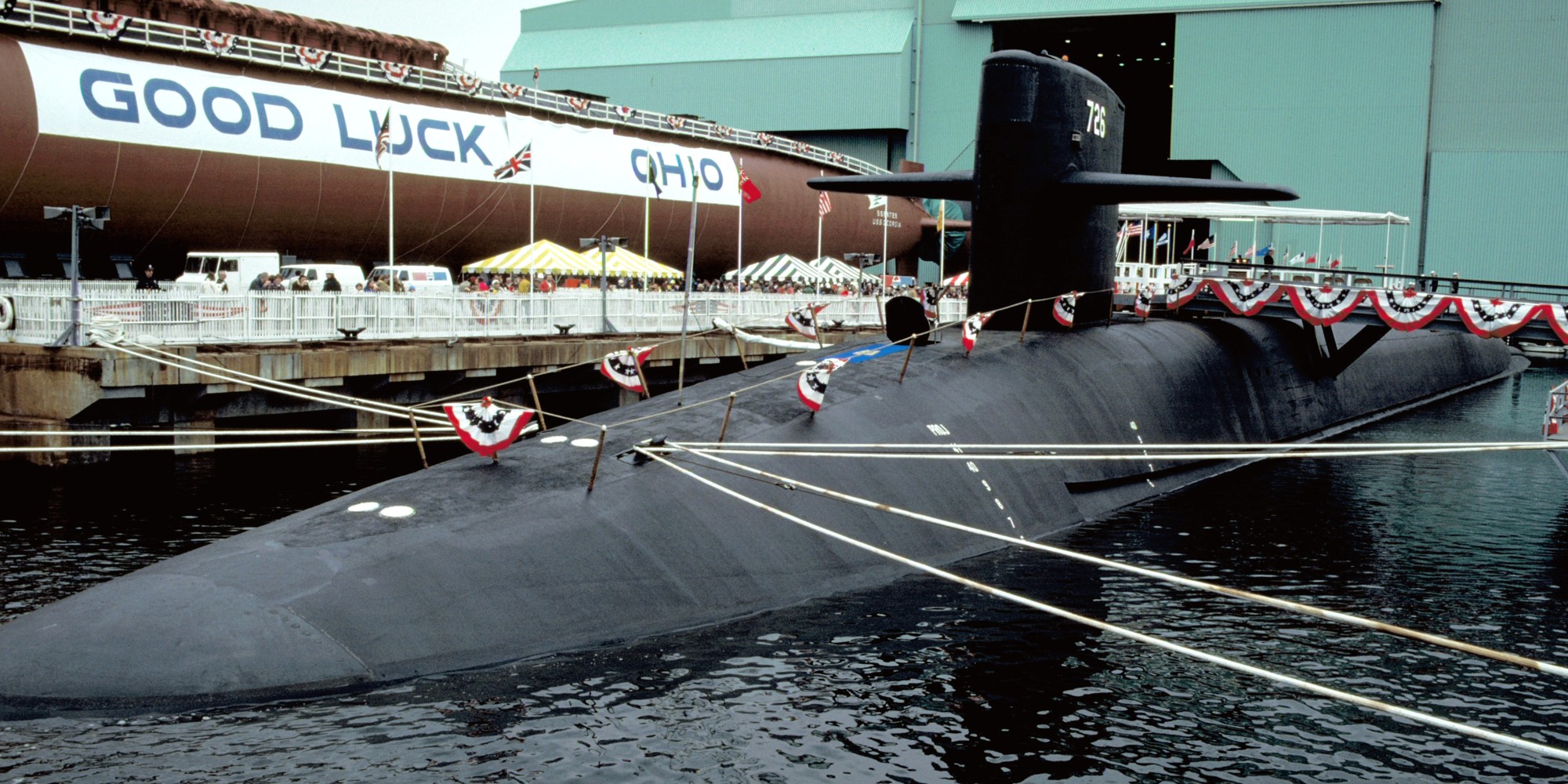  commissioning ceremony - November 11, 1981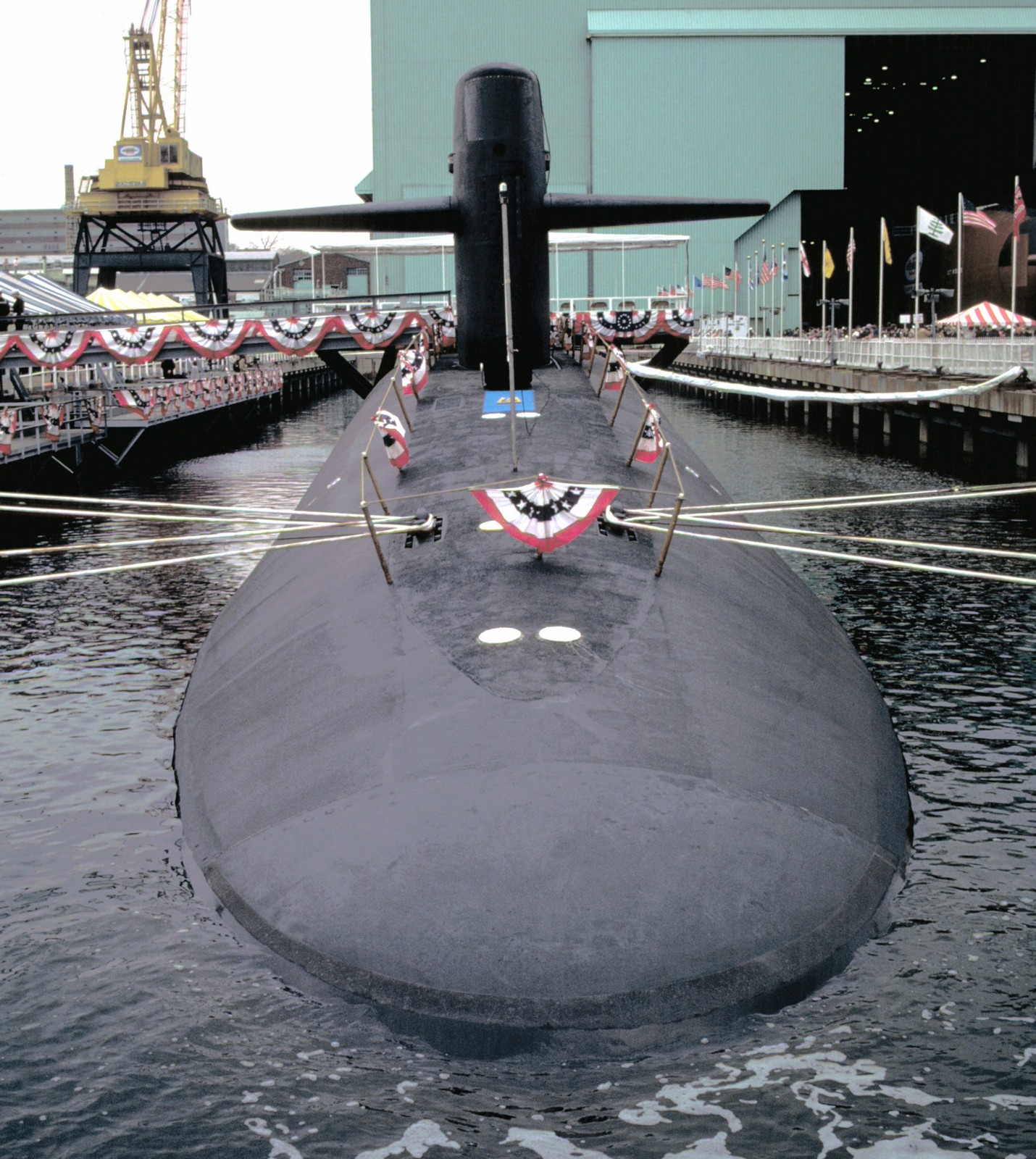  commissioning ceremony - November 11, 1981 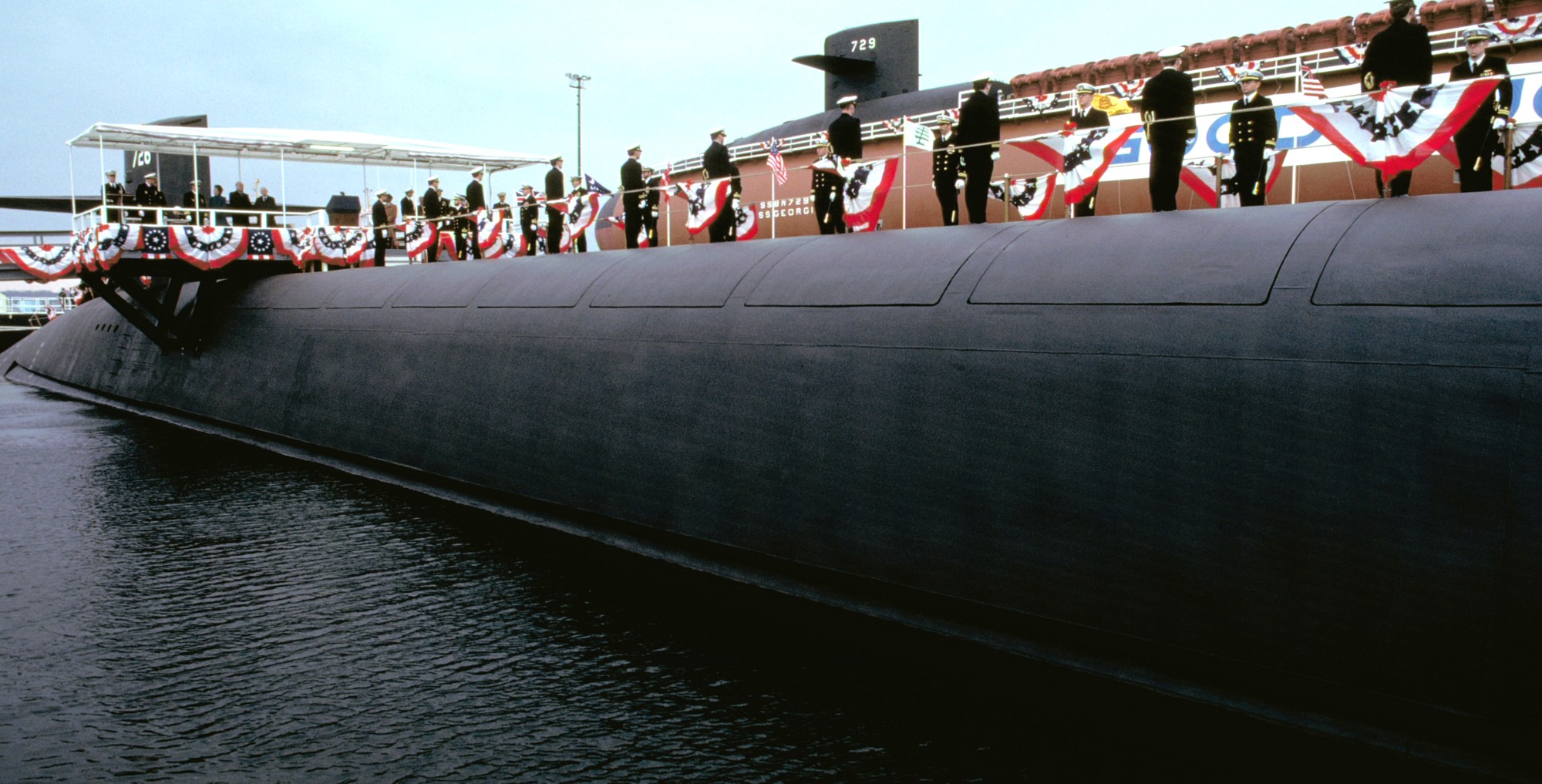 commissioning ceremony - November 11, 1981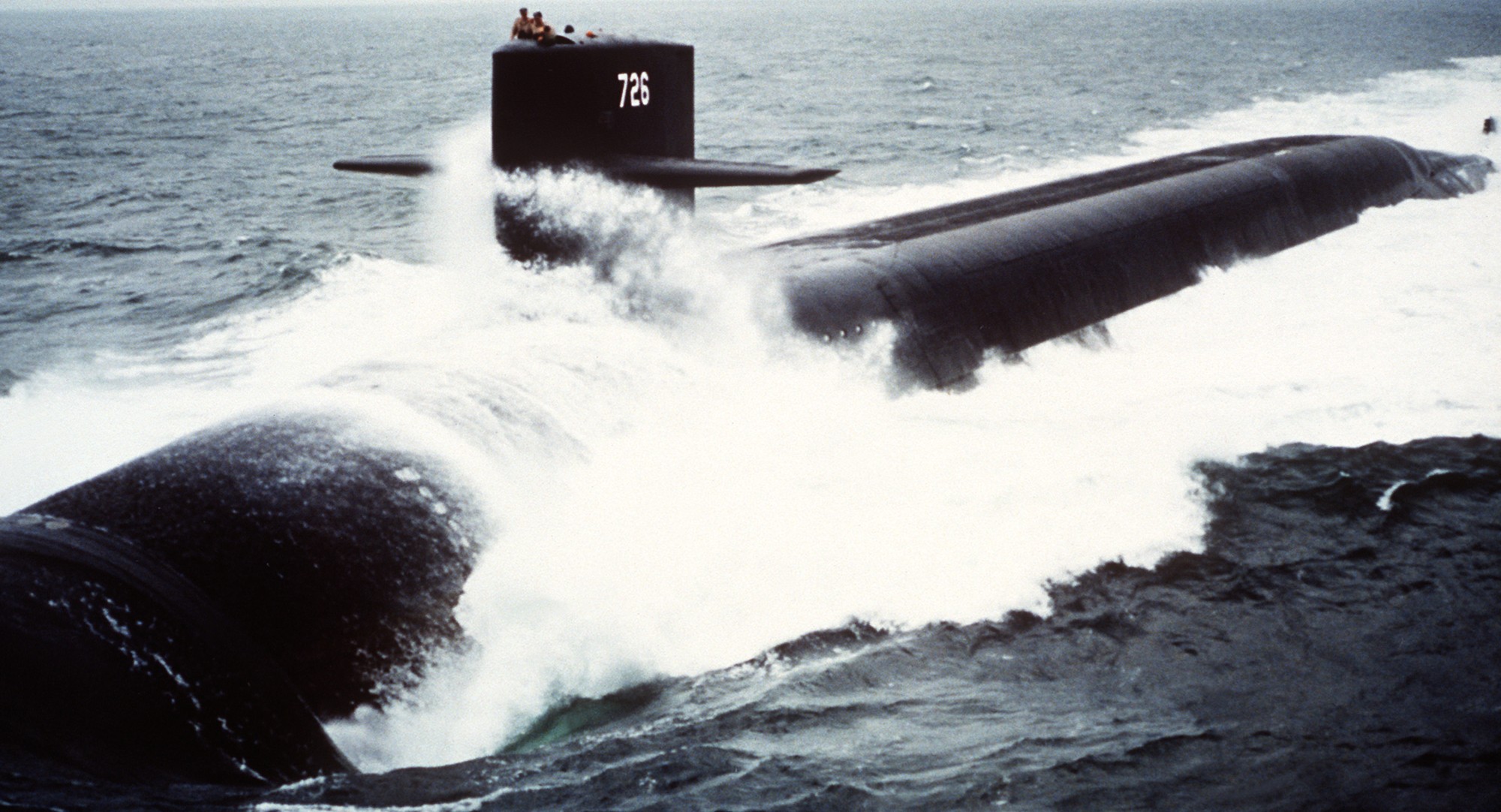  trials - 1981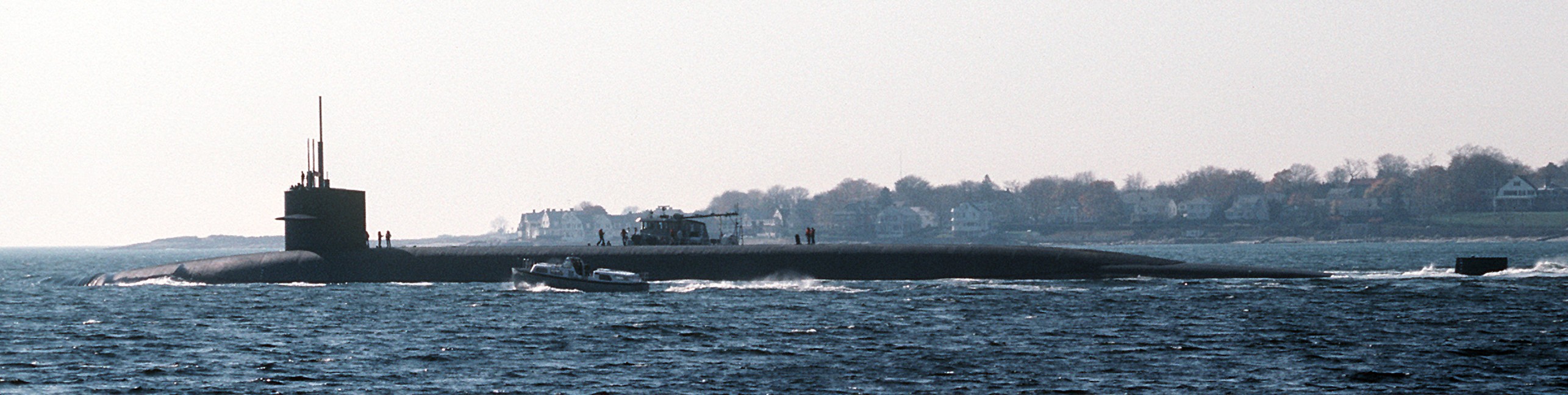  trials - 1981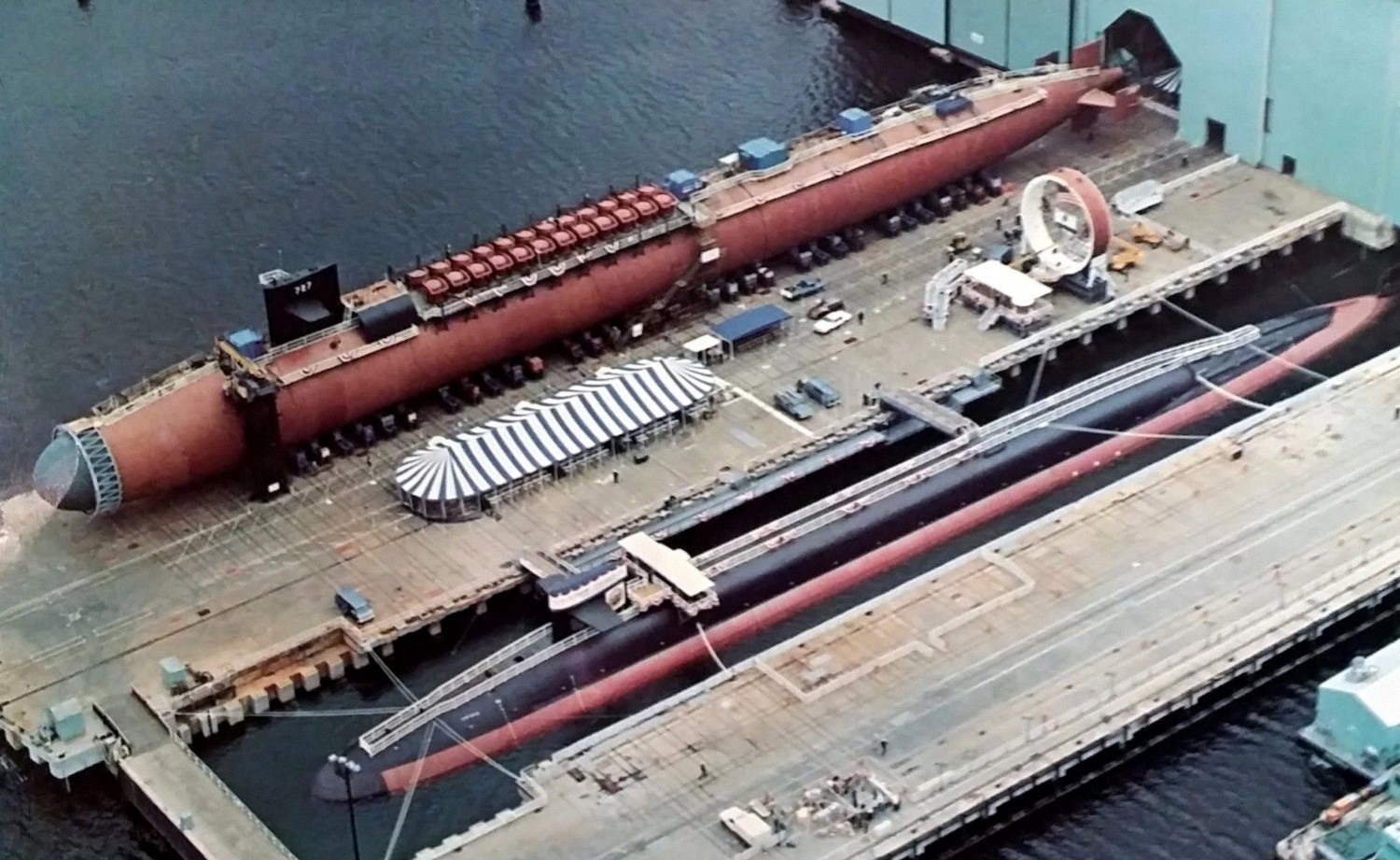  USS Ohio (SSBN 726) in the launching basin, USS Michigan (SSBN 727) largely finished on the pier alongside, and the "keel" (ring-shaped structure) of USS Georgia (SSBN 729) being "laid" between them - General Dynamics Electric Boat, Groton, Connecticut - April 7, 1979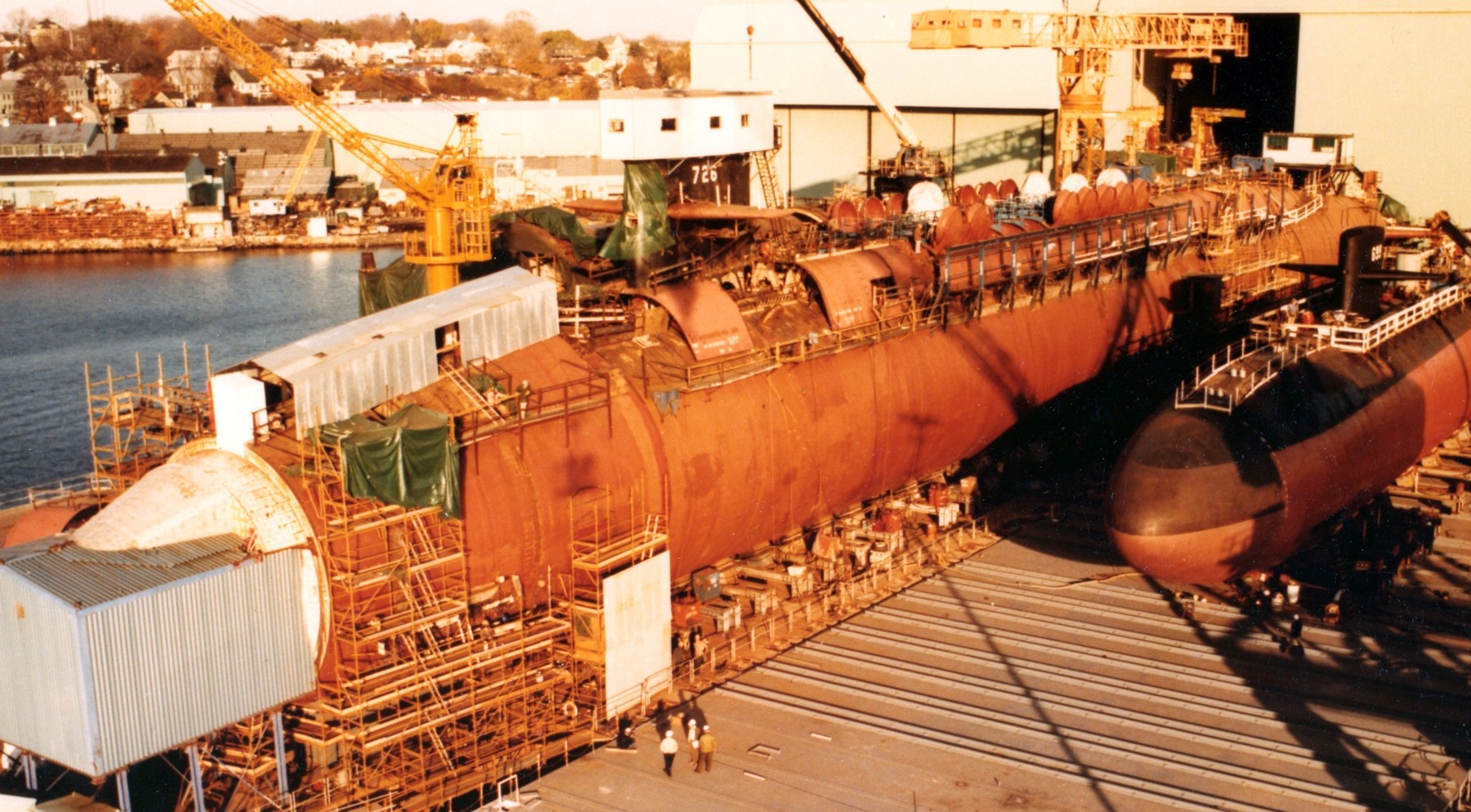  construction - undated |
||
|
USS Ohio (SSBN / SSGN 726): USS Ohio (SSGN 726) is the first of her class of ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) and guided missile submarines (SSGNs), and the fourth U.S. Navy ship to bear thename. The Ohio-class SSBN was conceived in the early 1970s as an eventual successor to the original group of 41 SSBNs - the famed "41 For Freedom" - commissioned between 1959 and 1967. At 560 feet, the Ohios became the largest submarines ever built by the U.S. Navy. Construction on Ohio, the fourth U.S. ship to bear the name, began April 10, 1976 at Groton, Connecticut, home of General Dynamics Electric Boat. Ohio was launched April 7, 1979 by Annie Glenn, wife of then-U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn. Ohio officially joined the U.S. Navy on Nov. 11, 1981, at Groton, with Capt. A. K. Thompson (Blue Crew) and Capt. A.F. Campbell (Gold Crew) assuming command. During the commissioning ceremony, Vice President George H.W. Bushtold the 8,000 guests that the Ohio and her class represented a "new dimension in our nation's strategic deterrence." Ohio began her long association with the Pacific Northwest Aug. 12, 1982, when she arrived at Naval Submarine Base Bangor as the first operational unit permanently assigned to Commander, Submarine Group 9. In October 1982, Ohio began her first strategic deterrent patrol; she would continue to patrol out of Bangor for the next 20 years. With the end of the Cold War, the first four Ohio-class SSBNs - Ohio, Michigan, Florida and Georgia - were scheduled to be decommissioned in the early 2000s. The other 14 would remain in service as SSBNs carrying the Trident II D-5 missile. But another plan was in the works - to use the versatile Ohio seaframe to carry Tomahawks or other payloads in lieu of ballistic missiles. The result would be four platforms capable of supporting strike or special warfare missions around the world. Under then plan, 22 Trident launch tubes were reconfigured to carry either canisters containing seven Tomahawks each - for a total of up to 154 missiles - or special operations weapons or equipment. The other two launch tubes were converted to lockout chambers, allowing for the embarkation and deployment of special operations forces such as Navy SEALs. Ohio completed its conversion and rejoined the fleet on Feb. 7, 2006 at Naval Base Kitsap-Bangor. A year later, she proceeded to Guam to begin the first SSGN forward deployment. In three decades of service, Ohio has captured the Battle Efficiency Award (Battle "E") multiple times, the most recent coming in 2012. source: SSGN-726 website - - - - - SSBN The contract to build her was awarded to the Electric Boat Division of General Dynamics Corporation in Groton, Connecticut on 1 July 1974 and her keel was laid down on 10 April 1976 by Mrs. Robert A. Taft, JR., wife of Senator Robert Taft Jr. of Ohio. On 2 February 1978, the Precommissioning Unit was formed with Commander A. K. Thompson as its commanding officer. Ohio was launched on 7 April 1979 sponsored by Mrs. Annie Glenn, wife of Senator John H. Glenn of Ohio. In the summer of 1981, sea trials were held to test the equipment and systems, and the submarine was delivered to the U.S. Navy on 28 October 1981. On 11 November 1981, Ohio was commissioned. The principal speaker, Vice President George H. W. Bush, remarked to the 8000 assembled guests that the boat introduced a "new dimension in our nation's strategic deterrence," and Admiral Hyman G. Rickover noted that Ohio should "strike fear in the hearts of our enemies." On that day, command of the two crews (designated Blue and Gold) of Ohio was assumed by Captain A. K. Thompson (Blue) and Captain A. F. Campbell (Gold). Following Post Shakedown Availability at Electric Boat Division, Ohio left the Atlantic and transited to her new home port, Bangor, Washington, by way of Cape Canaveral - where she tested her missile launch systems - and the Panama Canal, arriving on 12 August 1982. During August and September 1982, the first loadout of Trident C-4 missiles and a predeployment refit were conducted. Ohio and her Blue Crew departed on the first Trident Submarine Strategic Deterrent Patrol in October 1982. From June 1993 to June 1994 Ohio underwent overhaul at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Bremerton, Washington, receiving extensive upgrades to sonar, fire control, and navigation systems. Ohio resumed strategic deterrent patrols in January 1995 as part of Submarine Squadron Seventeen, Submarine Group Nine, Pacific Submarine Force. SSGN Following her conversion to a SSGN, Ohio rejoined the fleet on 7 February 2006. On 21 January 2007, the Gold Crew departed Naval Base Kitsap for Hawaii to conduct a forward-deployed crew exchange, the first such forward-deployed swap in approximately 20 years. Ballistic submarines of Ohio's class employ two crews, Blue and Gold, in order to facilitate continuous operation at sea, called "forward-presence" in USN parlance. Ohio left for her first mission as an SSGN on 15 October 2007. The Blue crew underwent several tests and inspections before completing a mission some time in December. Ohio was also the first one of the class to complete a mission. On 28 June 2010, Ohio was one of three Ohio-class submarines involved in a US response to Chinese missile testing in the contested East China Sea. Ohio, Michigan, and Florida all surfaced simultaneously in the waters of the Philippines, South Korea, and the British Indian Ocean Territory respectively. In November 2011, Lt. Britta Christianson became the first U.S. female officer, and first female overall, to complete submarine warfare qualification, while she was assigned to Ohio's Gold Crew. CSC Dominique Saavedra became the first enlisted female to earn her submarine qualification aboard Ohio in August 2016. She would go on to deploy with Michigan, the first sub specially modified with separate accommodations for enlisted female crew. In December 2020, it was announced that Ohio would be decommissioned and enter the Ship-Submarine Recycling Program by 2026. |
||
|
Ohio ... is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Canadian province of Ontario to the north (through Lake Erie), Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the west, and Michigan to the northwest. Of the 50 U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area. With a population of nearly 11.9 million, Ohio is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated state. Its capital and most populous city is Columbus, with other major metropolitan centers including Cleveland and Cincinnati, as well as Dayton, Akron, and Toledo. Ohio is nicknamed the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes". |
||
| patches + more | ||
  |
||
| | seaforces.org | USN ships start page | |